Capacity Analysis of Attractor Neural Networks with Binary Neurons and Discrete Synapses
... experiments, the attractor states of neural network dynamics are considered to be the underlying mechanism of memory storage in neural networks. For the simplest network with binary neurons and standard asynchronous dynamics, we show that the dynamics cannot be stable if all synapses are excitatory. ...
... experiments, the attractor states of neural network dynamics are considered to be the underlying mechanism of memory storage in neural networks. For the simplest network with binary neurons and standard asynchronous dynamics, we show that the dynamics cannot be stable if all synapses are excitatory. ...
The Nervous System
... • Accelerated breathing & heart rate (increases blood flow) • Inhibition or slowing of digestion • Pupils Dilate • Tunnel vision • Increased muscle tension for extra strength & speed ...
... • Accelerated breathing & heart rate (increases blood flow) • Inhibition or slowing of digestion • Pupils Dilate • Tunnel vision • Increased muscle tension for extra strength & speed ...
Unit 1 – Nervous and Endocrine System
... Transmission of a signal across a synapse Review Sheet 1. Number these events in the correct order. (a) ____ An action potential is stimulated at the postsynaptic membrane, and an impulse travels down the dendrite. (b) ____ An enzyme destroys the neurotransmitter substance and clears out the synapti ...
... Transmission of a signal across a synapse Review Sheet 1. Number these events in the correct order. (a) ____ An action potential is stimulated at the postsynaptic membrane, and an impulse travels down the dendrite. (b) ____ An enzyme destroys the neurotransmitter substance and clears out the synapti ...
CHAPTER 2 RAPID REVIEW
... dopamine have been linked to the psychological disorder known as schizophrenia. Endorphin is a special neurotransmitter called a neural regulator that controls the release of other neurotransmitters. When endorphin is released in the body, they neurons transmitting information about pain are not ab ...
... dopamine have been linked to the psychological disorder known as schizophrenia. Endorphin is a special neurotransmitter called a neural regulator that controls the release of other neurotransmitters. When endorphin is released in the body, they neurons transmitting information about pain are not ab ...
Biology 251 Fall 2015 1 TOPIC 7: PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Receptor cells constantly replaced; only neurons known that do this d) 5 million receptors of 1000 different kinds (compared to only 3 receptor types for color vision and 4 for taste) ...
... Receptor cells constantly replaced; only neurons known that do this d) 5 million receptors of 1000 different kinds (compared to only 3 receptor types for color vision and 4 for taste) ...
Nervous System
... the brain by way of the senses (touch, smell, see, etc.) Integration: the interpretation or translation of ...
... the brain by way of the senses (touch, smell, see, etc.) Integration: the interpretation or translation of ...
Lecture #13 – Animal Nervous Systems
... • If the action potential is of a fixed magnitude, how do we sense different levels of a stimulus??? • They can occur with varying frequency Frequency is part of the information ...
... • If the action potential is of a fixed magnitude, how do we sense different levels of a stimulus??? • They can occur with varying frequency Frequency is part of the information ...
The NERVOUS System
... Axon – Away- extends to other organs (muscles or glands). Myelin Sheath - increases the speed of nerve impulses. Nodes of Raniver – where signals transmitted. ...
... Axon – Away- extends to other organs (muscles or glands). Myelin Sheath - increases the speed of nerve impulses. Nodes of Raniver – where signals transmitted. ...
Cellular and Molecul..
... • odorant receptors themselves should exhibit significant diversity and are therefore likely to be encoded by a multigene family • expression of the odorant receptors should be restricted to the olfactory epithelium ...
... • odorant receptors themselves should exhibit significant diversity and are therefore likely to be encoded by a multigene family • expression of the odorant receptors should be restricted to the olfactory epithelium ...
Neuroscience and Behavior Term Explanation
... moment after you flush a toilet- until refractory period, the water returns back to its original as during this level you can’t flush again, similar period the neuron to a neuron returning back to -70 can’t fire until the before it can fire another action charge returns back potential to -70 Remembe ...
... moment after you flush a toilet- until refractory period, the water returns back to its original as during this level you can’t flush again, similar period the neuron to a neuron returning back to -70 can’t fire until the before it can fire another action charge returns back potential to -70 Remembe ...
3-Biological Bases-table - Miami Beach Senior High School
... information from other neurons communication between neurons will be quicker because neurotransmitters do not travel very far to the next neuron. Neurons don’t regenerate Axons- part of a neuron where neural impulses take The longest part of a neuron place, which enables information to be sent to ot ...
