Annotated Bibliography Ferdinando A. Mussa
... the one dimensional movement of a robotic arm. The importance of this breakthrough was that the rats could control the robotic arm without any explicit movement of their own body parts. Most research with BMI technology has been performed on the rhesus monkey. By implanting single neuron-recordings ...
... the one dimensional movement of a robotic arm. The importance of this breakthrough was that the rats could control the robotic arm without any explicit movement of their own body parts. Most research with BMI technology has been performed on the rhesus monkey. By implanting single neuron-recordings ...
Lesson 1 | The Nervous System
... 1. A stimulus is a change in an organism’s environment that causes a (thought/response). 2. Neuron is another name for a (new cell/nerve cell). 3. The three kinds of neurons are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and (interneurons/axons). ...
... 1. A stimulus is a change in an organism’s environment that causes a (thought/response). 2. Neuron is another name for a (new cell/nerve cell). 3. The three kinds of neurons are sensory neurons, motor neurons, and (interneurons/axons). ...
Tutorial 10: Temporal and Spatial Summation Figure 10: Temporal
... Sherrington noted the difference between the motor neurons and sensory neurons, which he called proprioceptors. With this distinction, the role of the nervous system in the integration of information emerged. The knee jerk reflex, he noted, was the result of interaction between two reciprocal forces ...
... Sherrington noted the difference between the motor neurons and sensory neurons, which he called proprioceptors. With this distinction, the role of the nervous system in the integration of information emerged. The knee jerk reflex, he noted, was the result of interaction between two reciprocal forces ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Coast Colleges Home Page
... Na+ Channels Close, K+ Channels Open & K+ Diffuses Out of Neuron Results In Repolarization (+ outside/- inside) Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
... Na+ Channels Close, K+ Channels Open & K+ Diffuses Out of Neuron Results In Repolarization (+ outside/- inside) Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
Nervous System Ch 10 Notes - Reading Community Schools
... • If a neuron responds at all, it responds completely • A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon • All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength ...
... • If a neuron responds at all, it responds completely • A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon • All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... Na+ Channels Close, K+ Channels Open & K+ Diffuses Out of Neuron Results In Repolarization (+ outside/- inside) Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
... Na+ Channels Close, K+ Channels Open & K+ Diffuses Out of Neuron Results In Repolarization (+ outside/- inside) Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
Sparse but not `Grandmother-cell` coding in the medial temporal lobe
... Although a large number of neuropsychological and imaging studies have demonstrated that the medial temporal lobe (MTL) plays an important role in human memory, there are few data regarding the activity of neurons involved in this process. The MTL receives massive inputs from visual cortical areas, ...
... Although a large number of neuropsychological and imaging studies have demonstrated that the medial temporal lobe (MTL) plays an important role in human memory, there are few data regarding the activity of neurons involved in this process. The MTL receives massive inputs from visual cortical areas, ...
Predicting voluntary movements from motor cortical activity with
... were recorded. The threshold was observed and adjusted online to compensate for long term changes in signal amplitude. The time stamps of spike occurrences along with behavioral events such as the preparatory signal, the response signal, movement onset, and movement end were stored at a time resolut ...
... were recorded. The threshold was observed and adjusted online to compensate for long term changes in signal amplitude. The time stamps of spike occurrences along with behavioral events such as the preparatory signal, the response signal, movement onset, and movement end were stored at a time resolut ...
Divisions of the Nervous System
... – Brain and spinal cord of dorsal body cavity – Integration and control center • Interprets sensory input and dictates motor output ...
... – Brain and spinal cord of dorsal body cavity – Integration and control center • Interprets sensory input and dictates motor output ...
excitatory neurotransmitter
... Glutamate is a neurotransmitter in the CNS. It is involved in a range of activities in the brain including: learning, memory, perception, thinking and movement. When glutamate is released into the synapse it is absorbed by NMDA receptor sites on the post-synaptic dendrites. Glutamate is excitatory, ...
... Glutamate is a neurotransmitter in the CNS. It is involved in a range of activities in the brain including: learning, memory, perception, thinking and movement. When glutamate is released into the synapse it is absorbed by NMDA receptor sites on the post-synaptic dendrites. Glutamate is excitatory, ...
peripheral nervous system
... When light enters the eye it first travels through a transparent layer of cells called the cornea. The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by muscles of the iris, which is the part of the eye that is colored. Behind the iris is the lens. The lens inverts the image and projects it onto the ...
... When light enters the eye it first travels through a transparent layer of cells called the cornea. The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by muscles of the iris, which is the part of the eye that is colored. Behind the iris is the lens. The lens inverts the image and projects it onto the ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... • Along with the endocrine system, its primary function is homeostasis of the internal environment • The majority of the activities of the autonomic system do not impinge on consciousness • The control exerted by the system is extremely rapid and widespread • The visceral receptors include chemorece ...
... • Along with the endocrine system, its primary function is homeostasis of the internal environment • The majority of the activities of the autonomic system do not impinge on consciousness • The control exerted by the system is extremely rapid and widespread • The visceral receptors include chemorece ...
Notes Intro to Nervous System and Neurons
... – Two subdivisions of the Motor (efferent) division 1. Somatic nervous system = voluntary Skeletal muscles (except reflexes) ...
