Neuroscience 7b – Cortical Motor Function
... Premotor Cortex: electrical stimuli from this area of the brain does not produce muscle movement unless the stimuli is very intense (much more so than in M1). This are of the brain prepares M1 for the motor act. It does this by facilitating multiple columns in M1. These neurones are more easily sti ...
... Premotor Cortex: electrical stimuli from this area of the brain does not produce muscle movement unless the stimuli is very intense (much more so than in M1). This are of the brain prepares M1 for the motor act. It does this by facilitating multiple columns in M1. These neurones are more easily sti ...
L8 slides
... • Once the basal ganglia elect an action to perform based on TD reinforcement learning, the cerebellum takes over once the action has been initiated, and uses error-driven learning to shape the performance of the action so that it is accurate and well-coordinated. • The cerebellum only receives inpu ...
... • Once the basal ganglia elect an action to perform based on TD reinforcement learning, the cerebellum takes over once the action has been initiated, and uses error-driven learning to shape the performance of the action so that it is accurate and well-coordinated. • The cerebellum only receives inpu ...
neurons
... biological bases of behavior and mental processes. This area of research is also called biopsychology. Both terms emphasize the idea of a biological approach to the study of psychological processes. Biological psychology is one of the scientific disciplines that makes important contributions to neur ...
... biological bases of behavior and mental processes. This area of research is also called biopsychology. Both terms emphasize the idea of a biological approach to the study of psychological processes. Biological psychology is one of the scientific disciplines that makes important contributions to neur ...
The Nervous System (Chapter 7)
... 22. Outline the steps of the generation of a nerve impulse along unmyelinated fibers using the reading on pages 202 and 203 and also the Figure 7.9 on page 203. ...
... 22. Outline the steps of the generation of a nerve impulse along unmyelinated fibers using the reading on pages 202 and 203 and also the Figure 7.9 on page 203. ...
The fertile brain - Health Research Council
... A recent Fertility New Zealand study found nearly 25 per cent of New Zealand women report they have been infertile - defined as having been unable to conceive after having tried for over a year. Although the brain clearly controls fertility, surprisingly little is known about how. Understanding that ...
... A recent Fertility New Zealand study found nearly 25 per cent of New Zealand women report they have been infertile - defined as having been unable to conceive after having tried for over a year. Although the brain clearly controls fertility, surprisingly little is known about how. Understanding that ...
The Nervous System
... •These are the suport cells in the peripheral nervous system. •Schwann cells provide the myelin sheath for peripheral axons. •Satellite cells serve a slightly similar function to astrocytes, supporting the cell bodies of peripheral neurons. ...
... •These are the suport cells in the peripheral nervous system. •Schwann cells provide the myelin sheath for peripheral axons. •Satellite cells serve a slightly similar function to astrocytes, supporting the cell bodies of peripheral neurons. ...
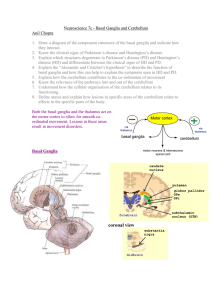
Neuroscience 7c – Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum
... 8. Define ataxia and explain how lesions in specific areas of the cerebellum relate to effects in the specific parts of the body. Both the basal ganglia and the thalamus act on the motor cortex to allow for smooth coordinated movement. Lesions in these areas result in movement disorders. ...
... 8. Define ataxia and explain how lesions in specific areas of the cerebellum relate to effects in the specific parts of the body. Both the basal ganglia and the thalamus act on the motor cortex to allow for smooth coordinated movement. Lesions in these areas result in movement disorders. ...
The mind`s mirror
... 5,449, pages 2,526-2,528), Iacoboni and his colleagues found activity in some of the same areas of the frontal cortex and the parietal lobule in both situations. The difference between the imaging studies in humans and the electrophysiological studies in monkeys is one of scale, explains psychologis ...
... 5,449, pages 2,526-2,528), Iacoboni and his colleagues found activity in some of the same areas of the frontal cortex and the parietal lobule in both situations. The difference between the imaging studies in humans and the electrophysiological studies in monkeys is one of scale, explains psychologis ...
Cranial Nerve Locations CN I Olfactory ----------
... Major alternative route (to the corticospinal pathway) for controlling spinal motor neurons directly and regulating spinal reflexes e.g., tonic inhibition of flexor reflexes allows only noxious stimuli to produce this reflex (part of descending pathways influence pain perception) ...
... Major alternative route (to the corticospinal pathway) for controlling spinal motor neurons directly and regulating spinal reflexes e.g., tonic inhibition of flexor reflexes allows only noxious stimuli to produce this reflex (part of descending pathways influence pain perception) ...
Drosophila as a model to study mechanisms underlying alcohol
... Korsching lab: http://www.genetik.uni-koeln.de/groups/Korsching/ ...
... Korsching lab: http://www.genetik.uni-koeln.de/groups/Korsching/ ...
