chapter 48
... Glia are supporting cells that _______________________________, insulate the _________________ ___________________, and regulate the __________________________________________________. o Some glia form the blood brain barrier restricts passage of most substances into the brain which controls the c ...
... Glia are supporting cells that _______________________________, insulate the _________________ ___________________, and regulate the __________________________________________________. o Some glia form the blood brain barrier restricts passage of most substances into the brain which controls the c ...
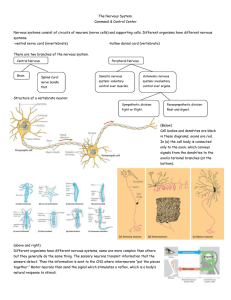
Central Nervous System
... slower to respond) and let K+ out which are repelled by + inside Na+ gates remain closed The inside becomes negative while outside become positive and this repolarizes membrane ...
... slower to respond) and let K+ out which are repelled by + inside Na+ gates remain closed The inside becomes negative while outside become positive and this repolarizes membrane ...
Chapter 9 Nervous
... Na ions are transferred out into extracellular fluid. K ions are transferred into cell within cytoplasm. This is threshold potential. The permeability of the cell membrane increases, allowing Na to rush into the cell. Cells interior takes a positive charge. (Called depolarization) Depolarization swe ...
... Na ions are transferred out into extracellular fluid. K ions are transferred into cell within cytoplasm. This is threshold potential. The permeability of the cell membrane increases, allowing Na to rush into the cell. Cells interior takes a positive charge. (Called depolarization) Depolarization swe ...
File
... 6.5.1 State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed of cells called neurons that can carry rapid electrical impulses. 6.5.2 Draw and label the structure of a motor neuron, include; dendrites, cell body with nucleus, axon, myelin sh ...
... 6.5.1 State that the nervous system consists of the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nerves, and is composed of cells called neurons that can carry rapid electrical impulses. 6.5.2 Draw and label the structure of a motor neuron, include; dendrites, cell body with nucleus, axon, myelin sh ...
Appendix 4 Mathematical properties of the state-action
... state-action sequence, and the SAANN is trained using the state St as input and the corresponding action at as target output. At each time step t of the sequence, the SAANN is updated using the newwinner-take-all rule: a previously unused neuron i is set to the “on” state, while all other neurons ...
... state-action sequence, and the SAANN is trained using the state St as input and the corresponding action at as target output. At each time step t of the sequence, the SAANN is updated using the newwinner-take-all rule: a previously unused neuron i is set to the “on” state, while all other neurons ...
6 BIO Neurotransmitters - Appoquinimink High School
... a neuron fires its message, there is a brief period of time before it can fire again. This is called a neuron’s refractory period. During the refractory period, excess neurotransmitters are reabsorbed by the sending neuron, called re-uptake, as well as the cell becoming polarized once again. ...
... a neuron fires its message, there is a brief period of time before it can fire again. This is called a neuron’s refractory period. During the refractory period, excess neurotransmitters are reabsorbed by the sending neuron, called re-uptake, as well as the cell becoming polarized once again. ...
Nervous System - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... Three kinds of neurons: Sensory Neuron: picks up stimuli and converts it into an impulse. Interneuron: carries impulse from one neuron to another neuron (within brain or spinal cord). Motor Neuron: brings impulse to muscle or gland which then reacts in response. Nerve impulse: begins in a nerve cell ...
... Three kinds of neurons: Sensory Neuron: picks up stimuli and converts it into an impulse. Interneuron: carries impulse from one neuron to another neuron (within brain or spinal cord). Motor Neuron: brings impulse to muscle or gland which then reacts in response. Nerve impulse: begins in a nerve cell ...
Neurons and the Brain
... Neurons stay at rest with their sodium ions on the outside of the cell body (or soma) and potassium ions on the inside. The Neuron isn’t ...
... Neurons stay at rest with their sodium ions on the outside of the cell body (or soma) and potassium ions on the inside. The Neuron isn’t ...
Prediction on Soccer Matches using Multi
... prediction. With this proposal, I hope to achieve an accurate prediction of the outcome of certain soccer matches by introducing a methodical method of predicting soccer scores. Getting all my predictions correct is what I hope to achieve, but realistically that is hard to achieve. Based on the resu ...
... prediction. With this proposal, I hope to achieve an accurate prediction of the outcome of certain soccer matches by introducing a methodical method of predicting soccer scores. Getting all my predictions correct is what I hope to achieve, but realistically that is hard to achieve. Based on the resu ...
