Neurons & Transmission of Information
... receptor such as those in the eye or ear to a more central location in the nervous system. •Also known as _________________________ –A motor neuron is a nerve cell that sends impulses from a central area of the nervous system to an _________________ such as a ...
... receptor such as those in the eye or ear to a more central location in the nervous system. •Also known as _________________________ –A motor neuron is a nerve cell that sends impulses from a central area of the nervous system to an _________________ such as a ...
neuron
... • Threshold: refers to the minimal level of stimulation required for a neural impulse to fire. ...
... • Threshold: refers to the minimal level of stimulation required for a neural impulse to fire. ...
Nervous System
... with sodium ions. The calcium ions on the outside hold a positive charge, and they therefore diffuse into the neuron. This intake of calcium stimulates a release of sodium ions in the form of an electric current. This current excites the neurotransmitters which are in vesicles, and they undergo exoc ...
... with sodium ions. The calcium ions on the outside hold a positive charge, and they therefore diffuse into the neuron. This intake of calcium stimulates a release of sodium ions in the form of an electric current. This current excites the neurotransmitters which are in vesicles, and they undergo exoc ...
PowerPoint
... called the Synapse. • One importance of the presence of Synapses is that they ensure one-way transmission of impulses in a living person. • The Axon Terminals at a Synapse contain tiny vesicles, or sacs. These are known as NEUROTRANSMITTERS. ...
... called the Synapse. • One importance of the presence of Synapses is that they ensure one-way transmission of impulses in a living person. • The Axon Terminals at a Synapse contain tiny vesicles, or sacs. These are known as NEUROTRANSMITTERS. ...
2. Peripheral Nervous System
... How a nerve impulse is transmitted 3) Repolarization – K+ moves outside, Na+ stays inside ◦ After inside flooded with NA+, K+ gates open and let K+ Out (while NA+ gates close) ...
... How a nerve impulse is transmitted 3) Repolarization – K+ moves outside, Na+ stays inside ◦ After inside flooded with NA+, K+ gates open and let K+ Out (while NA+ gates close) ...
9.3 Synaptic Transmission
... neurons are needed to create an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron. ...
... neurons are needed to create an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron. ...
ACTION POTENTIALS
... leaves the neruon at this point, due to the repelling polarity of positive sodium ions. After this the channels close, and the sodium pumps remove sodium ions from the membrane this repolarizes the membrane to a more negative charge than before the action potential. As potassium returns back into th ...
... leaves the neruon at this point, due to the repelling polarity of positive sodium ions. After this the channels close, and the sodium pumps remove sodium ions from the membrane this repolarizes the membrane to a more negative charge than before the action potential. As potassium returns back into th ...
Carrie Heath
... 4. Who invented the voltage clamp and who used it for further investigation into the movement of ions across the cell membrane? 5. What is the function of the cerebellum and the function of the cerebral cortex? How could one gather information about their functions if they were unknown? 6. Write out ...
... 4. Who invented the voltage clamp and who used it for further investigation into the movement of ions across the cell membrane? 5. What is the function of the cerebellum and the function of the cerebral cortex? How could one gather information about their functions if they were unknown? 6. Write out ...
Ch 11 Part 2 - Groch Biology
... 7. Structurally, the most common neurons are ______________. 8. A neuron that transmits impulses from pain receptors in your skin to your spinal cord is classified as a(n) _______________neuron. Structurally, this type of neuron is __________________. 9. Matching. a. absolute refractory period b. ac ...
... 7. Structurally, the most common neurons are ______________. 8. A neuron that transmits impulses from pain receptors in your skin to your spinal cord is classified as a(n) _______________neuron. Structurally, this type of neuron is __________________. 9. Matching. a. absolute refractory period b. ac ...
Lecture #21 Date
... Intracellular/extracellular ionic concentration difference K+ diffuses out (Na+ in); large anions cannot follow….why not? Net negative charge of about -70mV ...
... Intracellular/extracellular ionic concentration difference K+ diffuses out (Na+ in); large anions cannot follow….why not? Net negative charge of about -70mV ...
