02biologya
... Neurons and the Neurotransmitters • Glial cells – Cells that help to make the brain more efficient by holding neurons together, removing waste products such as dead neurons, making the myelin coating for the axons, and performing other manufacturing, nourishing, and cleanup tasks – Synapse – The ju ...
... Neurons and the Neurotransmitters • Glial cells – Cells that help to make the brain more efficient by holding neurons together, removing waste products such as dead neurons, making the myelin coating for the axons, and performing other manufacturing, nourishing, and cleanup tasks – Synapse – The ju ...
Nervous System
... synapse & binds to receptor protein on postsynaptic cell 4. Postsynaptic cell is excited or inhibited 5. Neurotransmitter in synapse is deactivated ...
... synapse & binds to receptor protein on postsynaptic cell 4. Postsynaptic cell is excited or inhibited 5. Neurotransmitter in synapse is deactivated ...
Slide ()
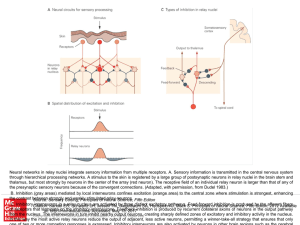
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
Nervous System
... synapse & binds to receptor protein on postsynaptic cell 4. Postsynaptic cell is excited or inhibited 5. Neurotransmitter in synapse is deactivated ...
... synapse & binds to receptor protein on postsynaptic cell 4. Postsynaptic cell is excited or inhibited 5. Neurotransmitter in synapse is deactivated ...
PNS Study Guide
... 5. What structures of the body make up the CNS and PNS? 6. What are the two functional classifications of the PNS? Describe the function of each (flow chart). 7. What are the 2 types of motor nerves? How are they different? 8. What are the 2 types of autonomic nerves? Make sure you know when they ar ...
... 5. What structures of the body make up the CNS and PNS? 6. What are the two functional classifications of the PNS? Describe the function of each (flow chart). 7. What are the 2 types of motor nerves? How are they different? 8. What are the 2 types of autonomic nerves? Make sure you know when they ar ...
mechanoreceptors
... 1-Tocuh receptors in the skin which are stimulated by light mechanical stimuli. 2-Pressure receptors in the subcutaneous tissues which are stimulated by deep mechanical stimuli. ...
... 1-Tocuh receptors in the skin which are stimulated by light mechanical stimuli. 2-Pressure receptors in the subcutaneous tissues which are stimulated by deep mechanical stimuli. ...
Control of Movement
... disproportionate amount of cortex for body parts high sensitivity: large cortical area ~ ...
... disproportionate amount of cortex for body parts high sensitivity: large cortical area ~ ...
nerve slide show
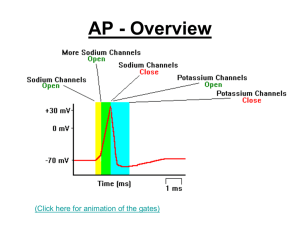
... neurotransmitters released by other neurons or other stimuli • Membrane becomes permeable to sodium ions through the opening of “gates” • Depolarization occurs and the inside is now more positive than the outside ...
... neurotransmitters released by other neurons or other stimuli • Membrane becomes permeable to sodium ions through the opening of “gates” • Depolarization occurs and the inside is now more positive than the outside ...
Nerve Cell Impulses
... • This neurotransmitter is the brain's major excitatory neurotransmitter. It is vital for creating the links between neurons that are the basis of learning and long-term memory. ...
... • This neurotransmitter is the brain's major excitatory neurotransmitter. It is vital for creating the links between neurons that are the basis of learning and long-term memory. ...
The Nervous System
... – The gap that separates adjacent neurons – Transmission of impulse across the synapse • Presynaptic cell to postsynaptic cell • Electrical or Chemical – Most synaptic clefts are traversed by chemicals ...
... – The gap that separates adjacent neurons – Transmission of impulse across the synapse • Presynaptic cell to postsynaptic cell • Electrical or Chemical – Most synaptic clefts are traversed by chemicals ...
Biology 30 NERVOUS SYSTEM
... state where there is an unequal distribution of + and – charges across the membrane. This is achieved because [Na+] is higher on the outside, while [K+] and [Cl-] concentrations are higher on the inside. The different concentrations of Na+ and K+ are maintained by a sodium / potassium pump. Gates fo ...
... state where there is an unequal distribution of + and – charges across the membrane. This is achieved because [Na+] is higher on the outside, while [K+] and [Cl-] concentrations are higher on the inside. The different concentrations of Na+ and K+ are maintained by a sodium / potassium pump. Gates fo ...
