Experiment HN-6: Hoffman Reflex using the Soleus Muscle
... The Hoffman reflex is studied regularly in sports medicine research because of its changes in response to injuries and various therapies. An example of this is clear in people who have recently sprained their ankle. The very definition of a sprain injury is damage to a ligament, however, ligaments a ...
... The Hoffman reflex is studied regularly in sports medicine research because of its changes in response to injuries and various therapies. An example of this is clear in people who have recently sprained their ankle. The very definition of a sprain injury is damage to a ligament, however, ligaments a ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Innervate organs through specific axon bundles called autonomic plexuses. Communication by chemical messengers, called neurotransmitters. specific in each division of the autonomic nervous system Usually all organs are innervated by both divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Maintains homeostas ...
... Innervate organs through specific axon bundles called autonomic plexuses. Communication by chemical messengers, called neurotransmitters. specific in each division of the autonomic nervous system Usually all organs are innervated by both divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Maintains homeostas ...
Sensory receptors
... deformation caused by stimuli such as pressure, stretch, motion, and sound • The sense of touch in mammals relies on mechanoreceptors that are dendrites of sensory neurons ...
... deformation caused by stimuli such as pressure, stretch, motion, and sound • The sense of touch in mammals relies on mechanoreceptors that are dendrites of sensory neurons ...
MicroRNA ablation affects Bergmann glial morphology and disrupts
... MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles during development of the central nervous system (CNS). Several reports indicate that tissue development and cellular differentiation in the developing forebrains are disrupted in the absence of miRNAs. However, miRNA functions during cerebellar development ha ...
... MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles during development of the central nervous system (CNS). Several reports indicate that tissue development and cellular differentiation in the developing forebrains are disrupted in the absence of miRNAs. However, miRNA functions during cerebellar development ha ...
FUNCTIONAL NEUROANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD LEARNING
... Posterior root ganglion → Tip of posterior gray column → Posteriolateral tract of Lissauer → Synapse in posterior column. Second order neuron axon cross obliquely to opposite side in anterior commissure ascend as lateral spinothalamic tract → In medulla joined by anterior spinothalamic and spinotect ...
... Posterior root ganglion → Tip of posterior gray column → Posteriolateral tract of Lissauer → Synapse in posterior column. Second order neuron axon cross obliquely to opposite side in anterior commissure ascend as lateral spinothalamic tract → In medulla joined by anterior spinothalamic and spinotect ...
FUNCTIONAL NEUROANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD LEARNING
... Like the lateral tract fibres enter the tip of posterior column contribute to posteriolateral tract of lissauer and synapses with cells of substantia gelatinosa → Second order neuron axon cross obliquely in anterior commissure → Joins spinal lemniscus remaining course is same as Lateral spinothalami ...
... Like the lateral tract fibres enter the tip of posterior column contribute to posteriolateral tract of lissauer and synapses with cells of substantia gelatinosa → Second order neuron axon cross obliquely in anterior commissure → Joins spinal lemniscus remaining course is same as Lateral spinothalami ...
408 3 Physiology and Anatomy for the Speed and Power
... Neural Fatigue. Sports performance concerns involve prevention of fatigue or deterioration of movement quality. Studies have shown that in prolonged voluntary contractions reduced force production could not be improved by direct motor nerve stimulation, indicating that failure of central drive mecha ...
... Neural Fatigue. Sports performance concerns involve prevention of fatigue or deterioration of movement quality. Studies have shown that in prolonged voluntary contractions reduced force production could not be improved by direct motor nerve stimulation, indicating that failure of central drive mecha ...
On-center off surround ganglion cells
... Retina ganglion cells receive both excitatory and inhibitory inputs from bipolar neurons In the figure shown, the ganglion cell receives excitatory inputs from cells corresponding to the on-center region, ...
... Retina ganglion cells receive both excitatory and inhibitory inputs from bipolar neurons In the figure shown, the ganglion cell receives excitatory inputs from cells corresponding to the on-center region, ...
invariant face and object recognition in the visual system
... neurons? If so, the output of the visual system might be confusing for structures which receive inputs from the temporal cortical visual areas. To investigate this we measured the responses of inferior temporal cortical neurons with face-selective responses in rhesus macaques performing a visual fix ...
... neurons? If so, the output of the visual system might be confusing for structures which receive inputs from the temporal cortical visual areas. To investigate this we measured the responses of inferior temporal cortical neurons with face-selective responses in rhesus macaques performing a visual fix ...
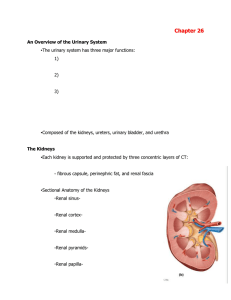
SChapter26
... -The outer wall of the capsule is lined by a simple squamous parietal epithelium, which is continuous with the visceral epithelium that covers the glomerular capillaries. -The visceral epithelium consists of large cells containing podocytes -Pedicles form filtration slits around the capillaries -Mes ...
... -The outer wall of the capsule is lined by a simple squamous parietal epithelium, which is continuous with the visceral epithelium that covers the glomerular capillaries. -The visceral epithelium consists of large cells containing podocytes -Pedicles form filtration slits around the capillaries -Mes ...
Axons
... • Lipid soluble; synthesized on demand from membrane lipids • Bind with G protein–coupled receptors in the brain • Involved in learning and memory ...
... • Lipid soluble; synthesized on demand from membrane lipids • Bind with G protein–coupled receptors in the brain • Involved in learning and memory ...
