Control_Systems11
... impulse travels up sensory neurons, to the spinal cord (interneuron), then immediately travels down motor neurons for a response. The pathway the impulse travels is called the reflex arc ...
... impulse travels up sensory neurons, to the spinal cord (interneuron), then immediately travels down motor neurons for a response. The pathway the impulse travels is called the reflex arc ...
ppt
... maggots eat the dead skin cells and bacteria. maggot therapy (also known as maggot debridement therapy (mdt), larval therapy, larva therapy, or larvae therapy) is the intentional introduction of live, disinfected maggots or fly larvae into non-healing skin or soft tissue wounds of a human or other a ...
... maggots eat the dead skin cells and bacteria. maggot therapy (also known as maggot debridement therapy (mdt), larval therapy, larva therapy, or larvae therapy) is the intentional introduction of live, disinfected maggots or fly larvae into non-healing skin or soft tissue wounds of a human or other a ...
The Nervous System
... • A neuron has a large cell body that contains the nucleus. • Dendrites - threadlike extensions on the cell body that carry impulses toward the neuron’s cell body. • Axon - carries impulses away from the cell body. ...
... • A neuron has a large cell body that contains the nucleus. • Dendrites - threadlike extensions on the cell body that carry impulses toward the neuron’s cell body. • Axon - carries impulses away from the cell body. ...
Slide ()
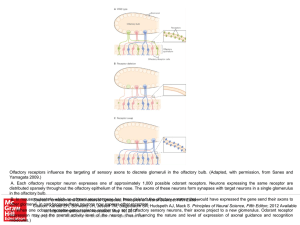
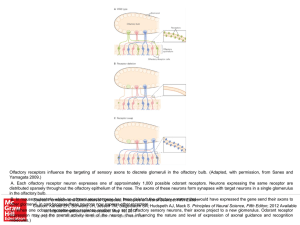
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
... Olfactory receptors influence the targeting of sensory axons to discrete glomeruli in the olfactory bulb. (Adapted, with permission, from Sanes and Yamagata 2009.) A. Each olfactory receptor neuron expresses one of approximately 1,000 possible odorant receptors. Neurons expressing the same receptor ...
Chapter 15 - missdannocksyear11biologyclass
... 2. Conduction (propagation) of an impulse along axons 3. Chemical transmission of a signal to another cell across a synapse Sensory nerves respond to stimuli by depolarising the nerve cell. It does this by making the inside of the cell less negative. If depolarisation is large enough an action poten ...
... 2. Conduction (propagation) of an impulse along axons 3. Chemical transmission of a signal to another cell across a synapse Sensory nerves respond to stimuli by depolarising the nerve cell. It does this by making the inside of the cell less negative. If depolarisation is large enough an action poten ...
System Introduction to Sensory Physiology: Sensory- Motor
... 2) MRO1- slow adaptation- IK (Ca), Na/K pump! 3) MRO1 and MRO2 have similar generator potentials! 4) MRO2 adapts more quickly to depolarization! ...
... 2) MRO1- slow adaptation- IK (Ca), Na/K pump! 3) MRO1 and MRO2 have similar generator potentials! 4) MRO2 adapts more quickly to depolarization! ...
Bio 17 – Nervous & Endocrine Systems
... low levels; important for sleep and low levels assoc with depression Runner’s High = DECREASED GABA ...
... low levels; important for sleep and low levels assoc with depression Runner’s High = DECREASED GABA ...
The Nervous System - Catherine Huff`s Site
... • Norepinephrine/epinephrine associated with "fight or flight" reactions of sympathetic nervous system • Dopamine - involved with autonomic functions and muscle control ...
... • Norepinephrine/epinephrine associated with "fight or flight" reactions of sympathetic nervous system • Dopamine - involved with autonomic functions and muscle control ...
The Nervous System
... • Norepinephrine/epinephrine associated with "fight or flight" reactions of sympathetic nervous system • Dopamine - involved with autonomic functions and muscle control ...
