M555 Medical Neuroscience
... Several serious and debilitating problems affect R.K., age 67 years. The primary sign of the disorder is orthostatic hypotension. In fact, blood pressure regulation overall is faulty. Sometimes while reclining, R.K.’s blood pressure rises dramatically. R.K. also experience irregular heartbeat, const ...
... Several serious and debilitating problems affect R.K., age 67 years. The primary sign of the disorder is orthostatic hypotension. In fact, blood pressure regulation overall is faulty. Sometimes while reclining, R.K.’s blood pressure rises dramatically. R.K. also experience irregular heartbeat, const ...
Abbreviated 11-15
... P type = (also known as beta or midget ganglion cells) are believed to be responsible for detecting details in vision. M type = (also known as alpha or parasol ganglion cells) are believed to be responsible for detecting motion. nonM-nonP type =are a diverse group of cell types that make up the rema ...
... P type = (also known as beta or midget ganglion cells) are believed to be responsible for detecting details in vision. M type = (also known as alpha or parasol ganglion cells) are believed to be responsible for detecting motion. nonM-nonP type =are a diverse group of cell types that make up the rema ...
Neurotest 3a Answers MC E 2) A 3) E 4) A 5) B Defs Habituation
... 4) Sensory neuron to interneuron to motor neuron diagram; reflexes allow swiftest response (unconscious) to noxious stimuli 5) (see Bowe) 6) Insomnia: inability to go to sleep or stay asleep Narcolepsy: falling asleep at inappropriate times throughout day Sleep Apnea: cessation of breathing during s ...
... 4) Sensory neuron to interneuron to motor neuron diagram; reflexes allow swiftest response (unconscious) to noxious stimuli 5) (see Bowe) 6) Insomnia: inability to go to sleep or stay asleep Narcolepsy: falling asleep at inappropriate times throughout day Sleep Apnea: cessation of breathing during s ...
Peripheral Nervous System - e
... “Rest and digest” Antagonistic control Dual innervation Exception: Sweat glands, vascular smooth muscle Multiple receptor types Both tonically active ...
... “Rest and digest” Antagonistic control Dual innervation Exception: Sweat glands, vascular smooth muscle Multiple receptor types Both tonically active ...
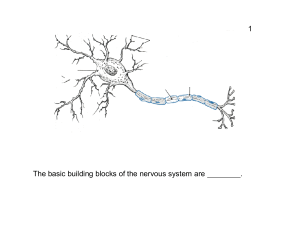
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
... areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, & speaking ...
Slide 1
... circuit consists of a population of excitatory neurons (E) that recurrently excite one another, and a population of inhibitory neurons (I) that recurrently inhibit one another (red/pink synapses are excitatory, black/grey synapses are inhibitory). The excitatory cells excite the inhibitory neurons, ...
... circuit consists of a population of excitatory neurons (E) that recurrently excite one another, and a population of inhibitory neurons (I) that recurrently inhibit one another (red/pink synapses are excitatory, black/grey synapses are inhibitory). The excitatory cells excite the inhibitory neurons, ...
Microscopic Nervous System and Reflexes with answers
... 3. Describe the structure and function of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). PNS is made up of nerves and sense receptors that lie outside the brain and spinal cord; it is divided into sensory (afferent)function and motor (efferent) function 4. What is the difference between afferent nerves and ef ...
... 3. Describe the structure and function of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). PNS is made up of nerves and sense receptors that lie outside the brain and spinal cord; it is divided into sensory (afferent)function and motor (efferent) function 4. What is the difference between afferent nerves and ef ...
Neuron Functioning
... • Interneurons found within the spinal cord connect sensory and motor neurons creating an “arc.” • Signals are rapidly sent along this arc to allow you to move quickly away from the potentially dangerous conditions. ...
... • Interneurons found within the spinal cord connect sensory and motor neurons creating an “arc.” • Signals are rapidly sent along this arc to allow you to move quickly away from the potentially dangerous conditions. ...
Auditory information processing at the cortical level
... characteristic frequency if they lie within the same column The nerve cells of the auditory cortex appear to reflect increased specialisation. The nerve cells become increasingly selective in their response to novel stimuli or certain features of the stimulus. ...
... characteristic frequency if they lie within the same column The nerve cells of the auditory cortex appear to reflect increased specialisation. The nerve cells become increasingly selective in their response to novel stimuli or certain features of the stimulus. ...
notes - Other Places you want to go
... Synapse – gap between the axon of a neuron and the receiving cell Neuroglia – support neurons by preforming various tasks so neurons can do their job **Know Figure 16.3 for test** (see Neuron handout) Parts of the Neuron: Dendrites – conduct electrical signals towards the neuron’s cell body Axon ...
... Synapse – gap between the axon of a neuron and the receiving cell Neuroglia – support neurons by preforming various tasks so neurons can do their job **Know Figure 16.3 for test** (see Neuron handout) Parts of the Neuron: Dendrites – conduct electrical signals towards the neuron’s cell body Axon ...
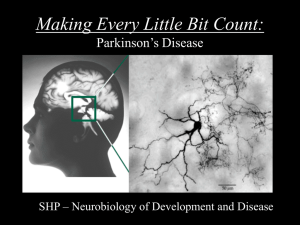
Brain`s Building Blocks
... ◦ includes symptoms of tremors and shakes in the limbs, a slowing of voluntary movements, muscle stiffness, problems with balance and coordination and feelings of depression ◦ as the disease progresses, patients develop a shuffling walk and may suddenly freeze in space for ...
