Nervous Systems
... • Carrying information to and from the brain • Integration of simple responses ...
... • Carrying information to and from the brain • Integration of simple responses ...
Nerve impulses and Synapses Electro
... • Neurons carry an electrical potential (voltage) across their membranes. • Opening and closing of ion channels changes the membrane potential. This can encode external stimuli as electrical signals. • To send signals over large distances through their axons, neurons need to generate action potentia ...
... • Neurons carry an electrical potential (voltage) across their membranes. • Opening and closing of ion channels changes the membrane potential. This can encode external stimuli as electrical signals. • To send signals over large distances through their axons, neurons need to generate action potentia ...
Doktryna neuronu
... Sodium channels are dense at the node of Ranvier but sparse or absent in the internodal regions of the axon membrane. The K+ channels are located beneath the myelin sheath in internodal regions. There are about 700 000 sodium channels per node, i.e., 12,000 per um2 of nodal membrane. Internodal memb ...
... Sodium channels are dense at the node of Ranvier but sparse or absent in the internodal regions of the axon membrane. The K+ channels are located beneath the myelin sheath in internodal regions. There are about 700 000 sodium channels per node, i.e., 12,000 per um2 of nodal membrane. Internodal memb ...
File
... that allow for a slow leakage of ions down their concentration gradients. K+ leaks out about 50x faster than Na+ leaks in promotion of negative resting potential (there are very few of these ‘open’ channels compared to the soon-to-be-mentioned ‘gates’ that open during an action potential). The pum ...
... that allow for a slow leakage of ions down their concentration gradients. K+ leaks out about 50x faster than Na+ leaks in promotion of negative resting potential (there are very few of these ‘open’ channels compared to the soon-to-be-mentioned ‘gates’ that open during an action potential). The pum ...
Neural Networks (NN)
... combination of heart rate, levels of various substances in the blood, respiration rate) can be monitored. The onset of a particular medical condition could be associated with a very complex (e.g., nonlinear and interactive) combination of changes on a subset of the variables being monitored. Neural ...
... combination of heart rate, levels of various substances in the blood, respiration rate) can be monitored. The onset of a particular medical condition could be associated with a very complex (e.g., nonlinear and interactive) combination of changes on a subset of the variables being monitored. Neural ...
Nerve cells - Dr Magrann
... Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS. They innervate muscles and glands 1. Receive a signal. Can be any type of stimulus (change in environment, signal from another neuron, etc). 2. Transmit a signal to another location. E.g. finger touching something signal to spinal cord or bra ...
... Motor (efferent) signals are carried away from the CNS. They innervate muscles and glands 1. Receive a signal. Can be any type of stimulus (change in environment, signal from another neuron, etc). 2. Transmit a signal to another location. E.g. finger touching something signal to spinal cord or bra ...
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... 1. The refractory period is the period in which a threshold stimulus will not trigger another impulse on an axon. 2. An absolute refractory period is the period when an axon’s membrane cannot be stimulated and is the first part of the refractory period. 3. A relative refractory period is the period ...
... 1. The refractory period is the period in which a threshold stimulus will not trigger another impulse on an axon. 2. An absolute refractory period is the period when an axon’s membrane cannot be stimulated and is the first part of the refractory period. 3. A relative refractory period is the period ...
12-2cut
... 2) extra K+ channels open and lots of K+ flows out This repolarizes membrane 3) Refractory period: time during which original state is regenerated by Na-K pumps. During this time, neuron __________ fire again. ...
... 2) extra K+ channels open and lots of K+ flows out This repolarizes membrane 3) Refractory period: time during which original state is regenerated by Na-K pumps. During this time, neuron __________ fire again. ...
How Neurons Talk to Each Other
... In addition to these proteins required for “replenishing”, the membranes of synaptic vesicles contain other components that enable the vesicles to fuse with the plasma membrane (including the SNARE protein synaptobrevin and the calcium sensor synaptotagmin). Once membrane fusion has occurred, they a ...
... In addition to these proteins required for “replenishing”, the membranes of synaptic vesicles contain other components that enable the vesicles to fuse with the plasma membrane (including the SNARE protein synaptobrevin and the calcium sensor synaptotagmin). Once membrane fusion has occurred, they a ...
E1 – Stimulus and response - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli. E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, mot ...
... receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli. E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, mot ...
Count the black dots
... distance s. The change in distance per unit time is the velocity. As the unit of time is made smaller, this rate becomes the derivative ds/dt = v. ...
... distance s. The change in distance per unit time is the velocity. As the unit of time is made smaller, this rate becomes the derivative ds/dt = v. ...
Nervous Systems
... depolarized. The depolarization causes even more Na+ ion channels to open (positive feedback) until a threshold is reached in the membrane potential • Step 3: Once the threshold is reached, positive feedback progresses at a rapid rate to create an action potential (the voltage that allows the membra ...