Reflexes and Homeostasis
... An example of the latter would be the stretch receptors that tell your stomach to start contracting harder after a big meal, or the pressure receptors (baroreceptors) in your carotid arteries which detect blood pressure and tell your heart to beat faster or slower, according to the pressure that the ...
... An example of the latter would be the stretch receptors that tell your stomach to start contracting harder after a big meal, or the pressure receptors (baroreceptors) in your carotid arteries which detect blood pressure and tell your heart to beat faster or slower, according to the pressure that the ...
reading guide
... in both vertebrates and invertebrates, and it is released by the neurons that synapse with muscle cells at the neuromuscular junction. If you look ahead to Chapter 50, Figure 50.29, you will see a synapse between a neuron and a muscle cell, resulting in depolarization of the muscle cell and its cont ...
... in both vertebrates and invertebrates, and it is released by the neurons that synapse with muscle cells at the neuromuscular junction. If you look ahead to Chapter 50, Figure 50.29, you will see a synapse between a neuron and a muscle cell, resulting in depolarization of the muscle cell and its cont ...
Endocrine System PowerPoint
... Prepares the body for action e.g. quickens and and strengthens Oestrogen progesterone heart rate, increases breathing Fertility rate, dilates pupils Secondary sex chars Sperm production/fertility Secondary sex chars Fertility ...
... Prepares the body for action e.g. quickens and and strengthens Oestrogen progesterone heart rate, increases breathing Fertility rate, dilates pupils Secondary sex chars Sperm production/fertility Secondary sex chars Fertility ...
The Nervous System
... Synapse - junction between two communicating neurons Nerve pathway - nerve impulse travels from neuron to neuron ...
... Synapse - junction between two communicating neurons Nerve pathway - nerve impulse travels from neuron to neuron ...
11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... c. Mechanically gated channels open when a membrane receptor is physically deformed. ...
... c. Mechanically gated channels open when a membrane receptor is physically deformed. ...
9.01 Exam #1 September 27, 2004 30 multiple
... d) Na+ / due to its large driving force e) Cl- / because it’s the only negatively charged ion 16) What effect does an intravenous injection of KCl have on behavior of neurons? a) Extracellular [K+] decreases and therefore the membrane potential gets closer to Na+ equilibrium potential. b) The membra ...
... d) Na+ / due to its large driving force e) Cl- / because it’s the only negatively charged ion 16) What effect does an intravenous injection of KCl have on behavior of neurons? a) Extracellular [K+] decreases and therefore the membrane potential gets closer to Na+ equilibrium potential. b) The membra ...
Sensory Organs
... Provide information to CNS on posture, orientation in space, pressure, etc. Fibers are heavily myelinated for rapid transmission. Sensory Receptor ...
... Provide information to CNS on posture, orientation in space, pressure, etc. Fibers are heavily myelinated for rapid transmission. Sensory Receptor ...
AP – All or nothing
... – Time is needed to restore the proteins of voltage sensitive ion channels to their original resting conditions. – Na+ channels cannot be opened, as it can’t be depolarised again. WHY? – AP travel in one direction only. – Produces discrete impulses. – Limits the frequency of impulses. ...
... – Time is needed to restore the proteins of voltage sensitive ion channels to their original resting conditions. – Na+ channels cannot be opened, as it can’t be depolarised again. WHY? – AP travel in one direction only. – Produces discrete impulses. – Limits the frequency of impulses. ...
Nervous Tissue - MrsSconyersAnatomy
... among neurons and effectors. Compare the basic type of ion channels, and explain how they relate to action potentials and graded potentials. Describe the factors that maintain a resting membrane potential. ...
... among neurons and effectors. Compare the basic type of ion channels, and explain how they relate to action potentials and graded potentials. Describe the factors that maintain a resting membrane potential. ...
Nervous Systems
... Chemoreception Many animals produce species-specific compounds called pheromones. Pheremones released into the environment carry information about territory, social hierarchy, sex and reproductive state. ...
... Chemoreception Many animals produce species-specific compounds called pheromones. Pheremones released into the environment carry information about territory, social hierarchy, sex and reproductive state. ...
Neurons, Synapses and Long-term Potentiation
... • Neuron to neuron communications are made possible by synapses • At the synapse, neurotransmitters are released in response to excitation of the presynaptic neuron, which then diffuses across the synaptic cleft, binding to receptors on the postsynaptic cell. ...
... • Neuron to neuron communications are made possible by synapses • At the synapse, neurotransmitters are released in response to excitation of the presynaptic neuron, which then diffuses across the synaptic cleft, binding to receptors on the postsynaptic cell. ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.