neural correlates of associative face memory in
... To estimate the stimulus selectivity of individual neurons, we also performed analysis using contrast index measures in ...
... To estimate the stimulus selectivity of individual neurons, we also performed analysis using contrast index measures in ...
The Nervous System
... monitor stimuli (sensory input) Control center processes and interprets sensory input and makes decisions about what to (integration) Sends a response by activating a system to take care of business, usually muscles or glands (motor output) ...
... monitor stimuli (sensory input) Control center processes and interprets sensory input and makes decisions about what to (integration) Sends a response by activating a system to take care of business, usually muscles or glands (motor output) ...
text
... representing proximal muscles are located medially. Neurons that innervate extensor muscles are represented superficially in the ventral horn by cell groups along its outer edge, while neurons for flexor muscles are positioned deeper in the ventral horn. The intermedio-lateral column This column is ...
... representing proximal muscles are located medially. Neurons that innervate extensor muscles are represented superficially in the ventral horn by cell groups along its outer edge, while neurons for flexor muscles are positioned deeper in the ventral horn. The intermedio-lateral column This column is ...
Information Processing.indd - Foundations of Exercise Science
... limit exists, rates remain amazingly fast, allowing a batter, for example, to swing at that pitch which seemed to be going outside but instead curved back over the plate. All synaptic transmissions are not of the same strength nor do they exert the same effects. In fact, they differ in terms of the ...
... limit exists, rates remain amazingly fast, allowing a batter, for example, to swing at that pitch which seemed to be going outside but instead curved back over the plate. All synaptic transmissions are not of the same strength nor do they exert the same effects. In fact, they differ in terms of the ...
Ch.10
... spike of an action potential. • Repolarizing the membrane is due to rapid closing of the sodium channels. Potassium gates open more slowly and stay open longer, repolarizing and hyperpolarizing the cell. ...
... spike of an action potential. • Repolarizing the membrane is due to rapid closing of the sodium channels. Potassium gates open more slowly and stay open longer, repolarizing and hyperpolarizing the cell. ...
Slide 1
... • Different gross morphology and behaviors from hermaphrodites • Slimmer than hermaphrodites (no eggs) and a clear (white) ventral gonad • The hermaphrodite gonad is U-shaped while the male gonad is J-shaped U-shaped gonad in hermaphrodites ...
... • Different gross morphology and behaviors from hermaphrodites • Slimmer than hermaphrodites (no eggs) and a clear (white) ventral gonad • The hermaphrodite gonad is U-shaped while the male gonad is J-shaped U-shaped gonad in hermaphrodites ...
Chapter 17:
... - the two hemispheres are connected by the corpus callosum allowing info to be shared between the hemispheres (a collection of nerve fibres) which are sometimes severed to control epilepsy leading to interesting results - the cerebrum can be subdivided into 4 lobes 1. Frontal (walking, speech, intel ...
... - the two hemispheres are connected by the corpus callosum allowing info to be shared between the hemispheres (a collection of nerve fibres) which are sometimes severed to control epilepsy leading to interesting results - the cerebrum can be subdivided into 4 lobes 1. Frontal (walking, speech, intel ...
Physiology Ch 55 p667-678 [4-25
... -motor cortex divided into primary motor cortex, premotor area, and supplementary motor area Primary Motor Cortex – in the 1st convolution of frontal lobes anterior to central sulcus; begins laterally in sylvian fissure and spreads superiorly to uppermost brain, into longitudinal fissure -more than ...
... -motor cortex divided into primary motor cortex, premotor area, and supplementary motor area Primary Motor Cortex – in the 1st convolution of frontal lobes anterior to central sulcus; begins laterally in sylvian fissure and spreads superiorly to uppermost brain, into longitudinal fissure -more than ...
Research Presentation Slides - Emory University School of Medicine
... The basal ganglia include the structures indicated in red. They are components of large segregated corBcal-‐sub-‐ corBcal neural networks ...
