Evidence for a modulatory effect of sulbutiamine on
... in the prefrontal cortex. In the cingular cortex, DA and DOPAC levels were decreased (234 and 226%, respectively), as compared to control animals. Finally, no change in dopaminergic transmission was observed in the nucleus accumbens. The decreased levels of DOPAC suggest a reduced release of DA in t ...
... in the prefrontal cortex. In the cingular cortex, DA and DOPAC levels were decreased (234 and 226%, respectively), as compared to control animals. Finally, no change in dopaminergic transmission was observed in the nucleus accumbens. The decreased levels of DOPAC suggest a reduced release of DA in t ...
Peripheral Nervous System, Autonomic Nervous System and reflexes
... by Elaine Marieb & Katja Hoehn ...
... by Elaine Marieb & Katja Hoehn ...
Nervous System - s3.amazonaws.com
... Sensory Nerve – composed of only sensory neurons Motor Nerve – composed only of motor neurons Mixed nerves – both sensory and motor neuron, most nerves are mixed, all spinal nerves are mixed! ...
... Sensory Nerve – composed of only sensory neurons Motor Nerve – composed only of motor neurons Mixed nerves – both sensory and motor neuron, most nerves are mixed, all spinal nerves are mixed! ...
Hearing, I: The Cochlea - American Journal of Neuroradiology
... The middle ear converts the sound to fluid motion. The inner ear, specifically the cochlea, transforms fluid motion into electric energy. The cochlea is a coiled structure consisting of two and three quarter turns (Figs 1 and 2). If it were elongated, the cochlea would be approximately 30 mm in leng ...
... The middle ear converts the sound to fluid motion. The inner ear, specifically the cochlea, transforms fluid motion into electric energy. The cochlea is a coiled structure consisting of two and three quarter turns (Figs 1 and 2). If it were elongated, the cochlea would be approximately 30 mm in leng ...
Précis of The Brain and Emotion
... to separate rewards related to internal homeostatic need states associated with (say) hunger and thirst, and to note that these rewards are not normally described as producing emotional states. In contrast, the great majority of rewards and punishers are external stimuli not related to internal need ...
... to separate rewards related to internal homeostatic need states associated with (say) hunger and thirst, and to note that these rewards are not normally described as producing emotional states. In contrast, the great majority of rewards and punishers are external stimuli not related to internal need ...
Restraining influence of A2 neurons in chronic control of arterial
... genetically target A2 neurons and induce expression of a potassium channel to reduce their electrical excitability and study how this impacts on long-term blood pressure control. Methods: We used a lentiviral vector with PRSx8 promoter for targeting noradrenergic neurons to express a human inwardly ...
... genetically target A2 neurons and induce expression of a potassium channel to reduce their electrical excitability and study how this impacts on long-term blood pressure control. Methods: We used a lentiviral vector with PRSx8 promoter for targeting noradrenergic neurons to express a human inwardly ...
Sensory Adaptation and Short Term Plasticity as Bayesian
... range of physiological adaptation phenomena. We examine shortterm synaptic depression at a single synapse and medium-term tuning curve adaptation in early visual cortex. Experimental results in both these domains are well-described by a model that implements excitability estimation at the level of s ...
... range of physiological adaptation phenomena. We examine shortterm synaptic depression at a single synapse and medium-term tuning curve adaptation in early visual cortex. Experimental results in both these domains are well-described by a model that implements excitability estimation at the level of s ...
types of muscle tissue
... line to which the thin filaments of the I band are attached. The nuclei are located peripherally, immediately under the plasma. The thickness of each fiber is uniform throughout its length and they do not branch out. Skeletal/ voluntary muscle is divided into two; a) Slow twitch These muscles are al ...
... line to which the thin filaments of the I band are attached. The nuclei are located peripherally, immediately under the plasma. The thickness of each fiber is uniform throughout its length and they do not branch out. Skeletal/ voluntary muscle is divided into two; a) Slow twitch These muscles are al ...
Solving the Problem of Negative Synaptic Weights in Cortical Models
... approach was used by Churchland (1995) in a model of stereoptic vision. However, this solution remains biologically unrealistic for two reasons. First it assumes that there are as many inhibitory cells as there are inhibitorily connected cells in the original model. Clearly, this will vary from mode ...
... approach was used by Churchland (1995) in a model of stereoptic vision. However, this solution remains biologically unrealistic for two reasons. First it assumes that there are as many inhibitory cells as there are inhibitorily connected cells in the original model. Clearly, this will vary from mode ...
Inferring functional connections between neurons
... unobserved common input generally confounds connectivity estimates. In the motor cortex, for instance, movement induces strong input correlations between many neurons. Fortunately, by including movement-related variables in the model, our estimates of functional connectivity may be improved. Given t ...
... unobserved common input generally confounds connectivity estimates. In the motor cortex, for instance, movement induces strong input correlations between many neurons. Fortunately, by including movement-related variables in the model, our estimates of functional connectivity may be improved. Given t ...
Characterising nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the plant parasitic
... explored the idea that the neurobiological basis of C. elegans locomotion is likely to be conserved between nematodes and provide a route to new molecular targets for pest control. Acetylcholine (ACh) is the excitatory neurotransmitter at C. elegans body wall neuromuscular junction, acting on nicoti ...
... explored the idea that the neurobiological basis of C. elegans locomotion is likely to be conserved between nematodes and provide a route to new molecular targets for pest control. Acetylcholine (ACh) is the excitatory neurotransmitter at C. elegans body wall neuromuscular junction, acting on nicoti ...
2.1 central nervous system: neurotransmission and
... of the body), Sensory (cause changes in any one of the senses. People with sensory seizures may smell or taste things that aren't there; hear clicking, ringing, or a person's voice when there is no actual sound; or feel a sensation of "pins and needles" or numbness), Psychic (cause changes in how pa ...