Reflexes
... iii. integration center- generally within CNS; may involve simply a synapse (monosynaptic) or may involve interneurons (polysynaptic) iv. motor neuron v. effector c. Somatic reflexes involve skeletal muscle responses; when they occur, the cerebral cortex will be notified and you will be aware of the ...
... iii. integration center- generally within CNS; may involve simply a synapse (monosynaptic) or may involve interneurons (polysynaptic) iv. motor neuron v. effector c. Somatic reflexes involve skeletal muscle responses; when they occur, the cerebral cortex will be notified and you will be aware of the ...
The Nervous System
... – Found in the CNS only. – They associate or “connect” sensory neurons and motor neurons. ...
... – Found in the CNS only. – They associate or “connect” sensory neurons and motor neurons. ...
02QUIZ02 ( 44K)
... 5. After Miguel's recent automobile accident, doctors detected damage to his frontal lobe in Broca's area. It is likely that Miguel will have difficulty: A) remembering past events. B) speaking fluently. C) reading. D) understanding other people when they speak. ...
... 5. After Miguel's recent automobile accident, doctors detected damage to his frontal lobe in Broca's area. It is likely that Miguel will have difficulty: A) remembering past events. B) speaking fluently. C) reading. D) understanding other people when they speak. ...
A View of Life
... 1) If you eat right hemispheric sheep brains biweekly, while watching the movie “The Man With Two Brains”, you will be more creative than someone who eats left hemispheric brains and watches the movie “The Wedding Crashers.” ...
... 1) If you eat right hemispheric sheep brains biweekly, while watching the movie “The Man With Two Brains”, you will be more creative than someone who eats left hemispheric brains and watches the movie “The Wedding Crashers.” ...
THE VISUAL SYSTEM: EYE TO CORTEX Outline
... Anticipation of a stimulus increases neural activity in the same circuits affected by the stimulus itself. ...
... Anticipation of a stimulus increases neural activity in the same circuits affected by the stimulus itself. ...
06 Motor Systems
... •Intrafusal fibers: gamma •Extrafusal fibers: alpha •Gamma feedback loop provides more control ...
... •Intrafusal fibers: gamma •Extrafusal fibers: alpha •Gamma feedback loop provides more control ...
CASE 47
... dopamine-containing nerve cells in the substantia nigra. Patients with Parkinson disease may have a combination of symptoms, including resting tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, disturbance of gait, and postural problems. The cause of Parkinson disease is unknown. ...
... dopamine-containing nerve cells in the substantia nigra. Patients with Parkinson disease may have a combination of symptoms, including resting tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, disturbance of gait, and postural problems. The cause of Parkinson disease is unknown. ...
Diseases and Disorders of the Nervous System
... • Death of neurons in the substantia nigra, which normally release dopamine in the basal nuclei, lead to the motor symptoms of the disease • Protein accumulation is associated with neuron degeneration • Possibly result of genetic and environmental factors • Management of symptoms: drugs such as L-do ...
... • Death of neurons in the substantia nigra, which normally release dopamine in the basal nuclei, lead to the motor symptoms of the disease • Protein accumulation is associated with neuron degeneration • Possibly result of genetic and environmental factors • Management of symptoms: drugs such as L-do ...
document
... FIGURE 29.7 Somatotopic maps in M1. (A) Map by Woolsey et al. (1952) in which each figurine represents in black and gray the body parts that moved a lot or a little, respectively, when the cortical surface at that site was stimulated. In addition to the primary representation on the convexity, thei ...
... FIGURE 29.7 Somatotopic maps in M1. (A) Map by Woolsey et al. (1952) in which each figurine represents in black and gray the body parts that moved a lot or a little, respectively, when the cortical surface at that site was stimulated. In addition to the primary representation on the convexity, thei ...
Nervous Tissue
... The part of the neuron which immediately surrounds the nucleus Usually used synonymously with neuron or soma ...
... The part of the neuron which immediately surrounds the nucleus Usually used synonymously with neuron or soma ...
9.3 Synaptic Transmission
... Excitatory neurotransmitters cause an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron to continue the transmission of the nerve impulse. ...
... Excitatory neurotransmitters cause an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron to continue the transmission of the nerve impulse. ...
Fundamentals of Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... going to skeletal muscles and Visceral Motor – going to smooth or cardiac muscles. Inter-neurons receive information from sensory neurons and integrate it, interpret the meaning and pass instructions to motor neurons to act. Neurons (on basis # of appendages) Multipolar Neurons – many dendrites and ...
... going to skeletal muscles and Visceral Motor – going to smooth or cardiac muscles. Inter-neurons receive information from sensory neurons and integrate it, interpret the meaning and pass instructions to motor neurons to act. Neurons (on basis # of appendages) Multipolar Neurons – many dendrites and ...
Inside the brain
... Substantia nigra: The ‘black substance’ contains cells that produce the neurotransmitter dopamine and the pigment melatonin, giving it a black appearance. ...
... Substantia nigra: The ‘black substance’ contains cells that produce the neurotransmitter dopamine and the pigment melatonin, giving it a black appearance. ...