control of movement by the CNS - motor neurons found in anterior
... cells in one column may fire when muscle is active in a specific movement (synergy) same cells may be silent when same muscle participates in a different movement not necessary to represent every possible muscle synergy finite set of cardinal synergies, which can be combined and weighted - coding di ...
... cells in one column may fire when muscle is active in a specific movement (synergy) same cells may be silent when same muscle participates in a different movement not necessary to represent every possible muscle synergy finite set of cardinal synergies, which can be combined and weighted - coding di ...
Localization of the GABA, Receptor in the Rat Brain with a
... fusion of the spleen cells with the myeloma line P3X63Ag8.6.5.3. The receptor complex was purified by affinity chromatography on the immobilized benzodiazepine Ro7- 198611, followed by DEAE-Sephacel ion-exchange chromatography, as described elsewhere (see Vitorica et al., 1988, the following paper). ...
... fusion of the spleen cells with the myeloma line P3X63Ag8.6.5.3. The receptor complex was purified by affinity chromatography on the immobilized benzodiazepine Ro7- 198611, followed by DEAE-Sephacel ion-exchange chromatography, as described elsewhere (see Vitorica et al., 1988, the following paper). ...
The Nervous System
... bundles of nerve fibers (axons) in CNS Types of tracts: - sensory or ascending contain nerve fibers that carry impulses up the spinal cord to the brain - motor or descending contain nerve fibers that carry impulses down SC ...
... bundles of nerve fibers (axons) in CNS Types of tracts: - sensory or ascending contain nerve fibers that carry impulses up the spinal cord to the brain - motor or descending contain nerve fibers that carry impulses down SC ...
How Inhibition Shapes Cortical Activity
... manipulations selectively decreasing either inhibition or excitation shift cortical activity to a hyperexcitable (epileptiform) or silent (comatose) state (Dudek and Sutula, 2007). Thus, not only does excitation and inhibition increase and decrease together during physiological cortical activity (va ...
... manipulations selectively decreasing either inhibition or excitation shift cortical activity to a hyperexcitable (epileptiform) or silent (comatose) state (Dudek and Sutula, 2007). Thus, not only does excitation and inhibition increase and decrease together during physiological cortical activity (va ...
Document
... Have students complete the Interactive Review on the book’s web site for this chapter in which they identify the parts of the neuron. The Study of the Nervous System in Psychology Ask students the following questions about the study of the nervous system: 1. Why does a course on psychology begin by ...
... Have students complete the Interactive Review on the book’s web site for this chapter in which they identify the parts of the neuron. The Study of the Nervous System in Psychology Ask students the following questions about the study of the nervous system: 1. Why does a course on psychology begin by ...
The parasympathetic system
... Sweat gland secrete large amounts of sweat with sympathetic stimulation – No effect with parasympathetic stimulation – However, sweat glands are stimulated primarily through centers in the hypothalamus that are considered to be parasympathetic centers – sweating may be called a parasympathetic funct ...
... Sweat gland secrete large amounts of sweat with sympathetic stimulation – No effect with parasympathetic stimulation – However, sweat glands are stimulated primarily through centers in the hypothalamus that are considered to be parasympathetic centers – sweating may be called a parasympathetic funct ...
Some historical perspectives on thermoregulation
... activity with a fall in discharge frequency beyond the peaks. The dynamic response of the warm receptors involves a short-lived burst of firing when the temperature is abruptly raised, whereas that of the cold receptor involves a transient rapid fall in firing frequency. The transduction of the temp ...
... activity with a fall in discharge frequency beyond the peaks. The dynamic response of the warm receptors involves a short-lived burst of firing when the temperature is abruptly raised, whereas that of the cold receptor involves a transient rapid fall in firing frequency. The transduction of the temp ...
The Spinal Cord
... Like the brain, the spinal cord is covered by meninges and bathed in CSF within bony vertebral canal. The spinal cord is divided into segments that correspond to the segments of the bony vertebral column (cervical, thoracic,lumber….).The spinal nerve fibers of the spinal nerves enter and exit the co ...
... Like the brain, the spinal cord is covered by meninges and bathed in CSF within bony vertebral canal. The spinal cord is divided into segments that correspond to the segments of the bony vertebral column (cervical, thoracic,lumber….).The spinal nerve fibers of the spinal nerves enter and exit the co ...
(See Page 85) The
... Temporal lobes Regions of the cerebral cortex -below the parietal lobes and in front of the occipital lobes -- important for processing auditory information, for memory, and for object and face perception. (See page 98) ...
... Temporal lobes Regions of the cerebral cortex -below the parietal lobes and in front of the occipital lobes -- important for processing auditory information, for memory, and for object and face perception. (See page 98) ...
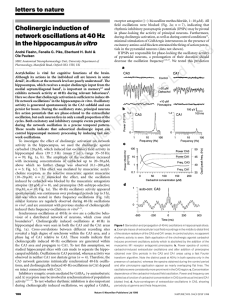
Cholinergic induction of network oscillations at 40 Hz in the
... hippocampus, which receives a major cholinergic input from the medial septum/diagonal band3, is important in memory4,5 and exhibits network activity at 40 Hz during relevant behaviours6. Here we show that cholinergic activation is sufficient to induce 40Hz network oscillations7 in the hippocampus in ...
... hippocampus, which receives a major cholinergic input from the medial septum/diagonal band3, is important in memory4,5 and exhibits network activity at 40 Hz during relevant behaviours6. Here we show that cholinergic activation is sufficient to induce 40Hz network oscillations7 in the hippocampus in ...
Neurons in the Most Superficial Lamina of the Mouse Superior
... feature of the visual world (Dhande and Huberman, 2014). However, the functional properties of SGS neurons cannot be inferred easily from anatomical projection patterns, in part because different RGC subtypes often project to the same SGS sublaminae. For example, the upper SGS, in addition to receiv ...