... The basal ganglia include the structures indicated in red. They are components of large segregated corBcal-‐sub-‐ corBcal neural networks ...
17- The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
... is associated with paralysis and Alzheimer’s disease. An oversupply of dopamine—involved with learning, emotional arousal, and movement—is linked to schizophrenia, while an undersupply is linked to Parkinson’s disease. An undersupply of norepinephrine and serotonin may result in depression. Neuron A ...
... is associated with paralysis and Alzheimer’s disease. An oversupply of dopamine—involved with learning, emotional arousal, and movement—is linked to schizophrenia, while an undersupply is linked to Parkinson’s disease. An undersupply of norepinephrine and serotonin may result in depression. Neuron A ...
Chp 9: NERVOUS TISSUE
... ______________________________: have several dendrites and one axon; most in brain and spinal cord ______________________________: have one main dendrite and one axon; retina of the eye, inner ear, olfactory area of brain ______________________________: dendrites and one axon fused together fo ...
... ______________________________: have several dendrites and one axon; most in brain and spinal cord ______________________________: have one main dendrite and one axon; retina of the eye, inner ear, olfactory area of brain ______________________________: dendrites and one axon fused together fo ...
What and Where Pathways
... Figure 4.35 fMRI responses of the human brain to various types of stimuli: (a) areas that were most strongly activated by houses, faces, and chairs; (b) all areas activated by each type of stimulus. (From Alumit Ishai, Leslie G. Ungerleider, Alex Martin, & James V.Haxby,”The representation of objec ...
... Figure 4.35 fMRI responses of the human brain to various types of stimuli: (a) areas that were most strongly activated by houses, faces, and chairs; (b) all areas activated by each type of stimulus. (From Alumit Ishai, Leslie G. Ungerleider, Alex Martin, & James V.Haxby,”The representation of objec ...
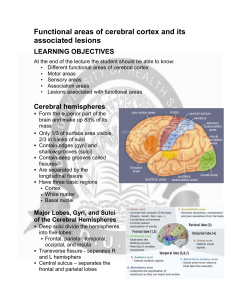
Functional areas of cerebral cortex and its associated lesions
... Composed of pyramidal cells Large neurons whose axons make up the corticospinal tracts Allows conscious control of precise, skilled, voluntary movements i.e., controls skeletal muscle Motor homunculus – caricature of relative amounts of cortical tissue devoted to each motor function Premot ...
... Composed of pyramidal cells Large neurons whose axons make up the corticospinal tracts Allows conscious control of precise, skilled, voluntary movements i.e., controls skeletal muscle Motor homunculus – caricature of relative amounts of cortical tissue devoted to each motor function Premot ...
The Cerebellum Anatomically consists of two hemispheres and
... 1. From vermis to medullary and pontine regions ...
... 1. From vermis to medullary and pontine regions ...
Nervous System Cells - Dr. M`s Classes Rock
... Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters: means by which neurons communicate with one another; more than 30 compounds are known to be neurotransmitters, and dozens of others are suspected Common classification of neurotransmitters: o Function: determined by the postsynaptic receptor; two major funct ...
... Neurotransmitters Neurotransmitters: means by which neurons communicate with one another; more than 30 compounds are known to be neurotransmitters, and dozens of others are suspected Common classification of neurotransmitters: o Function: determined by the postsynaptic receptor; two major funct ...
lecture - McLoon Lab - University of Minnesota
... Upper motor neuron in motor cortex (most axons cross to the opposite side of the body) ...
... Upper motor neuron in motor cortex (most axons cross to the opposite side of the body) ...
Neurons
... impulses from specialized structures to the Central Nervous System Efferent- conduct electrical signals from the CNS to muscle or glad cells Inter- reside entirely within the CNS and make up about 99% of all neurons ...
... impulses from specialized structures to the Central Nervous System Efferent- conduct electrical signals from the CNS to muscle or glad cells Inter- reside entirely within the CNS and make up about 99% of all neurons ...