... ◦ includes symptoms of tremors and shakes in the limbs, a slowing of voluntary movements, muscle stiffness, problems with balance and coordination and feelings of depression ◦ as the disease progresses, patients develop a shuffling walk and may suddenly freeze in space for ...
Parts of the Neuron 45
... also convey messages to your glands, causing them to release hormones, chemical substances that help regulate bodily processes. Interneurons (also called associative neurons) are the most common type of neuron in the nervous system. They connect neurons to neurons. In the spinal cord, they connect s ...
... also convey messages to your glands, causing them to release hormones, chemical substances that help regulate bodily processes. Interneurons (also called associative neurons) are the most common type of neuron in the nervous system. They connect neurons to neurons. In the spinal cord, they connect s ...
Study Guide Solutions - Elsevier: Baars and Gage
... This classical neuron accepts input from other nerve cells in its dendritic branches, evoking graded membrane potentials. That is, the voltages across the dendritic membranes can have continuous values. These graded potentials add up and, if the total voltage during a brief time interval exceeds abo ...
... This classical neuron accepts input from other nerve cells in its dendritic branches, evoking graded membrane potentials. That is, the voltages across the dendritic membranes can have continuous values. These graded potentials add up and, if the total voltage during a brief time interval exceeds abo ...
MPTP - Columbia University
... • After 2-4yrs of treatment, patients develop a “wearing off” where the drug seems to stop working in between doses. Now the effect of the drug is dependent on serum concentration (known as the short duration effect. • Longterm use is associated with levodopa-induced dyskinesias. • Taking too much o ...
... • After 2-4yrs of treatment, patients develop a “wearing off” where the drug seems to stop working in between doses. Now the effect of the drug is dependent on serum concentration (known as the short duration effect. • Longterm use is associated with levodopa-induced dyskinesias. • Taking too much o ...
A1987F573800001
... H-thymidine, I found that in the rhesus monkey, granule cells have their last mitotic division during the late gestational and early neonatal period. How do postmitotic cells find their way through neural tissue that, at this age, is already densely packed with synapses? ...
... H-thymidine, I found that in the rhesus monkey, granule cells have their last mitotic division during the late gestational and early neonatal period. How do postmitotic cells find their way through neural tissue that, at this age, is already densely packed with synapses? ...
Organization and Development of the Nervous System
... NEURON: Mitosis (Make New Cells/Neurons) and ...
... NEURON: Mitosis (Make New Cells/Neurons) and ...
Molecular prosthetics for vision restoration based on freely
... Molecular prosthetics for vision restoration based on freely-diffusible and covalently bound photoswitches Light-regulated drugs allow remotely photoswitching biological activity and enable plausible therapies based on small molecules. We develop efficient compounds to manipulate neuronal activity f ...
... Molecular prosthetics for vision restoration based on freely-diffusible and covalently bound photoswitches Light-regulated drugs allow remotely photoswitching biological activity and enable plausible therapies based on small molecules. We develop efficient compounds to manipulate neuronal activity f ...
The Nervous System
... from the base of the brain to the lower back • Runs through the spinal canal and is protected by the bones of the spine (vertebrae) ...
... from the base of the brain to the lower back • Runs through the spinal canal and is protected by the bones of the spine (vertebrae) ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... There are currently at least 50 identified neurotransmitters. Agonists – increase the effects of a neurotransmitter, makes more of it, or stops the minimizing of it Antagonist – slows down neurotransmitters either because they destroy or inhibit production, or they “paste over” dendrites so that neu ...
... There are currently at least 50 identified neurotransmitters. Agonists – increase the effects of a neurotransmitter, makes more of it, or stops the minimizing of it Antagonist – slows down neurotransmitters either because they destroy or inhibit production, or they “paste over” dendrites so that neu ...
Nervous System
... Neural Integration of the CNS • Qualitative information (salty, pain or temperature) depends upon which neurons are propagating APs • Quantitative (strength) information depend on: – the number of neurons that are firing APs – the frequency of APs fired per neuron ...
... Neural Integration of the CNS • Qualitative information (salty, pain or temperature) depends upon which neurons are propagating APs • Quantitative (strength) information depend on: – the number of neurons that are firing APs – the frequency of APs fired per neuron ...
Nervous System
... Neural Integration of the CNS • Qualitative information (salty, pain or temperature) depends upon which neurons are propagating APs • Quantitative (strength) information depend on: – the number of neurons that are firing APs – the frequency of APs fired per neuron ...
... Neural Integration of the CNS • Qualitative information (salty, pain or temperature) depends upon which neurons are propagating APs • Quantitative (strength) information depend on: – the number of neurons that are firing APs – the frequency of APs fired per neuron ...
Nervous System
... Arousal is a state of awareness while sleep is external stimuli that isn’t consciously perceived Multiple brain areas contribute ...
... Arousal is a state of awareness while sleep is external stimuli that isn’t consciously perceived Multiple brain areas contribute ...
Spinal Cord – Gross Anatomy
... A butterfly shaped structure that occupies the central portion of the cord ...
... A butterfly shaped structure that occupies the central portion of the cord ...