... feature of the visual world (Dhande and Huberman, 2014). However, the functional properties of SGS neurons cannot be inferred easily from anatomical projection patterns, in part because different RGC subtypes often project to the same SGS sublaminae. For example, the upper SGS, in addition to receiv ...
On the computational architecture of the neocortex
... from an area with one sort of concern to another. A persistent theme is to distinguish lower cortical areas, with direct sensory or motor connections from higher ones which are associating information from lower areas, so that information moves first from lower, more sensory areas to higher, more co ...
... from an area with one sort of concern to another. A persistent theme is to distinguish lower cortical areas, with direct sensory or motor connections from higher ones which are associating information from lower areas, so that information moves first from lower, more sensory areas to higher, more co ...
THE SPINAL CORD
... innervate the same muscle. The Golgi tendon circuit is thus a negative feedback system that regulates muscle tension, decreasing the activation of muscles when exceptionally large forces are generated. This reflex circuit also operates at reduced levels of muscle force, counteracting small changes i ...
... innervate the same muscle. The Golgi tendon circuit is thus a negative feedback system that regulates muscle tension, decreasing the activation of muscles when exceptionally large forces are generated. This reflex circuit also operates at reduced levels of muscle force, counteracting small changes i ...
Towards an Empirically Grounded Predictive Coding Account of
... (2014) precluded the ability to definitively label any of their mirror neurons as error units because there was no way to measure any errors in predictions. However, reactive mirror neurons may be potential candidates because they were involved in processing the sensory/incoming signals. One clever ...
... (2014) precluded the ability to definitively label any of their mirror neurons as error units because there was no way to measure any errors in predictions. However, reactive mirror neurons may be potential candidates because they were involved in processing the sensory/incoming signals. One clever ...
BIO 154: Exam 2006
... results are disappointing. They never gain language competence and often request that the implant be removed. In contrast, early cochlear implantation in congenitally or prelingually deafened children can lead to nearly perfect acoustic communication and language competence. What may explain this ph ...
... results are disappointing. They never gain language competence and often request that the implant be removed. In contrast, early cochlear implantation in congenitally or prelingually deafened children can lead to nearly perfect acoustic communication and language competence. What may explain this ph ...
Artificial Intelligence
... • The neuron receives inputs from other neurons along its dendrites, and when this input signal exceeds a certain threshold, the neuron “fires”—in fact, a chemical reaction occurs, which causes an electrical pulse, known as an action potential, to be sent down the axon (the output of the neuron), to ...
... • The neuron receives inputs from other neurons along its dendrites, and when this input signal exceeds a certain threshold, the neuron “fires”—in fact, a chemical reaction occurs, which causes an electrical pulse, known as an action potential, to be sent down the axon (the output of the neuron), to ...
Physiology of endocrine system
... secrete chemical signals into the circulatory system. • The secretory products of endocrine glands are called hormones (hoЇrmoЇnz), a term derived from the Greek word hormon, meaning to set into motion. • Traditionally, a hormone is defined as a chemical signal, or ligand, that (1) is produced in mi ...
... secrete chemical signals into the circulatory system. • The secretory products of endocrine glands are called hormones (hoЇrmoЇnz), a term derived from the Greek word hormon, meaning to set into motion. • Traditionally, a hormone is defined as a chemical signal, or ligand, that (1) is produced in mi ...
Abnormal Electric Activity Insertional Activity --Normal is 100
... --commonly high amplitude with poor recruitment --occur when there is an increase in number of fibers in a unit or loss of synchrony of firing fibers --seen in: motor neuron diseases, axonal neuropathies with collateral sprouting, chronic radiculopathies, chronic mononeuropathies, residual of neurop ...
... --commonly high amplitude with poor recruitment --occur when there is an increase in number of fibers in a unit or loss of synchrony of firing fibers --seen in: motor neuron diseases, axonal neuropathies with collateral sprouting, chronic radiculopathies, chronic mononeuropathies, residual of neurop ...
Dr. Mustafa Neuroanatomy lectures (8) Diencephalon The
... cerebri (pituitary gland) to carry the stimulatory or inhibitory factors to pituitary gland. 2- The neural pathway through tuber cinnerum → median eminence → infundibulum that pass through opening in the diaphragma sellae to end in the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. Thus, the neuronal bodies ...
... cerebri (pituitary gland) to carry the stimulatory or inhibitory factors to pituitary gland. 2- The neural pathway through tuber cinnerum → median eminence → infundibulum that pass through opening in the diaphragma sellae to end in the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland. Thus, the neuronal bodies ...
5-NeuralNetworks
... • A neuron is connected to other neurons via its input and output links. • Each incoming neuron has an activation value and each connection has a weight associated with it. • The neuron sums the incoming weighted values and this value is input to an activation function. • The output of the activatio ...
... • A neuron is connected to other neurons via its input and output links. • Each incoming neuron has an activation value and each connection has a weight associated with it. • The neuron sums the incoming weighted values and this value is input to an activation function. • The output of the activatio ...
Consciousness_12
... every part of "the writing" contains information about the whole. A hologram (the material manifestation of a holograph) is a photographic emulsion in which information about a scene is recorded in a very special way. When the hologram is illuminated, you see a realistic, 3-dimensional representatio ...
... every part of "the writing" contains information about the whole. A hologram (the material manifestation of a holograph) is a photographic emulsion in which information about a scene is recorded in a very special way. When the hologram is illuminated, you see a realistic, 3-dimensional representatio ...
LPN Nervous System 2017
... Connect brain with the neck and structures in the thorax and abdomen ...
... Connect brain with the neck and structures in the thorax and abdomen ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.