... depolarized. The depolarization causes even more Na+ ion channels to open (positive feedback) until a threshold is reached in the membrane potential • Step 3: Once the threshold is reached, positive feedback progresses at a rapid rate to create an action potential (the voltage that allows the membra ...
Chapter Three Study Guide
... --The average brain is about the size of a grapefruit --About 3 lbs in weight --100 billion nerve cells – each cells connects to up to 10,000 other nerve cells --At age 70, a person retains about 98% of their nerve cells --The brain has three main parts: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brain s ...
... --The average brain is about the size of a grapefruit --About 3 lbs in weight --100 billion nerve cells – each cells connects to up to 10,000 other nerve cells --At age 70, a person retains about 98% of their nerve cells --The brain has three main parts: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brain s ...
Slide ()
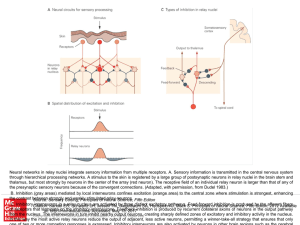
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
ch 48 clicker questions
... The use of organophosphate pesticides that inhibit acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine, could cause skeletal muscle cells to a) undergo more graded depolarizations, because acetylcholine would remain in the synaptic cleft longer. b) undergo more graded hyperpolarizations, ...
... The use of organophosphate pesticides that inhibit acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine, could cause skeletal muscle cells to a) undergo more graded depolarizations, because acetylcholine would remain in the synaptic cleft longer. b) undergo more graded hyperpolarizations, ...
Lecture 3
... outweighs inhibition, the cell may reach threshold causing another action potential. The cycle begins again in the next cell. ...
... outweighs inhibition, the cell may reach threshold causing another action potential. The cycle begins again in the next cell. ...
File
... •Physiology of Attraction and Love •Sleep and circadian rhythm •Drug Use and Abuse •Physiology of Risk Taking •Physiology of Happiness •Memory and Learning •Visual Perception and Visual Disorders ...
... •Physiology of Attraction and Love •Sleep and circadian rhythm •Drug Use and Abuse •Physiology of Risk Taking •Physiology of Happiness •Memory and Learning •Visual Perception and Visual Disorders ...
Chapter 12 - Nervous Tissue
... _________ muscles, causing them to contract. 3. ________ motor (autonomic) neurons relay impulses via cranial & spinal nerves to _______ & _______ muscles, and ______. C. Association (_____________) neurons 1. Found only in the ____ 2. _________ nerve impulses from one neuron to another (e.g., from ...
... _________ muscles, causing them to contract. 3. ________ motor (autonomic) neurons relay impulses via cranial & spinal nerves to _______ & _______ muscles, and ______. C. Association (_____________) neurons 1. Found only in the ____ 2. _________ nerve impulses from one neuron to another (e.g., from ...
Lessons 1
... potential and currents that need to maintain this potential level are recorded The axon was immersed in sea water, so Vm represented the difference between the inside of the axon and the water HH inserted 2 silver electrodes in the axon, one measuring Vm and the other transmitting a current able to ...
... potential and currents that need to maintain this potential level are recorded The axon was immersed in sea water, so Vm represented the difference between the inside of the axon and the water HH inserted 2 silver electrodes in the axon, one measuring Vm and the other transmitting a current able to ...
Unit 12 ~ Learning Guide Name
... impulse can travel up to 200m/s. In unmyelinated fibers, the impulse can be as slow as 0.5 m/s. This difference in speed is because the action potential is able to jump over the myelin sheath. Depolarization only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. ...
... impulse can travel up to 200m/s. In unmyelinated fibers, the impulse can be as slow as 0.5 m/s. This difference in speed is because the action potential is able to jump over the myelin sheath. Depolarization only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. ...
Slide 1
... FIGURE 47.10 Schematic representation of possible loci for cellular changes involved in the enhancement of synaptic efficacy. The efficacy of a synapse can be potentiated through at least sixmechanisms. First, there could be an increase in the fraction (release probability) of available presynaptic ...
... FIGURE 47.10 Schematic representation of possible loci for cellular changes involved in the enhancement of synaptic efficacy. The efficacy of a synapse can be potentiated through at least sixmechanisms. First, there could be an increase in the fraction (release probability) of available presynaptic ...
Neurons: Our Building Blocks
... -The axon gets its energy from charged chemicals called ions. In its normal state, the ions have a small negative charge called resting potential. -This negative balance can be easily upset, however. When the cell becomes excited, it triggers the action potential, which reverses the charge and cause ...
... -The axon gets its energy from charged chemicals called ions. In its normal state, the ions have a small negative charge called resting potential. -This negative balance can be easily upset, however. When the cell becomes excited, it triggers the action potential, which reverses the charge and cause ...