... – Two subdivisions of the Motor (efferent) division 1. Somatic nervous system = voluntary Skeletal muscles (except reflexes) ...
Of Toasters and Molecular Ticker Tapes
... each neuron may interact with each other neuron. This, in turn, leads to models with many free parameters, which requires new statistical methods of fitting these parameters. Molecular biology has seen accelerating progress over the last decades. One readily quantifiable cost in molecular biology is ...
... each neuron may interact with each other neuron. This, in turn, leads to models with many free parameters, which requires new statistical methods of fitting these parameters. Molecular biology has seen accelerating progress over the last decades. One readily quantifiable cost in molecular biology is ...
2-Motor Unit2016-12-11 07:274.3 MB
... • The higher the motor unit recruitment , the stronger the muscle contraction . • The force produced by a single motor unit is determined by (1) the number of muscle fibers in the unit , & (2) the frequency with which the muscle fibers are stimulated by their ...
... • The higher the motor unit recruitment , the stronger the muscle contraction . • The force produced by a single motor unit is determined by (1) the number of muscle fibers in the unit , & (2) the frequency with which the muscle fibers are stimulated by their ...
BOX 43.1 THE OPTICAL FRACTIONATOR STEREOLOGICAL
... of the sections is then chosen for analysis (positions represented schematically in top panel). This first level of sampling, the “section fraction,” therefore comprises the fraction of the total number of sections examined. For example, if every tenth section through the hippocampus is analyzed, th ...
... of the sections is then chosen for analysis (positions represented schematically in top panel). This first level of sampling, the “section fraction,” therefore comprises the fraction of the total number of sections examined. For example, if every tenth section through the hippocampus is analyzed, th ...
The Cellular Level of Organization
... Structural Classification of Neurons Bipolar neuron - 2 extensions from cell body – Examples: rods and cones (shapes of dendrites) of retina, olfactory neurons, inner ear neurons Multipolar neuron - many extensions from cell ...
... Structural Classification of Neurons Bipolar neuron - 2 extensions from cell body – Examples: rods and cones (shapes of dendrites) of retina, olfactory neurons, inner ear neurons Multipolar neuron - many extensions from cell ...
Thalamus & Hypothalamus
... • Forms floor and lower walls of third ventricle • Contains various classes of peptidergic neuroendocrine cells which control endocrine function • Communicates with cortex via limbic system and also via direct projections ...
... • Forms floor and lower walls of third ventricle • Contains various classes of peptidergic neuroendocrine cells which control endocrine function • Communicates with cortex via limbic system and also via direct projections ...
Unit 8 Nervous System
... Input travels along several pathways Important in higher-level mental functioning Ex. Smell reminds you of an odor and associated experience ...
... Input travels along several pathways Important in higher-level mental functioning Ex. Smell reminds you of an odor and associated experience ...
CORTEX I. GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS a. Cerebral cortex = grey
... iii. Callosal (commissural) inputs L3 (interconnect homologous areas in two hemispheres) *area 17, hand area of somatosensory cortex have NO callosal connections b. Outputs to cortex i. Transcortical and callosal efferents: from L3 (go to L3, L1) ii. Long projection pathways: from L5 to brainstem, ...
... iii. Callosal (commissural) inputs L3 (interconnect homologous areas in two hemispheres) *area 17, hand area of somatosensory cortex have NO callosal connections b. Outputs to cortex i. Transcortical and callosal efferents: from L3 (go to L3, L1) ii. Long projection pathways: from L5 to brainstem, ...
Session 2. Synaptic Plasticity (Chair, H. Kamiguchi)
... mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Both kinases then translocate into the nucleus where they can activate transcription factors such as ApCREB1, ApCREB2, and ApAF, expressed in sensory neurons. Repeated pulses of serotonin (5-HT) induce long-term facilitation (LTF) of the synapses between sens ...
... mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Both kinases then translocate into the nucleus where they can activate transcription factors such as ApCREB1, ApCREB2, and ApAF, expressed in sensory neurons. Repeated pulses of serotonin (5-HT) induce long-term facilitation (LTF) of the synapses between sens ...
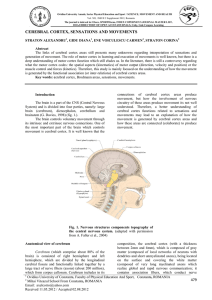
cerebral cortex, sensations and movements
... nucleus, substantia nigra, etc.). In Brodmann area 8 there are nerve centers (part of the oculocephalogyric area) that control combined eye and head movements; so, the nerve center of the right hemisphere produce simultaneous head and eyes left turns and vice versa. Premotor area is located above Br ...
... nucleus, substantia nigra, etc.). In Brodmann area 8 there are nerve centers (part of the oculocephalogyric area) that control combined eye and head movements; so, the nerve center of the right hemisphere produce simultaneous head and eyes left turns and vice versa. Premotor area is located above Br ...
Dynamical systems view
... Criticism of the representational approach An epic, twenty-year battle was fought over the cortical representation of movement. Do motor cortex neurons represent the direction of the hand during reaching, or do they represent other features of movement such as joint rotation or muscle output? Grazi ...
... Criticism of the representational approach An epic, twenty-year battle was fought over the cortical representation of movement. Do motor cortex neurons represent the direction of the hand during reaching, or do they represent other features of movement such as joint rotation or muscle output? Grazi ...