Tayler
... Membrane potential – when a neuron is not stimulated Threshold – the critical level to which membrane potential must be depolarized in order to initiate an action potential Polarization of the neuron’s membrane: Sodium is on the outside and potassium is on the inside Resting potential gives ...
... Membrane potential – when a neuron is not stimulated Threshold – the critical level to which membrane potential must be depolarized in order to initiate an action potential Polarization of the neuron’s membrane: Sodium is on the outside and potassium is on the inside Resting potential gives ...
Nervous
... Blood-brain barrier: a specialized capillary arrangement in the brain that restricts the passage of most substances into the brain, thereby preventing dramatic fluctuations in the brain’s environment. Radial glia: in an embryo, supporting cells that form tracks along which newly formed neurons migra ...
... Blood-brain barrier: a specialized capillary arrangement in the brain that restricts the passage of most substances into the brain, thereby preventing dramatic fluctuations in the brain’s environment. Radial glia: in an embryo, supporting cells that form tracks along which newly formed neurons migra ...
Introduction to Neural Networks
... means of directed communication links, each with associated weight. ...
... means of directed communication links, each with associated weight. ...
Chapter 2 quiz level - easy topic: neurons
... A) conduct electrical impulses toward other neurons B) insulate against leakage of electrical impulses C) regulate the neuron's life processes D) receive messages from neighboring neurons ...
... A) conduct electrical impulses toward other neurons B) insulate against leakage of electrical impulses C) regulate the neuron's life processes D) receive messages from neighboring neurons ...
Nervous System Review ANSWERS File
... 40. Which statement is NOT true about the development of an action potential? A. There is a rapid change in polarity from about -65mV to about + 40 mV B. It can be produced by an electric shock or a sudden change in pH C. The action potential ends when the polarity across the membrane reaches +40mV ...
... 40. Which statement is NOT true about the development of an action potential? A. There is a rapid change in polarity from about -65mV to about + 40 mV B. It can be produced by an electric shock or a sudden change in pH C. The action potential ends when the polarity across the membrane reaches +40mV ...
Nervous System - Creston High School
... The action potential must jump from one node of Ranvier to the next. This makes the action potential move faster down the axon. Some can reach speeds of 100 m/s. Unmyelinated neurons propagate slow action potentials that must move from one site to the next. This is called continuous conduction ...
... The action potential must jump from one node of Ranvier to the next. This makes the action potential move faster down the axon. Some can reach speeds of 100 m/s. Unmyelinated neurons propagate slow action potentials that must move from one site to the next. This is called continuous conduction ...
Sample Prelab Assignment - Neurobiology Laboratory
... There are two types of synapses in the brain, electrical and chemical synapses. In this lab, we will study chemical synapses by examining excitatory post synaptic potentials which are caused by the opening of ion channels. The transmission of information at a chemical synapse involves the convers ...
... There are two types of synapses in the brain, electrical and chemical synapses. In this lab, we will study chemical synapses by examining excitatory post synaptic potentials which are caused by the opening of ion channels. The transmission of information at a chemical synapse involves the convers ...
Nervous System Vocab1 - Everglades High School
... 27. Myelin Sheath: A tight coil of wrapped membranes encloses the axon 28. Neurilemma: Part of the schwann cell, external to the myelin sheath 29. Nodes of Ranvier: gaps or indentations between the schwann cells 30. Ganglia: Small collection of cell bodies outside of the CNS 31. White Matter: Dense ...
... 27. Myelin Sheath: A tight coil of wrapped membranes encloses the axon 28. Neurilemma: Part of the schwann cell, external to the myelin sheath 29. Nodes of Ranvier: gaps or indentations between the schwann cells 30. Ganglia: Small collection of cell bodies outside of the CNS 31. White Matter: Dense ...
Slide ()
... A perceptron implementing the Hubel-Wiesel model of selectivity and invariance. The network in Figure E–2C can be extended to grids of many cells by specifying synaptic connectivity at all locations in the visual field. The resulting network can be repeated four times, one for each preferred orienta ...
... A perceptron implementing the Hubel-Wiesel model of selectivity and invariance. The network in Figure E–2C can be extended to grids of many cells by specifying synaptic connectivity at all locations in the visual field. The resulting network can be repeated four times, one for each preferred orienta ...