Nature Versus Nurture
... internal environment to maintain a stable, constant condition Responds to internal environment Responds to external environment ...
... internal environment to maintain a stable, constant condition Responds to internal environment Responds to external environment ...
Nervous System and Senses - Avon Community School Corporation
... Flows through ventricles (spaces in brain), in the subarachnoid space, and through the central canal of the spinal ...
... Flows through ventricles (spaces in brain), in the subarachnoid space, and through the central canal of the spinal ...
Lesson 3 Brain Communication
... • They receive messages from other nerve cells and send it through the neuron. • The have DENDRITIC RECEPTORS on the ends: • Receivers on the end of each dendrite which catch the chemicals as they jump from the previous neuron. They then send the message down the dendrites. ...
... • They receive messages from other nerve cells and send it through the neuron. • The have DENDRITIC RECEPTORS on the ends: • Receivers on the end of each dendrite which catch the chemicals as they jump from the previous neuron. They then send the message down the dendrites. ...
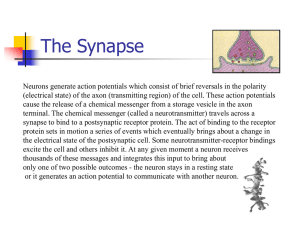
The Synapse
... Neurons generate action potentials which consist of brief reversals in the polarity (electrical state) of the axon (transmitting region) of the cell. These action potentials cause the release of a chemical messenger from a storage vesicle in the axon terminal. The chemical messenger (called a neurot ...
... Neurons generate action potentials which consist of brief reversals in the polarity (electrical state) of the axon (transmitting region) of the cell. These action potentials cause the release of a chemical messenger from a storage vesicle in the axon terminal. The chemical messenger (called a neurot ...
CHAPTER NINE: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
... a. A ___________ that mediated information transfer form one neuron to another neuron or an effector cell b. Presynaptic neuron- conducts impulses ___________ the synapse c. Postsynaptic neuron- transmits impulses ________ from the synapse d. Types of synapses i. Axodendritic- between the axon of on ...
... a. A ___________ that mediated information transfer form one neuron to another neuron or an effector cell b. Presynaptic neuron- conducts impulses ___________ the synapse c. Postsynaptic neuron- transmits impulses ________ from the synapse d. Types of synapses i. Axodendritic- between the axon of on ...
The Nervous System : communication
... 1. Neuron membrane maintains resting potential 2. Threshold stimulus is received 3. Sodium channels open 4. Sodium ions diffuse inward, depolarizing the membrane 5. Potassium channels open 6. Potassium ions diffuse outward, repolarizing the membrane 7. The resulting action potential causes a local ...
... 1. Neuron membrane maintains resting potential 2. Threshold stimulus is received 3. Sodium channels open 4. Sodium ions diffuse inward, depolarizing the membrane 5. Potassium channels open 6. Potassium ions diffuse outward, repolarizing the membrane 7. The resulting action potential causes a local ...
Ch 09 Nervous System
... 1. Neuron membrane maintains resting potential 2. Threshold stimulus is received 3. Sodium channels open 4. Sodium ions diffuse inward, depolarizing the membrane 5. Potassium channels open 6. Potassium ions diffuse outward, repolarizing the membrane 7. The resulting action potential causes a local ...
... 1. Neuron membrane maintains resting potential 2. Threshold stimulus is received 3. Sodium channels open 4. Sodium ions diffuse inward, depolarizing the membrane 5. Potassium channels open 6. Potassium ions diffuse outward, repolarizing the membrane 7. The resulting action potential causes a local ...
Reflex Arc - TangHua2012-2013
... (-60mv means that the inside is 60 mv _________________________________). If we hook up our voltmeter to a machine called an oscilloscope, we can see the change in voltage over a period of time. There is a difference in ________________________ on either side of the membrane of a neuron. At Rest-___ ...
... (-60mv means that the inside is 60 mv _________________________________). If we hook up our voltmeter to a machine called an oscilloscope, we can see the change in voltage over a period of time. There is a difference in ________________________ on either side of the membrane of a neuron. At Rest-___ ...
The skin performs all of the following except
... Students will know… Explain what an action potential is? K+ ions are entering the neuron Negatively charged proteins are leaving the neuron Na+ ions are entering the neuron The myelin coat has broken down and ions are ...
... Students will know… Explain what an action potential is? K+ ions are entering the neuron Negatively charged proteins are leaving the neuron Na+ ions are entering the neuron The myelin coat has broken down and ions are ...
Slide 1
... Which Model to Use for Cortical Spiking Neurons? To understand how the brain works, we need to combine experimental studies of animal and human nervous systems with numerical simulation of large-scale brain models. As we develop such large-scale brain models consisting of spiking neurons, we must f ...
... Which Model to Use for Cortical Spiking Neurons? To understand how the brain works, we need to combine experimental studies of animal and human nervous systems with numerical simulation of large-scale brain models. As we develop such large-scale brain models consisting of spiking neurons, we must f ...
