Peripheral Nervous System
... the outside under resting conditions due to distribution of ions controlled by Na+/K+ pump that require ATP • Nerve impulse starts when the membrane of the nerve depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical, temp. changes, mechanical, etc…. • Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na+ which causes ...
... the outside under resting conditions due to distribution of ions controlled by Na+/K+ pump that require ATP • Nerve impulse starts when the membrane of the nerve depolarizes due to some stimulus, chemical, temp. changes, mechanical, etc…. • Depolarization is caused by the influx of Na+ which causes ...
Slide ()
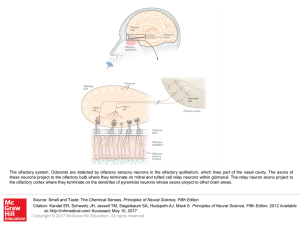
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... occurs when a neuron send information down an axon, away from the soma. Neuroscientists use the words such as “spike” or “impulse” for the action potential. ...
... occurs when a neuron send information down an axon, away from the soma. Neuroscientists use the words such as “spike” or “impulse” for the action potential. ...
PPt #2 Human Body Nervous system
... • 4. I can identify and explain different areas of the brain and their functions. • 5. I can explain how the nervous system passes information between the external environment and the many parts of the body. ...
... • 4. I can identify and explain different areas of the brain and their functions. • 5. I can explain how the nervous system passes information between the external environment and the many parts of the body. ...
Nervous Tissue
... the voltage difference across their membrane • Communicate with 2 types of electric signals – action potentials that can travel long distances – graded potentials that are local membrane changes only ...
... the voltage difference across their membrane • Communicate with 2 types of electric signals – action potentials that can travel long distances – graded potentials that are local membrane changes only ...
Recognition by Variance: Learning Rules for Spatiotemporal Patterns
... background pattern. The model therefore reduces the high dimensional input to a one dimensional output. We emphasize that in the task that we consider in this paper, the selected group of learned patterns is to be distinguished from infintely many other random patterns, as opposed to the task of cla ...
... background pattern. The model therefore reduces the high dimensional input to a one dimensional output. We emphasize that in the task that we consider in this paper, the selected group of learned patterns is to be distinguished from infintely many other random patterns, as opposed to the task of cla ...
Study Guide Solutions - Elsevier: Baars and Gage
... Arrays, maps and hierarchies support spatial coding in neurons. For example the visual thalamus and area V1 (the first visual projection area) can be seen as maps of the retina. Maps represent spatial arrangements in the world. But the brain makes use of temporal coding as well. Figure 3.23 shows an ...
... Arrays, maps and hierarchies support spatial coding in neurons. For example the visual thalamus and area V1 (the first visual projection area) can be seen as maps of the retina. Maps represent spatial arrangements in the world. But the brain makes use of temporal coding as well. Figure 3.23 shows an ...
Topic Presentation: Biopsychology
... Students: Please note that this is a lecture outline that I share with you to help you with your note taking. It is not an exact duplicate of any power points and/or discussions that may be conducted in class. Topic Presentation: Neuroscience and Behavior I. How the Body Communicates Internally A. T ...
... Students: Please note that this is a lecture outline that I share with you to help you with your note taking. It is not an exact duplicate of any power points and/or discussions that may be conducted in class. Topic Presentation: Neuroscience and Behavior I. How the Body Communicates Internally A. T ...
chapt10_holes_lecture_animation
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
PowerPoint to accompany Hole’s Human Anatomy and
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
The Action Potential
... The depolarization phase of action potential is abrupt and very rapid: in takes place in less than one milisecond. Soon after reaching the maximum peak of depolarization ( which inverts the membrane potential to some +10 to+ 20 mV), it begins to return to normal, that is, towards its value at rest. ...
... The depolarization phase of action potential is abrupt and very rapid: in takes place in less than one milisecond. Soon after reaching the maximum peak of depolarization ( which inverts the membrane potential to some +10 to+ 20 mV), it begins to return to normal, that is, towards its value at rest. ...
Real Neurons for Engineers
... their membranes. This changes ion concentrations and the potential across their membrane. The ions then function in various ways to cause changes in the neuron. • Bob will teach this. I will show you how to model it. ...
... their membranes. This changes ion concentrations and the potential across their membrane. The ions then function in various ways to cause changes in the neuron. • Bob will teach this. I will show you how to model it. ...
Keshara Senanayake Towle Notes Chapter 50 "Nervous System
... >called neurotransmitters --> turn elicit electrical activity in a second neuron >this the signaling activity of the nervous system is composed of electrical activity within neurons and chemical flow between neurons >neuron function is dependant on electrical activity -neurons have an electrical cha ...
... >called neurotransmitters --> turn elicit electrical activity in a second neuron >this the signaling activity of the nervous system is composed of electrical activity within neurons and chemical flow between neurons >neuron function is dependant on electrical activity -neurons have an electrical cha ...
A Point Process Model for Auditory Neurons Considering
... The CIF is for a point process a history-dependent generalization of the rate function of a Poisson process. To obtain a discrete formulation of the CIF we choose K sufficiently large so that each subinterval Δ = K−1T contains at most one spike. We index the subintervals k = 1, …, K and define nk to ...
... The CIF is for a point process a history-dependent generalization of the rate function of a Poisson process. To obtain a discrete formulation of the CIF we choose K sufficiently large so that each subinterval Δ = K−1T contains at most one spike. We index the subintervals k = 1, …, K and define nk to ...