... • Norepinephrine/epinephrine associated with "fight or flight" reactions of sympathetic nervous system • Dopamine - involved with autonomic functions and muscle control ...
Unit XIV: Regulation
... - nerves are bundles of neurons 1 – Sensory Neurons – located in sense organs – receptors carry impulses to the spinal cord and brain 2 – Interneurons – located in the central nervous system interpret impulses 3 – Motor Neurons – located at effectors carry impulses from the CNS to muscles and glands ...
... - nerves are bundles of neurons 1 – Sensory Neurons – located in sense organs – receptors carry impulses to the spinal cord and brain 2 – Interneurons – located in the central nervous system interpret impulses 3 – Motor Neurons – located at effectors carry impulses from the CNS to muscles and glands ...
Unit 2: Nervous System
... • Spinal cord = communication highway • All nerves communicate through Spine ...
... • Spinal cord = communication highway • All nerves communicate through Spine ...
Nervous Tissue
... • White matter = myelinated processes (white in color) • Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons and neuroglia (gray color) – In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core surrounded by white matter – In the brain = a thin outer shell ...
... • White matter = myelinated processes (white in color) • Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons and neuroglia (gray color) – In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core surrounded by white matter – In the brain = a thin outer shell ...
Lecture 7 – Synaptic Transmission II -
... 5. NMDA receptors are blocked by external Mg2+, which binds to a site within the pore at negative resting potentials. Thus, current carried by AMPA and kainate receptors largely determines EPSP at negative resting potentials. However, during strong synaptic activity, the postsynaptic cell depolarize ...
... 5. NMDA receptors are blocked by external Mg2+, which binds to a site within the pore at negative resting potentials. Thus, current carried by AMPA and kainate receptors largely determines EPSP at negative resting potentials. However, during strong synaptic activity, the postsynaptic cell depolarize ...
SBI 4U Homeostasis 2
... effect on the postsynaptic membrane. • If the effect is excitatory, the receptor proteins will allow positive ions, such as sodium to flow into the postsynaptic neuron and the membrane will depolarize. • If the neurotransmitter is inhibitory, the receptor will trigger potassium ions to open, allowin ...
... effect on the postsynaptic membrane. • If the effect is excitatory, the receptor proteins will allow positive ions, such as sodium to flow into the postsynaptic neuron and the membrane will depolarize. • If the neurotransmitter is inhibitory, the receptor will trigger potassium ions to open, allowin ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... Possibly caused by stimulation from neurons that used to receive signals from the appendage. Possibly from the brain and its sense of body ...
... Possibly caused by stimulation from neurons that used to receive signals from the appendage. Possibly from the brain and its sense of body ...
暨 南 大 学 考 试 试 卷
... The basic way for nervous regulation is the reflex which is the regular response to adapt to the stimulus under the involvement of central nervous system. ...
... The basic way for nervous regulation is the reflex which is the regular response to adapt to the stimulus under the involvement of central nervous system. ...
Mod 07-Lecture - Phoenix Military Academy
... NTs have either an excitatory effect, making it more likely the receiving neuron will fire; or an inhibitory effect, making it less likely. Particular NTs seem to effect particular behavior and emotions. Dopamine = affects learning, attention and emotion (alertness and movement); excess D activity i ...
... NTs have either an excitatory effect, making it more likely the receiving neuron will fire; or an inhibitory effect, making it less likely. Particular NTs seem to effect particular behavior and emotions. Dopamine = affects learning, attention and emotion (alertness and movement); excess D activity i ...
electrochemical impulse
... threshold level before the signal will be sent. This threshold is important for it prevents small changes that don’t have an effect from sending a signal to the brain. Without the threshold, the sensory neurons would send signals continuously which would overwhelm the brain. • Once the threshold lev ...
... threshold level before the signal will be sent. This threshold is important for it prevents small changes that don’t have an effect from sending a signal to the brain. Without the threshold, the sensory neurons would send signals continuously which would overwhelm the brain. • Once the threshold lev ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.