Sending Signals Notes
... • Neurotransmitters may be broken down by ENZYMES, taken up again by the axon terminal and recycled, or they may simply diffuse away. • NERVE GAS prevents enzymes from breaking down neurotransmitters, as a result muscles in the respiratory and nervous system becomes paralyzed. ...
... • Neurotransmitters may be broken down by ENZYMES, taken up again by the axon terminal and recycled, or they may simply diffuse away. • NERVE GAS prevents enzymes from breaking down neurotransmitters, as a result muscles in the respiratory and nervous system becomes paralyzed. ...
Electrochemical Impulses
... to K+ than Na+ , K+ moves out of the cell faster than Na+ moves in. • This results in an electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane, and an overall external positive charge which is referred to as resting potential. ...
... to K+ than Na+ , K+ moves out of the cell faster than Na+ moves in. • This results in an electrochemical gradient across the cell membrane, and an overall external positive charge which is referred to as resting potential. ...
Slideshow
... • As the figure shows, a Na+ / K+ pump in the cell membrane pumps sodium out of the cell and potassium into it. ...
... • As the figure shows, a Na+ / K+ pump in the cell membrane pumps sodium out of the cell and potassium into it. ...
PowerPoint Slides
... • The Von Neumann architecture uses a single processing unit; – Tens of millions of operations per ...
... • The Von Neumann architecture uses a single processing unit; – Tens of millions of operations per ...
Slide ()
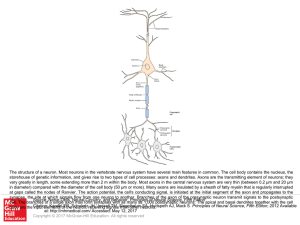
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
Nervous System Quiz Answers
... NOTE: I did not list the Schwann cells because they are part of the PNS not CNS. 2. How does a nerve send a “message” when stimulated? (8pts) -A resting neuron is polarized when more Na+ is outside the membrane the K+ inside the membrane (-70mv). + (pos) outside and – (neg) inside the membrane 1. Re ...
... NOTE: I did not list the Schwann cells because they are part of the PNS not CNS. 2. How does a nerve send a “message” when stimulated? (8pts) -A resting neuron is polarized when more Na+ is outside the membrane the K+ inside the membrane (-70mv). + (pos) outside and – (neg) inside the membrane 1. Re ...
Lecture 9
... • At rest the Na channels are largely closed and only very little Na can flow in • The K and Cl channels are somewhat open yielding a rest potential of -70mV • No net current flow; concentration gradient of ions is actively maintained with ion-pumps and exchangers (these proteins move ions across th ...
... • At rest the Na channels are largely closed and only very little Na can flow in • The K and Cl channels are somewhat open yielding a rest potential of -70mV • No net current flow; concentration gradient of ions is actively maintained with ion-pumps and exchangers (these proteins move ions across th ...
Lecture 2 - Nerve Impulse
... becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the inside of the axon becomes negative again, after AP. K+ ions move to the outside of cell. Neuron can’t respond to new stimuli. ...
... becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the inside of the axon becomes negative again, after AP. K+ ions move to the outside of cell. Neuron can’t respond to new stimuli. ...
AP Psychology - HOMEWORK 9
... During the resting pause following an action potential, called the ___________________ the neuron pumps positively charged ions outside the cell. (1 pt) ...
... During the resting pause following an action potential, called the ___________________ the neuron pumps positively charged ions outside the cell. (1 pt) ...
here
... 4. What are three types of information that neurons must process? What does each type allow us to do? ...
... 4. What are three types of information that neurons must process? What does each type allow us to do? ...
Nervous System II – Neurons
... along the axon because the impulses can hop between the _______________________________. __________________ in myelin sheath. Allow for ____________________ across the cell membrane which propagates the electrical impulses. The _______________________ projects of the neuron. Releases _______________ ...
... along the axon because the impulses can hop between the _______________________________. __________________ in myelin sheath. Allow for ____________________ across the cell membrane which propagates the electrical impulses. The _______________________ projects of the neuron. Releases _______________ ...