SENSORY AND MOTOR SYSTEMS: REFLEXES
... DETECTOR(SENSORY FIBERS) • TYPE Ia NERVE FIBERS: TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT LENGTH AND VELOCITY TO THE CNS • TYPE II NERVE FIBERS:TRANSMIT ...
... DETECTOR(SENSORY FIBERS) • TYPE Ia NERVE FIBERS: TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT LENGTH AND VELOCITY TO THE CNS • TYPE II NERVE FIBERS:TRANSMIT ...
Printable version
... C. membrane potentials that act as signals 1. a graded potential is a small, brief potential change that acts as a short-distance signal 2. an action potential, or nerve impulse, is a large, brief depolarization signal a. it is an all-or-none phenomenon; strong stimuli can lead to more signals but w ...
... C. membrane potentials that act as signals 1. a graded potential is a small, brief potential change that acts as a short-distance signal 2. an action potential, or nerve impulse, is a large, brief depolarization signal a. it is an all-or-none phenomenon; strong stimuli can lead to more signals but w ...
nervous system
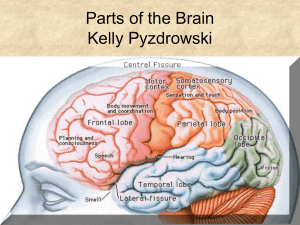
... -Ridges are called convolutions or ____ -Grooves are called _____ (deepest sulci are called fissures) -Divided into two halves- ________ -Hemispheres connected by the _________ ...
... -Ridges are called convolutions or ____ -Grooves are called _____ (deepest sulci are called fissures) -Divided into two halves- ________ -Hemispheres connected by the _________ ...
NATURAL PRODUCT EXTRACTS TO PROTECT
... that causes death to neurons relevant to most neurological injuries). These results invite the promise of new treatments based on natural product extracts to counter the toxic environment in the brain foll ...
... that causes death to neurons relevant to most neurological injuries). These results invite the promise of new treatments based on natural product extracts to counter the toxic environment in the brain foll ...
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... the success of massage in pain relief). These sensations are lost with amputations and thus their inhibitory effect. ...
... the success of massage in pain relief). These sensations are lost with amputations and thus their inhibitory effect. ...
perceptionlecture5
... Brainstem circuits for saccades. Omnipause neurons (OPN) in the nucleus raphe interpositus (RIP) tonically inhibit excitatory burst neurons (EBN) located in the paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF). When OPNs pause, the EBNs emit a burst of spikes, which activate motor neurons (MN) i ...
... Brainstem circuits for saccades. Omnipause neurons (OPN) in the nucleus raphe interpositus (RIP) tonically inhibit excitatory burst neurons (EBN) located in the paramedian pontine reticular formation (PPRF). When OPNs pause, the EBNs emit a burst of spikes, which activate motor neurons (MN) i ...
The Neuron - University of Connecticut
... pons - arousal and attention cerebellum - integration of muscles to perform fine movements, but no coordination / direction of these movements; balance cat transected above hindbrain: can move but not act midbrain: forms movements into acts; controls whole body responses to visual and auditory stimu ...
... pons - arousal and attention cerebellum - integration of muscles to perform fine movements, but no coordination / direction of these movements; balance cat transected above hindbrain: can move but not act midbrain: forms movements into acts; controls whole body responses to visual and auditory stimu ...
Neuroscience 14b – Organisation of the Cerebral Cortex
... This is the oldest method of studying cortical function. The effects of cerebral lesions were observed and the consequences produced gave us an indication as to the regular physiology of the cortical area this was however very limited in a number ways. - poor reproducability - inter-subject variatio ...
... This is the oldest method of studying cortical function. The effects of cerebral lesions were observed and the consequences produced gave us an indication as to the regular physiology of the cortical area this was however very limited in a number ways. - poor reproducability - inter-subject variatio ...
Nádasdy Zoltán Cal Tech
... (Encoding and decoding information by the phase of action potentials) Experimental evidence, such as task-dependent coherency between single-unit activity and local field potentials (LFPs), together with the dependency of action potential (AP) initiation on the subthreshold membrane oscillation (SMO ...
... (Encoding and decoding information by the phase of action potentials) Experimental evidence, such as task-dependent coherency between single-unit activity and local field potentials (LFPs), together with the dependency of action potential (AP) initiation on the subthreshold membrane oscillation (SMO ...
Chapter 13
... – Violent Forceful Flinging of Arms and Legs – Most violent form of dyskinesia (movement disorder) – Usually associated with lesions in the sub-thalamic nucleus (which regulates the globus pallidus) – Hemiballism: unilateral ballism (e.g. unilateral stroke) – Can be treated with dopamine blockade or ...
... – Violent Forceful Flinging of Arms and Legs – Most violent form of dyskinesia (movement disorder) – Usually associated with lesions in the sub-thalamic nucleus (which regulates the globus pallidus) – Hemiballism: unilateral ballism (e.g. unilateral stroke) – Can be treated with dopamine blockade or ...
Unit 2 bio-behavior review guide
... d. only controls our bodily movements 4. Balance and coordination are regulated by the a. cerebellum b. thalamus c. hypothalamus d. frontal association area 5. The reticular activating system a. regulates sleepiness b. regulates alertness c. takes a reading of the level of activity throughout the bo ...
... d. only controls our bodily movements 4. Balance and coordination are regulated by the a. cerebellum b. thalamus c. hypothalamus d. frontal association area 5. The reticular activating system a. regulates sleepiness b. regulates alertness c. takes a reading of the level of activity throughout the bo ...