Chapter 17:
... - the two hemispheres are connected by the corpus callosum allowing info to be shared between the hemispheres (a collection of nerve fibres) which are sometimes severed to control epilepsy leading to interesting results - the cerebrum can be subdivided into 4 lobes 1. Frontal (walking, speech, intel ...
... - the two hemispheres are connected by the corpus callosum allowing info to be shared between the hemispheres (a collection of nerve fibres) which are sometimes severed to control epilepsy leading to interesting results - the cerebrum can be subdivided into 4 lobes 1. Frontal (walking, speech, intel ...
Nervous Nellie Circuit Lesson Summary: Neurons, or nerve cells
... Working in pairs, ask students to open the Virtual Neurons software. ...
... Working in pairs, ask students to open the Virtual Neurons software. ...
Pontine Respiratory Center
... the walls of bronchi and bronchioles, this in turn stimulates the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve then inhibits the apneustic centre thus switching off the inspiration . • This is a protective mechanism preventing excess inflation of the lungs. The threshold for this reflex is tidal volume more than 1. ...
... the walls of bronchi and bronchioles, this in turn stimulates the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve then inhibits the apneustic centre thus switching off the inspiration . • This is a protective mechanism preventing excess inflation of the lungs. The threshold for this reflex is tidal volume more than 1. ...
The Dancing Cockroach Leg
... During the beats (low frequency, high amplitude waves) or higher volume portions of the song. 3) Why doesn’t the cockroach leg move during the first 30 sec of the song? The woman is singing in a higher pitch (high frequency, low amplitude waves), which is not sufficient to bring the motor neuron to ...
... During the beats (low frequency, high amplitude waves) or higher volume portions of the song. 3) Why doesn’t the cockroach leg move during the first 30 sec of the song? The woman is singing in a higher pitch (high frequency, low amplitude waves), which is not sufficient to bring the motor neuron to ...
Chapter 1: Concepts and Methods in Biology - Rose
... 2. Electrical signal –> chemical signal –> electrical signal a. Presynaptic membrane depolarizes (due to arrival of action potential) b. Depolarization triggers an influx of Ca2+ c. Ca2+ influx causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with presynaptic membrane d. Vesicles release neurotransmitter into synap ...
... 2. Electrical signal –> chemical signal –> electrical signal a. Presynaptic membrane depolarizes (due to arrival of action potential) b. Depolarization triggers an influx of Ca2+ c. Ca2+ influx causes synaptic vesicles to fuse with presynaptic membrane d. Vesicles release neurotransmitter into synap ...
The Nervous System
... Functional Subdivisions of the PNS Sensory division: (Afferent) PNSCNS Motor division: (Efferent) CNS Muscles and Glands ...
... Functional Subdivisions of the PNS Sensory division: (Afferent) PNSCNS Motor division: (Efferent) CNS Muscles and Glands ...
PSYC465 - neuroanatomy
... some large-molecules and proteins into the brain. Not all large molecules are impeded (e.g., glucose). Sex hormones readily pass through to certain brain areas where the BBB is weak. ...
... some large-molecules and proteins into the brain. Not all large molecules are impeded (e.g., glucose). Sex hormones readily pass through to certain brain areas where the BBB is weak. ...
Bio 103 Lecture Outline:
... 2. Association Areas - regions that are not primary motor or sensory areas - widespread throughout the cerebral cortex - analyze and interpret sensory experiences Frontal Lobe Association Areas: Parietal Lobe Association Areas: Temporal Lobe Association Areas: Occipital Lobe Association Areas: ...
... 2. Association Areas - regions that are not primary motor or sensory areas - widespread throughout the cerebral cortex - analyze and interpret sensory experiences Frontal Lobe Association Areas: Parietal Lobe Association Areas: Temporal Lobe Association Areas: Occipital Lobe Association Areas: ...