NNIntro
... Recurrent connection • At any given moment, the whole history of past excitations influences neuron output • The concept of temporal memory emerges • The past influences present to the degree determined by the weight of the recurrent connection • This weight is effectively a „forgetting ...
... Recurrent connection • At any given moment, the whole history of past excitations influences neuron output • The concept of temporal memory emerges • The past influences present to the degree determined by the weight of the recurrent connection • This weight is effectively a „forgetting ...
Post-pubertal Emergence of Prefrontal Cortical Up
... D1 + NMDA-induced membrane potential oscillations could reflect activity of a local neural network impinging on the recorded neuron. Holding the membrane potential to its baseline value failed to block plateau depolarizations induced by D1--NMDA in six of six cells tested (Fig. 4a), suggesting that v ...
... D1 + NMDA-induced membrane potential oscillations could reflect activity of a local neural network impinging on the recorded neuron. Holding the membrane potential to its baseline value failed to block plateau depolarizations induced by D1--NMDA in six of six cells tested (Fig. 4a), suggesting that v ...
Survival of cultured hippocampal neurons upon hypoxia
... used in the treatment of partial epilepsy and neuropathic pain [6,7]. Although originally designed as a GABA mimetic, GBP has no significant activity on GABA receptors [8]. GBP blocks �������������������������������� ...
... used in the treatment of partial epilepsy and neuropathic pain [6,7]. Although originally designed as a GABA mimetic, GBP has no significant activity on GABA receptors [8]. GBP blocks �������������������������������� ...
Introduction to Psychology, 7th Edition, Rod Plotnik Module 3
... PERIPHERAL & CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM • Nerves – stringlike bundles of axons and dendrites that come from the spinal cord and are held together by connective tissue – carry information from the senses, skin, muscles, and the body’s organs to and from the spinal cord – nerves in the peripheral nervous ...
... PERIPHERAL & CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM • Nerves – stringlike bundles of axons and dendrites that come from the spinal cord and are held together by connective tissue – carry information from the senses, skin, muscles, and the body’s organs to and from the spinal cord – nerves in the peripheral nervous ...
A multi-level account of selective attention
... whether attention could modulate responses at the earliest anatomical levels of processing by showing response modulation in V1 with moving (Gandhi, Heeger, and Boynton 1999; Somers, Dale, Seiffert, and Tootell 1999) and stationary stimuli (Martinez et al. 1999). Even stronger evidence in support of ...
... whether attention could modulate responses at the earliest anatomical levels of processing by showing response modulation in V1 with moving (Gandhi, Heeger, and Boynton 1999; Somers, Dale, Seiffert, and Tootell 1999) and stationary stimuli (Martinez et al. 1999). Even stronger evidence in support of ...
PAPER Glucosensing neurons do more than just sense glucose
... function and neuronal activity. This distinguishes glucosensing neurons from the majority of neurons which utilize glucose simply as a metabolic substrate to fuel increases in neuronal activity and metabolic demands. As it turns out, glucosensing neurons respond to more than just short-term alterati ...
... function and neuronal activity. This distinguishes glucosensing neurons from the majority of neurons which utilize glucose simply as a metabolic substrate to fuel increases in neuronal activity and metabolic demands. As it turns out, glucosensing neurons respond to more than just short-term alterati ...
Module 3 - Psychology 40S with Susan Lawrie, M.Ed.
... PERIPHERAL & CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM • Nerves – stringlike bundles of axons and dendrites that come from the spinal cord and are held together by connective tissue – carry information from the senses, skin, muscles, and the body’s organs to and from the spinal cord – nerves in the peripheral nervous ...
... PERIPHERAL & CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM • Nerves – stringlike bundles of axons and dendrites that come from the spinal cord and are held together by connective tissue – carry information from the senses, skin, muscles, and the body’s organs to and from the spinal cord – nerves in the peripheral nervous ...
interaction: the nervous and endocrine systems
... a neuron is s+mulated, some electrical changes originate in the membrane and these transmit the electric signal from the dendrites towards the axon. Neurons are not isolated. They work with one another to establish connec+ons called synapses. vesicles ...
... a neuron is s+mulated, some electrical changes originate in the membrane and these transmit the electric signal from the dendrites towards the axon. Neurons are not isolated. They work with one another to establish connec+ons called synapses. vesicles ...
Cortico–basal ganglia circuit mechanism for a decision threshold in
... in which neural groups selective for opposite directions of motion compete with each other through local recurrent synaptic inhibition. Moreover, the model proposes a candidate cellular mechanism (slow reverberatory network dynamics mediated by NMDA receptors) for the continuous accumulation of the ...
... in which neural groups selective for opposite directions of motion compete with each other through local recurrent synaptic inhibition. Moreover, the model proposes a candidate cellular mechanism (slow reverberatory network dynamics mediated by NMDA receptors) for the continuous accumulation of the ...
Highly Specific Olfactory Receptor Neurons for Types of Amino
... (Sorensen and Caprio 1998). Some fishes, such as catfish, are well-known experimental animals in the study of vertebrate olfaction (Sorensen and Caprio 1998). Results of the present investigation provide the opportunity to determine the logic of how specific biologically relevant odorants, such as a ...
... (Sorensen and Caprio 1998). Some fishes, such as catfish, are well-known experimental animals in the study of vertebrate olfaction (Sorensen and Caprio 1998). Results of the present investigation provide the opportunity to determine the logic of how specific biologically relevant odorants, such as a ...
Central Nervous System CNS
... All the neurons are interneurons By definition confined to the CNS They have to synapse somewhere before the info passes to the peripheral nerves ...
... All the neurons are interneurons By definition confined to the CNS They have to synapse somewhere before the info passes to the peripheral nerves ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.