Local Cortical Circuits
... Synaptic Relations Between Adjacent Neurons Sources of Excitation Within Groups of Neurons Is the Cortical Network Randomly Connected? ...
... Synaptic Relations Between Adjacent Neurons Sources of Excitation Within Groups of Neurons Is the Cortical Network Randomly Connected? ...
11-5_TheMulti-CenterAspectOfMotorControl. _NagyD
... different regions of the cerebral cortex are involved in controlling the body's movements. Similarly, in the human brain, planning for any given movement is done mainly in the forward portion of the frontal lobe. This part of the cortex receives information about the individual's current position fr ...
... different regions of the cerebral cortex are involved in controlling the body's movements. Similarly, in the human brain, planning for any given movement is done mainly in the forward portion of the frontal lobe. This part of the cortex receives information about the individual's current position fr ...
Slide ()
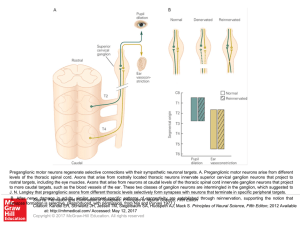
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
7 - smw15.org
... Messages from the brain must eventually reach the medulla and spinal cord, which control the muscles Corticospinal tracts • These are paths from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord • Two paths: lateral and medial corticospinal tracts • Nearly all movements rely on a combination of both tracts, bu ...
... Messages from the brain must eventually reach the medulla and spinal cord, which control the muscles Corticospinal tracts • These are paths from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord • Two paths: lateral and medial corticospinal tracts • Nearly all movements rely on a combination of both tracts, bu ...
Slide ()
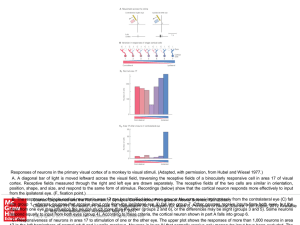
... A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. Receptive fields measured through the right and left eye are drawn separately. The receptive fields of the two cells are similar in orie ...
... A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. Receptive fields measured through the right and left eye are drawn separately. The receptive fields of the two cells are similar in orie ...
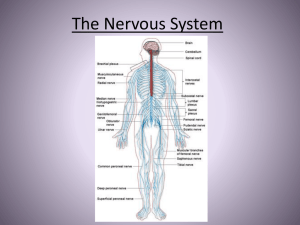
Nervous System
... reflex action is a very fast unconscious response to an unexpected and potentially dangerous stimulus. Examples of reflex action: knee jerk, eye blink, pupil size alteration, closure of the glottis on swallowing. A reflex arc is a specific nerve pathway involved in a fast, unconscious response t ...
... reflex action is a very fast unconscious response to an unexpected and potentially dangerous stimulus. Examples of reflex action: knee jerk, eye blink, pupil size alteration, closure of the glottis on swallowing. A reflex arc is a specific nerve pathway involved in a fast, unconscious response t ...
Motor control
... Goal-based representations • Why all this redundancy? That doesn’t make a lot of sense for a hierarchical system. • It seems to be the case that we develop our motor plans in reverse order of the motions necessary to achieve a goal. In other words, our motor planning is goal based rather than direc ...
... Goal-based representations • Why all this redundancy? That doesn’t make a lot of sense for a hierarchical system. • It seems to be the case that we develop our motor plans in reverse order of the motions necessary to achieve a goal. In other words, our motor planning is goal based rather than direc ...
Slide ()
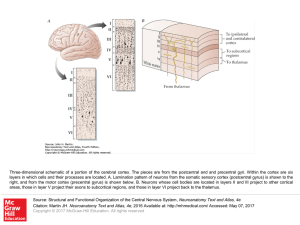
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
Basal Gang Dental 2011
... hemisphere in front of the precentral gyrus. 2. Supplementary motor cortex is the part of area 6 on the medial surface of the hemisphere. . 3. These areas then project to area 4 (the precentral gyrus), primary motor cortex and hence to the corticospinal tract. III. Striatal Motor Functions The stria ...
... hemisphere in front of the precentral gyrus. 2. Supplementary motor cortex is the part of area 6 on the medial surface of the hemisphere. . 3. These areas then project to area 4 (the precentral gyrus), primary motor cortex and hence to the corticospinal tract. III. Striatal Motor Functions The stria ...
Slide
... Overview of the visual system as related to visual prostheses. In most retinal dystrophies, the first order photoreceptor neurons (rods and cones) are lost. Thus, second order neurons (bipolar cells) are the earliest viable target, typically for subretinal and suprachoroidal devices. Epiretinal devi ...