... of the body), Sensory (cause changes in any one of the senses. People with sensory seizures may smell or taste things that aren't there; hear clicking, ringing, or a person's voice when there is no actual sound; or feel a sensation of "pins and needles" or numbness), Psychic (cause changes in how pa ...
Reinforcement - Karl Pribram
... alerting and are known as the orienting reaction. As the experiment proceeds, these indices of orienting become progressively more attenuated until the beep of the tone no longer seems to have any effect. This is habituation. At this point Sokolov reduced tJ:!.e intensity of the_tone:, without chang ...
... alerting and are known as the orienting reaction. As the experiment proceeds, these indices of orienting become progressively more attenuated until the beep of the tone no longer seems to have any effect. This is habituation. At this point Sokolov reduced tJ:!.e intensity of the_tone:, without chang ...
Dexamethasone Rapidly Increases GABA Release in the Dorsal
... innervation of thoracic organs. Neurons of the DMV exhibit regular action potential firing [2,3]. This makes the neurons susceptible to small changes in membrane potential induced by synaptic currents. This is especially true for inhibitory ...
... innervation of thoracic organs. Neurons of the DMV exhibit regular action potential firing [2,3]. This makes the neurons susceptible to small changes in membrane potential induced by synaptic currents. This is especially true for inhibitory ...
View Paper - Dundee Life Sciences
... Spinal cord cells include motor neurons, sensory neurons and multiple classes of interneuron that together mediate movement and sensation of the body. The molecular mechanisms that specify these different kinds of neuron in the spinal cord have been wellcharacterized (Jessell, 2000; Price and Brisco ...
... Spinal cord cells include motor neurons, sensory neurons and multiple classes of interneuron that together mediate movement and sensation of the body. The molecular mechanisms that specify these different kinds of neuron in the spinal cord have been wellcharacterized (Jessell, 2000; Price and Brisco ...
Chapter 23 The Animal Kingdom
... • Insects are the largest group of arthropods • They have three body sections – Head – very elaborate, with one pair of antennae and elaborate mouthparts and compound eyes – Thorax – has three segments as well, each of which have one pair of legs; most insects have two pairs of wings attached to the ...
... • Insects are the largest group of arthropods • They have three body sections – Head – very elaborate, with one pair of antennae and elaborate mouthparts and compound eyes – Thorax – has three segments as well, each of which have one pair of legs; most insects have two pairs of wings attached to the ...
Neuroscience
... Neurodegeneration refers to the progressive loss of structure and/or function of neurons often beginning at the synaptic distal ends of axons. Neurodegenerative diseases exhibit a broad range of clinical symptoms, which share several common pathological features. Prominent cellular features include ...
... Neurodegeneration refers to the progressive loss of structure and/or function of neurons often beginning at the synaptic distal ends of axons. Neurodegenerative diseases exhibit a broad range of clinical symptoms, which share several common pathological features. Prominent cellular features include ...
neurons that transmit messages from sensory receptors
... cells that nourish and insulate neurons, direct their growth, and remove waste products from the nervous system ...
... cells that nourish and insulate neurons, direct their growth, and remove waste products from the nervous system ...
The Distribution of Immunoreactivity for
... estrogen (ER) and androgen receptors (AR) maintain. While clearly more abundant, however, less is known about the cortical distribution of intracellular AR as compared with ER proteins. Available evidence suggests, though, that at least in rats these two hormone pathways occupy distinct niches among ...
... estrogen (ER) and androgen receptors (AR) maintain. While clearly more abundant, however, less is known about the cortical distribution of intracellular AR as compared with ER proteins. Available evidence suggests, though, that at least in rats these two hormone pathways occupy distinct niches among ...
Capturing Brain Dynamics: a combined neuroscience and
... http://animatlab.com/Help/Documentation/NeuralNetworkEditor/NeuralSimulationPlugins/FiringRateNeuralPlugin/NeuronBasics/tabid/117/Default.aspx ...
... http://animatlab.com/Help/Documentation/NeuralNetworkEditor/NeuralSimulationPlugins/FiringRateNeuralPlugin/NeuronBasics/tabid/117/Default.aspx ...
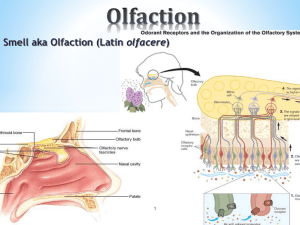
olfaction
... to increase in the firing rate of neurons but triggers changes in the perceived quality of the odorant. ...
... to increase in the firing rate of neurons but triggers changes in the perceived quality of the odorant. ...
Gene Transfer to the Peripheral Nervous System: Treatments for
... horn between the primary nociceptor and secondorder neurons projecting rostrally is subject to complex modulatory influence. This influence is mediated by inhibitory neurotransmitters released from interneurons under the control of descending inputs. Pharmacological activation of these inhibitory ne ...
... horn between the primary nociceptor and secondorder neurons projecting rostrally is subject to complex modulatory influence. This influence is mediated by inhibitory neurotransmitters released from interneurons under the control of descending inputs. Pharmacological activation of these inhibitory ne ...
From Nerve Cells to Cognition: The Internal
... aspects of the visual image—form, movement, and color. These separate inputs are eventually integrated into coherent images according to the brain’s own rules, rules that are embodied in the circuitry of the visual system. Different modalities of perception—an object seen, a face touched, or a melod ...
... aspects of the visual image—form, movement, and color. These separate inputs are eventually integrated into coherent images according to the brain’s own rules, rules that are embodied in the circuitry of the visual system. Different modalities of perception—an object seen, a face touched, or a melod ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.