Artificial Neural Networks
... • An Artificial Neural Network is a network of interconnected artificial neurons. • Like in a biological neural network, artificial neurons communicate by sending signals to one another. • Each input to an artificial neuron can either inhibit or excite the artificial neuron. ...
... • An Artificial Neural Network is a network of interconnected artificial neurons. • Like in a biological neural network, artificial neurons communicate by sending signals to one another. • Each input to an artificial neuron can either inhibit or excite the artificial neuron. ...
spiking neuron models - Assets - Cambridge
... potential. Without any spike input, the neuron is at rest corresponding to a constant membrane potential. After the arrival of a spike, the potential changes and finally decays back to the resting potential, cf. Fig. 1.3A. If the change is positive, the synapse is said to be excitatory. If the chang ...
... potential. Without any spike input, the neuron is at rest corresponding to a constant membrane potential. After the arrival of a spike, the potential changes and finally decays back to the resting potential, cf. Fig. 1.3A. If the change is positive, the synapse is said to be excitatory. If the chang ...
Biology 3201 - Corner Brook Regional High
... • The Ear is divided into three sections: • 1. Outer Ear - consists of the pinna and auditory canal. • 2. Middle Ear - consists of the tympanic membrane, the ossicles, (malleus, incus, and stapes), the eustachian tube, and the round and oval window. • 3. Inner Ear - consists of the cochlea, vestibul ...
... • The Ear is divided into three sections: • 1. Outer Ear - consists of the pinna and auditory canal. • 2. Middle Ear - consists of the tympanic membrane, the ossicles, (malleus, incus, and stapes), the eustachian tube, and the round and oval window. • 3. Inner Ear - consists of the cochlea, vestibul ...
The biological basis of behavior
... The synapse • Synapse: area composed of the axon terminal of one neuron, the synaptic space, and the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron. • Neurotransmitters: chemicals released by the synaptic vesicles that travel across the synaptic space and affect adjacent neurons. ...
... The synapse • Synapse: area composed of the axon terminal of one neuron, the synaptic space, and the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron. • Neurotransmitters: chemicals released by the synaptic vesicles that travel across the synaptic space and affect adjacent neurons. ...
Chp 9: Nervous tissue chp 11: autonomic nervous system chp 12
... axon; retina of the eye, inner ear, olfactory area of brain Unipolar neurons: dendrites and one axon fused together forming a continuous process that emerges from cell body; begin in embryo as bipolar neurons; most function as sensory receptors for touch, pressure, pain, or thermal stimuli. Cell b ...
... axon; retina of the eye, inner ear, olfactory area of brain Unipolar neurons: dendrites and one axon fused together forming a continuous process that emerges from cell body; begin in embryo as bipolar neurons; most function as sensory receptors for touch, pressure, pain, or thermal stimuli. Cell b ...
Biological of Behavior
... membrane cause a postsynaptic potential (PSP); a voltage charge at a receptor site. Two types of messages can be sent from cell to cell: excitatory and inhibitory. An excitatory PSP is a positive voltage shift that increases the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will fire an action potenti ...
... membrane cause a postsynaptic potential (PSP); a voltage charge at a receptor site. Two types of messages can be sent from cell to cell: excitatory and inhibitory. An excitatory PSP is a positive voltage shift that increases the likelihood that the postsynaptic neuron will fire an action potenti ...
Chapter 48 and 49 Name_______________________________
... 9. What change in the permeability of the cell’s membrane to K+ and/or Na+ could cause the cell’s membrane potential to shift from -70mV to -90mV? The opening of ion channels in the plasma membrane converts chemical potential to electrical potential A neuron at resting potential contains many open K ...
... 9. What change in the permeability of the cell’s membrane to K+ and/or Na+ could cause the cell’s membrane potential to shift from -70mV to -90mV? The opening of ion channels in the plasma membrane converts chemical potential to electrical potential A neuron at resting potential contains many open K ...
here - WPI
... cell’s membrane potential when the neurotransmitter is in place. This triggers a reaction from the cell that is particular to its function, which could be anything from the contraction of a muscle to the generation of another action potential (Society for Neuroscience, 2012). To facilitate the trave ...
... cell’s membrane potential when the neurotransmitter is in place. This triggers a reaction from the cell that is particular to its function, which could be anything from the contraction of a muscle to the generation of another action potential (Society for Neuroscience, 2012). To facilitate the trave ...
Motor neuron
... cord by way of the dorsal root 3. The sensory neuron synapses with many neurons in the spinal cord of the CNS: - an interneuron may carry the signal to the brain to ’advise it’ about the situation. - another interneuron carries the impulse to a motor neuron 4. A motor neuron carries the impulse from ...
... cord by way of the dorsal root 3. The sensory neuron synapses with many neurons in the spinal cord of the CNS: - an interneuron may carry the signal to the brain to ’advise it’ about the situation. - another interneuron carries the impulse to a motor neuron 4. A motor neuron carries the impulse from ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 5.1 Intracellular recording of the
... FIGURE 5.2 Differential distribution of ions inside and outside plasma membrane of neurons and neuronal processes, showing ionic channels for Na+, K+, Cl−, and Ca2+, as well as an electrogenic Na+– K+ ionic pump (also known as Na+, K+-ATPase). Concentrations (in millimoles except that for intracellu ...
... FIGURE 5.2 Differential distribution of ions inside and outside plasma membrane of neurons and neuronal processes, showing ionic channels for Na+, K+, Cl−, and Ca2+, as well as an electrogenic Na+– K+ ionic pump (also known as Na+, K+-ATPase). Concentrations (in millimoles except that for intracellu ...