... Overview of the visual system as related to visual prostheses. In most retinal dystrophies, the first order photoreceptor neurons (rods and cones) are lost. Thus, second order neurons (bipolar cells) are the earliest viable target, typically for subretinal and suprachoroidal devices. Epiretinal devi ...
Cellular Neuroscience - How Your Brain Works
... synthesis. It kills dopaminergic neurons and makes people (or animals) instantly Parkinsonian. • Some successes have been reported in treating MPTP poisoned addicts with embryonic tissue grafts. ...
... synthesis. It kills dopaminergic neurons and makes people (or animals) instantly Parkinsonian. • Some successes have been reported in treating MPTP poisoned addicts with embryonic tissue grafts. ...
Brumberg - QC Queens College
... further work focuses on the interaction between the neural and vascular systems Our results have shown that neurons participating in different pathways (eg. callosal – connecting the two hemispheres versus cortical feedback to an important midbrain nucleus the thalamus) have distinct intrinsic anato ...
... further work focuses on the interaction between the neural and vascular systems Our results have shown that neurons participating in different pathways (eg. callosal – connecting the two hemispheres versus cortical feedback to an important midbrain nucleus the thalamus) have distinct intrinsic anato ...
BN21 subcortical motor control
... Subcortical Motor Systems: Cerebellum & Basal Ganglia Lecture 21 ...
... Subcortical Motor Systems: Cerebellum & Basal Ganglia Lecture 21 ...
Mirror Neurons & You
... It was an accidental discovery that occurred while conducting research on motor neurons in monkeys. ...
... It was an accidental discovery that occurred while conducting research on motor neurons in monkeys. ...
Seminar in Neuroscience Why Corticospinal Motor Neurons Are Important For
... translate and transmit the brain's input to the spinal cord targets allow them to function as the spokesperson for the cerebral cortex for the initiation and modulation of voluntary movement. CSMN vulnerability and progressive degeneration is key in numerous motor neuron diseases, such as primary la ...
... translate and transmit the brain's input to the spinal cord targets allow them to function as the spokesperson for the cerebral cortex for the initiation and modulation of voluntary movement. CSMN vulnerability and progressive degeneration is key in numerous motor neuron diseases, such as primary la ...
Sensory and Motor Systems
... People that use ASL as their first language use Broca’s and Wernicke’s as we do! So they are not necessarily for say auditory processing They are for language Only we have ‘em ...
... People that use ASL as their first language use Broca’s and Wernicke’s as we do! So they are not necessarily for say auditory processing They are for language Only we have ‘em ...
Slide 1
... – What do you think this might be? – How do you think it might cause MS symptoms? – Which divisions of the NS might be involved? ...
... – What do you think this might be? – How do you think it might cause MS symptoms? – Which divisions of the NS might be involved? ...
Motor Cortex
... Different populations of neurons active during planning (targeting) & execution (trigger stimulus) PM active before movement ~ ...
... Different populations of neurons active during planning (targeting) & execution (trigger stimulus) PM active before movement ~ ...
Mirror Neurons
... Neurons in the premotor area that fire in preparation for upcoming movements also fire when we observe someone else carry out that action. Common brain regions thus process both the perception and production of a movement. The infant's observation of her parent's projecting tongue fires the premoto ...
... Neurons in the premotor area that fire in preparation for upcoming movements also fire when we observe someone else carry out that action. Common brain regions thus process both the perception and production of a movement. The infant's observation of her parent's projecting tongue fires the premoto ...
abstract in inglese A. Parziale
... To unveil the "code" used for executing voluntary movements we investigated the interaction between the motor cortex and the spinal cord, the main recipient of the descending signals departing from M1 neurons. In particular, the research presented in this thesis aims at understanding how primary mot ...
... To unveil the "code" used for executing voluntary movements we investigated the interaction between the motor cortex and the spinal cord, the main recipient of the descending signals departing from M1 neurons. In particular, the research presented in this thesis aims at understanding how primary mot ...
Lecture 4:
... Also named efferent neurons: Carry messages away from the CNS (brain and/or spinal cord). ...
... Also named efferent neurons: Carry messages away from the CNS (brain and/or spinal cord). ...
The effects of electrical microstimulation on cortical signal propagation
... • In the BMI with somatosensory input, one monkey controlled cursor movements directly by using motor cortical activity while receiving somatosensory instructive signals (ICMS) in S1. • The second monkey also controlled the cursor using motor cortical activity but, since PP ICMS was ineffective, rec ...
... • In the BMI with somatosensory input, one monkey controlled cursor movements directly by using motor cortical activity while receiving somatosensory instructive signals (ICMS) in S1. • The second monkey also controlled the cursor using motor cortical activity but, since PP ICMS was ineffective, rec ...