PAPER #3: EMBARGOED PRESS RELEASE STRICTLY UNDER
... show that the ventral subiculum recruits the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis to drive a persistent hyperactivity of dopamine neurons and control cocaine-induced activity." Surprisingly, a single stimulation of the ventral subiculum (which lasts about 10 minutes in an anesthetized rat) had the sa ...
... show that the ventral subiculum recruits the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis to drive a persistent hyperactivity of dopamine neurons and control cocaine-induced activity." Surprisingly, a single stimulation of the ventral subiculum (which lasts about 10 minutes in an anesthetized rat) had the sa ...
Lecture 3
... • Motor control for muscle coordination and in planning complicated movements • Cognitive tasks involved in learning and memory of motor task. • Lesions to humans or animals shows that distinct areas of the cb are necessary for spatial reasoning, keeping muscle tone during voluntary movement ...
... • Motor control for muscle coordination and in planning complicated movements • Cognitive tasks involved in learning and memory of motor task. • Lesions to humans or animals shows that distinct areas of the cb are necessary for spatial reasoning, keeping muscle tone during voluntary movement ...
9.14 Lecture 16: Descending Pathways and Evolution Notes
... Why would diaschisis effects of lesions of one of the descending pathways in the study be greater in humans than in the monkeys? What are major manifestations of such effects? After recovery of spinal reflexes, the enduring effects ...
... Why would diaschisis effects of lesions of one of the descending pathways in the study be greater in humans than in the monkeys? What are major manifestations of such effects? After recovery of spinal reflexes, the enduring effects ...
conductance versus current-based integrate-and - Neuro
... currents are hard to handle analytically and it has been difficult to gain insight into the quantitative behaviour of ensembles of such neurons. A much-simplified model neuron, the integrate-and-fire (IF) neuron captures many of the broad features that biological neurons share and has become a stand ...
... currents are hard to handle analytically and it has been difficult to gain insight into the quantitative behaviour of ensembles of such neurons. A much-simplified model neuron, the integrate-and-fire (IF) neuron captures many of the broad features that biological neurons share and has become a stand ...
ALH 1002 Chapter 5 - Biosocial Development
... Experience-related aspects of brain function: • Experience-expectant : require basic common experiences in to develop normally (i.e. people who love them) • Experience-dependent: these happen to some infants but not all, not necessary for brain function (i.e. language baby hears) ...
... Experience-related aspects of brain function: • Experience-expectant : require basic common experiences in to develop normally (i.e. people who love them) • Experience-dependent: these happen to some infants but not all, not necessary for brain function (i.e. language baby hears) ...
Invitation to the Life Span by Kathleen Stassen Berger
... Experience-related aspects of brain function: • Experience-expectant : require basic common experiences in to develop normally (i.e. people who love them) • Experience-dependent: these happen to some infants but not all, not necessary for brain function (i.e. language baby hears) ...
... Experience-related aspects of brain function: • Experience-expectant : require basic common experiences in to develop normally (i.e. people who love them) • Experience-dependent: these happen to some infants but not all, not necessary for brain function (i.e. language baby hears) ...
Traffic Sign Recognition Using Artificial Neural Network
... matching. Pattern matching can solve many problems to which algorithms are not exist or very complicated. ...
... matching. Pattern matching can solve many problems to which algorithms are not exist or very complicated. ...
File
... 2. The Hypothalamus- monitors the internal systems to maintain the normal state of the body (homeostasis) by controlling the release of hormones it can moderate body functions (sleep, food intake, and liquid intake) WARNING- if out of balance difficult to concentrate ...
... 2. The Hypothalamus- monitors the internal systems to maintain the normal state of the body (homeostasis) by controlling the release of hormones it can moderate body functions (sleep, food intake, and liquid intake) WARNING- if out of balance difficult to concentrate ...
Ch05LifespanPPT
... Experience-related aspects of brain function: • Experience-expectant : require basic common experiences in to develop normally (i.e. people who love them) • Experience-dependent: these happen to some infants but not all, not necessary for brain function (i.e. language baby hears) ...
... Experience-related aspects of brain function: • Experience-expectant : require basic common experiences in to develop normally (i.e. people who love them) • Experience-dependent: these happen to some infants but not all, not necessary for brain function (i.e. language baby hears) ...
Neurons & the Nervous System
... • Dendrites: branch-like end of neuron which receives messages • Cell body (soma): contains nucleus • Axon: long tail-like end of neuron which transmits (sends) messages ...
... • Dendrites: branch-like end of neuron which receives messages • Cell body (soma): contains nucleus • Axon: long tail-like end of neuron which transmits (sends) messages ...
Chapter 10
... information from different types of sensory receptors • allows nervous system to collect, process, and respond to information • makes it possible for a neuron to sum impulses from different sources ...
... information from different types of sensory receptors • allows nervous system to collect, process, and respond to information • makes it possible for a neuron to sum impulses from different sources ...
Early Brain Development
... The brain has different sections, each section controls a specific function. One of the most important parts is the cortex. The cortex is the part of the brain that its growth permits more complex learning. Neurons in the baby’s brain are tiny messengers that transmit information in the brain and ne ...
... The brain has different sections, each section controls a specific function. One of the most important parts is the cortex. The cortex is the part of the brain that its growth permits more complex learning. Neurons in the baby’s brain are tiny messengers that transmit information in the brain and ne ...