... information from other neurons communication between neurons will be quicker because neurotransmitters do not travel very far to the next neuron. Neurons don’t regenerate Axons- part of a neuron where neural impulses take The longest part of a neuron place, which enables information to be sent to ot ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Guide migration of neurons during development Create blood-brain barrier, nourish neurons ...
... Guide migration of neurons during development Create blood-brain barrier, nourish neurons ...
The Biology of Mind Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... 3. Which type of cell communicates within the central nervous system and processes information between incoming and outgoing messages? ANSWER A. B. C. D. ...
... 3. Which type of cell communicates within the central nervous system and processes information between incoming and outgoing messages? ANSWER A. B. C. D. ...
Neurons - University of San Diego Home Pages
... K+ flux via passive (leaky) K+ channels is most important contributor to Vm Na+ flux also contributes to Vm ...
... K+ flux via passive (leaky) K+ channels is most important contributor to Vm Na+ flux also contributes to Vm ...
The Nervous System
... The cells that transmit the electrical signals of the nervous system are called neurons Sensory neurons carry information (impulses) from the sense organs to the central nervous system (CNS). Motor neurons carry information (impulses) from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles and glands. ...
... The cells that transmit the electrical signals of the nervous system are called neurons Sensory neurons carry information (impulses) from the sense organs to the central nervous system (CNS). Motor neurons carry information (impulses) from the central nervous system (CNS) to the muscles and glands. ...
Poster Sensopac
... Granular layer model. Explicit and implicit context encoding approach. Each granule cell receives an explicit context signal and three randomly-chosen mossy fibers from current and desired positions and velocities The cerebellum module consists of a network which contains a considerable amount of sp ...
... Granular layer model. Explicit and implicit context encoding approach. Each granule cell receives an explicit context signal and three randomly-chosen mossy fibers from current and desired positions and velocities The cerebellum module consists of a network which contains a considerable amount of sp ...
File
... distances throughout the body and have longer effects than neurotransmitters. They take a little longer time to exert their effects, but they can affect cells and organs distant from the source of the hormone’s production. Some neurotransmitters also function as neurohormones. Examples: Dopamine is ...
... distances throughout the body and have longer effects than neurotransmitters. They take a little longer time to exert their effects, but they can affect cells and organs distant from the source of the hormone’s production. Some neurotransmitters also function as neurohormones. Examples: Dopamine is ...
nervous system - Doctor Jade Main
... Step 3: Inactivation of Na channels & activation of K channels – as membrane potential passes 0 mV, sodium gates are inactivatedbegin to close – by the time they all close and Na inflow ceases voltage peaks at about +35mV Na channels close & voltage regulated K channels open – both electrical & c ...
... Step 3: Inactivation of Na channels & activation of K channels – as membrane potential passes 0 mV, sodium gates are inactivatedbegin to close – by the time they all close and Na inflow ceases voltage peaks at about +35mV Na channels close & voltage regulated K channels open – both electrical & c ...
Signature Assignment, Action Potential Graphing, Biology 231
... In the space below draw a graph of an action potential generated in the presence of TEA (assume 50% of the K+ channels are blocked) ...
... In the space below draw a graph of an action potential generated in the presence of TEA (assume 50% of the K+ channels are blocked) ...
Terms being described
... 9. It refers to the action potential firing to maximum amplitude or not at all. [3 words] 11. It’s another name for motor neurons because of their direction of conduction. 13. It’s another name for sensory neurons because of their direction of conduction. 15. It’s the ability of a potential change t ...
... 9. It refers to the action potential firing to maximum amplitude or not at all. [3 words] 11. It’s another name for motor neurons because of their direction of conduction. 13. It’s another name for sensory neurons because of their direction of conduction. 15. It’s the ability of a potential change t ...
Slide ()
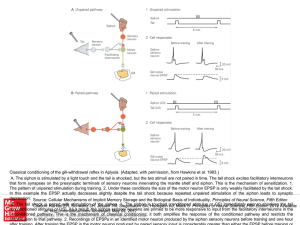
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
NeuralNets273ASpring09
... • Neurons communicate by receiving signals on their dendrites. Adding these signals and firing off a new signal along the axon if the total input exceeds a threshold. • The axon connects to new dendrites through synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) buil ...
... • Neurons communicate by receiving signals on their dendrites. Adding these signals and firing off a new signal along the axon if the total input exceeds a threshold. • The axon connects to new dendrites through synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) buil ...
ppt
... • Neurons communicate by receiving signals on their dendrites. Adding these signals and firing off a new signal along the axon if the total input exceeds a threshold. • The axon connects to new dendrites through synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) buil ...
... • Neurons communicate by receiving signals on their dendrites. Adding these signals and firing off a new signal along the axon if the total input exceeds a threshold. • The axon connects to new dendrites through synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) buil ...