Brain & Behavior
... • Massive, brief reversal of membrane potential from –70 to +50 mV • After an action potential, neuron has to recharge, so to speak • K(+) pumped out of cell, (-) charge restored • Refractory period – neuron cannot fire again during this process ...
... • Massive, brief reversal of membrane potential from –70 to +50 mV • After an action potential, neuron has to recharge, so to speak • K(+) pumped out of cell, (-) charge restored • Refractory period – neuron cannot fire again during this process ...
No Slide Title
... • Nerve pathway is a series of separate cells • neural communication = mechanisms for producing electrical potentials and currents – electrical potential - different concentrations of charged particles in different parts of the cell – electrical current - flow of charged particles from one point to ...
... • Nerve pathway is a series of separate cells • neural communication = mechanisms for producing electrical potentials and currents – electrical potential - different concentrations of charged particles in different parts of the cell – electrical current - flow of charged particles from one point to ...
12-1 Chapter 12 Lecture Outline See PowerPoint Image Slides for
... • Nerve pathway is a series of separate cells • neural communication = mechanisms for producing electrical potentials and currents – electrical potential - different concentrations of charged particles in different parts of the cell – electrical current - flow of charged particles from one point to ...
... • Nerve pathway is a series of separate cells • neural communication = mechanisms for producing electrical potentials and currents – electrical potential - different concentrations of charged particles in different parts of the cell – electrical current - flow of charged particles from one point to ...
Chapter 12
... • Nerve pathway is a series of separate cells • neural communication = mechanisms for producing electrical potentials and currents – electrical potential - different concentrations of charged particles in different parts of the cell – electrical current - flow of charged particles from one point to ...
... • Nerve pathway is a series of separate cells • neural communication = mechanisms for producing electrical potentials and currents – electrical potential - different concentrations of charged particles in different parts of the cell – electrical current - flow of charged particles from one point to ...
Nerve Cells and Electrical Signaling
... Type the question and your answer, in complete sentences, on a separate sheet of paper. Turn in your answers to the Lab Instructor. 1) Describe the anatomical organization of the nervous system, including how those nerves are organized within the nervous system. 2) Describe the structure of a neuron ...
... Type the question and your answer, in complete sentences, on a separate sheet of paper. Turn in your answers to the Lab Instructor. 1) Describe the anatomical organization of the nervous system, including how those nerves are organized within the nervous system. 2) Describe the structure of a neuron ...
Excitatory_Inhibitory_Neural_Network_1
... Theoretical Neuroscience, by Peter Dayan and Larry Abbott, MIT Press, 2005 pp. 266-269 The system studied here is one the simplest types of neural networks to exhibit oscillatory activity. It can be regarded as a simplified model of a fully-connected network comprised of a large number of excitatory ...
... Theoretical Neuroscience, by Peter Dayan and Larry Abbott, MIT Press, 2005 pp. 266-269 The system studied here is one the simplest types of neural networks to exhibit oscillatory activity. It can be regarded as a simplified model of a fully-connected network comprised of a large number of excitatory ...
receptor
... Group 4: While on the T, Joe reviews for a Spanish quiz. He looks at flashcards with vocabulary to test his memory. Model the neurons and their connections to see the flashcards and test language memory. Group 5: At basketball practice, Joe warms up by practicing his free throw. Model the neurons an ...
... Group 4: While on the T, Joe reviews for a Spanish quiz. He looks at flashcards with vocabulary to test his memory. Model the neurons and their connections to see the flashcards and test language memory. Group 5: At basketball practice, Joe warms up by practicing his free throw. Model the neurons an ...
Information processes in neurons
... with few modifications, namely we assume that input µ is constant in time and the process starts at the resting level x0 . The (constant) parameters C, R form the so-called membrane time constant τ = RC, which we use here ...
... with few modifications, namely we assume that input µ is constant in time and the process starts at the resting level x0 . The (constant) parameters C, R form the so-called membrane time constant τ = RC, which we use here ...
Two-Compartment Models
... – The shape of the action potentials are more or less the same – At the synapse, the action potential events translate into transmitter release – As far as neuronal communication is concerned, the exact shape of the action potentials is not important, rather its time of occurrence is important ...
... – The shape of the action potentials are more or less the same – At the synapse, the action potential events translate into transmitter release – As far as neuronal communication is concerned, the exact shape of the action potentials is not important, rather its time of occurrence is important ...
The Nervous System
... • The area within the neuron that contains all the components of a typical eukaryotic cell. • Genetic material (DNA) is stored here. ...
... • The area within the neuron that contains all the components of a typical eukaryotic cell. • Genetic material (DNA) is stored here. ...
Nervous Sys Learning targets
... 4. Define neuron, describe its important structural components and relate each to its functional role 5. Explain the importance of the myelin sheath and describe how it is formed in the central and peripheral ns 6. Classify neurons by structure and function ...
... 4. Define neuron, describe its important structural components and relate each to its functional role 5. Explain the importance of the myelin sheath and describe how it is formed in the central and peripheral ns 6. Classify neurons by structure and function ...