e.4.1 state that some presynaptic neurons excite post synaptic
... ____________ = -Aminobutyric acid GABA is a NT that opens _______________________ on the postsynaptic membrane. Cl- rushes in, _____________________ the post-synaptic neuron and _____________ APs. GABA is important in regulating nervous processes – a “_____________” or depressive effect (reduci ...
... ____________ = -Aminobutyric acid GABA is a NT that opens _______________________ on the postsynaptic membrane. Cl- rushes in, _____________________ the post-synaptic neuron and _____________ APs. GABA is important in regulating nervous processes – a “_____________” or depressive effect (reduci ...
Document
... Please note that due to differing operating systems, some animations will not appear until the presentation is viewed in Presentation Mode (Slide Show view). You may see blank slides in the “Normal” or “Slide Sorter” views. All animations will appear after viewing in Presentation Mode and playing ea ...
... Please note that due to differing operating systems, some animations will not appear until the presentation is viewed in Presentation Mode (Slide Show view). You may see blank slides in the “Normal” or “Slide Sorter” views. All animations will appear after viewing in Presentation Mode and playing ea ...
The Nervous System
... electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous system (brain/spinal cord) • Motor neurons: carry impulses fro ...
... electrical signals to communicate with other cells • An impulse is: an electrical signal travelling through a neuron • A nerve is: a bundle of neurons • Sensory neurons: carry impulses from receptors (e.g. in skin) to the central nervous system (brain/spinal cord) • Motor neurons: carry impulses fro ...
File
... a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane ...
... a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane ...
Unlocking Single-Trial Dynamics in Parietal Cortex During Decision-Making
... that is commonly believed to reflect the accumulation of sensory evidence during decisionmaking. However, ramping that appears in trial-averaged responses does not necessarily imply spike rate ramps on single trials; a ramping average could also arise from instantaneous steps that occur at different ...
... that is commonly believed to reflect the accumulation of sensory evidence during decisionmaking. However, ramping that appears in trial-averaged responses does not necessarily imply spike rate ramps on single trials; a ramping average could also arise from instantaneous steps that occur at different ...
Chapter 12 Notes: Nervous Tissue 2014
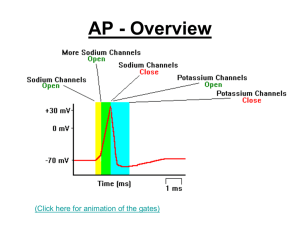
... A typical value for the resting membrane potential is -70mV inside and the membrane is said to be polarized. 2. When a stimulus causes the inside of the cell membrane to become positive (+30mV), and the outside negative, the membrane is said to be depolarized and has an action potential which travel ...
... A typical value for the resting membrane potential is -70mV inside and the membrane is said to be polarized. 2. When a stimulus causes the inside of the cell membrane to become positive (+30mV), and the outside negative, the membrane is said to be depolarized and has an action potential which travel ...
Introduction to Psychology
... excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity (threshold) the neuron fires an action potential. ...
... excitatory and inhibitory signals from many neurons. When the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceed a minimum intensity (threshold) the neuron fires an action potential. ...
neural plasticity
... FIGURE 3. A pattern of neuronal synaptic connections being made via neural facilitation is analogous to water etching a deeper and deeper pathway into the side of a mountain over a period of time. Illustration : Giovanni Rimasti : Modeled from Box 17-1 Figure, Kinesiology, The Skeletal System and M ...
... FIGURE 3. A pattern of neuronal synaptic connections being made via neural facilitation is analogous to water etching a deeper and deeper pathway into the side of a mountain over a period of time. Illustration : Giovanni Rimasti : Modeled from Box 17-1 Figure, Kinesiology, The Skeletal System and M ...
Chapter 10 Slides
... capacity for accurate axonal growth is lost in maturity Regeneration is virtually nonexistent in the CNS of adult mammals and unlikely, but possible, in the PNS ...
... capacity for accurate axonal growth is lost in maturity Regeneration is virtually nonexistent in the CNS of adult mammals and unlikely, but possible, in the PNS ...
– Cell loss Brain, Neuron
... cresyl violet or with more sophisticated techniques of morphometry and stereology. Figure 1 is an example of hippocampal neuronal cell loss in the CA3 region. Note the pyramidal neuronal ...
... cresyl violet or with more sophisticated techniques of morphometry and stereology. Figure 1 is an example of hippocampal neuronal cell loss in the CA3 region. Note the pyramidal neuronal ...
nervous system text a - powerpoint presentation
... ganglia. Developmentally, this type of neuron starts out as a bipolar neuron. ...
... ganglia. Developmentally, this type of neuron starts out as a bipolar neuron. ...
brain
... • Disorders of planning or social cognition • Apraxias (disorders in action) • Agnosias (disorders in perception) • Aphasias (disorders of language) ...
... • Disorders of planning or social cognition • Apraxias (disorders in action) • Agnosias (disorders in perception) • Aphasias (disorders of language) ...
brain
... • Disorders of planning or social cognition • Apraxias (disorders in action) • Agnosias (disorders in perception) • Aphasias (disorders of language) ...
... • Disorders of planning or social cognition • Apraxias (disorders in action) • Agnosias (disorders in perception) • Aphasias (disorders of language) ...
The Brain Implements Optimal Decision Making between Alternative Actions
... concerning the firing rates of STN and GP neurons as a function of their input, with published experimental data. In order to make this comparison, model variables (e.g. yi(T), STNi(T), GPi(T)) are assumed to be proportional to experimentally observed neuronal firing rates. Note, however, that propo ...
... concerning the firing rates of STN and GP neurons as a function of their input, with published experimental data. In order to make this comparison, model variables (e.g. yi(T), STNi(T), GPi(T)) are assumed to be proportional to experimentally observed neuronal firing rates. Note, however, that propo ...
Student Worksheet
... body, and the axon. These nerves cells transmit electrochemical signals to cells such as other neurons, muscles, and endocrine cells. This signal transmission is, for example, how the brain tells muscles to contract. Multiple signals enter the neuron through the dendrites. The separate electrical im ...
... body, and the axon. These nerves cells transmit electrochemical signals to cells such as other neurons, muscles, and endocrine cells. This signal transmission is, for example, how the brain tells muscles to contract. Multiple signals enter the neuron through the dendrites. The separate electrical im ...
AP – All or nothing
... • There is a time after depolarisation where no new AP can start – called the refractory period. – Time is needed to restore the proteins of voltage sensitive ion channels to their original resting conditions. – Na+ channels cannot be opened, as it can’t be depolarised again. WHY? – AP travel in one ...
... • There is a time after depolarisation where no new AP can start – called the refractory period. – Time is needed to restore the proteins of voltage sensitive ion channels to their original resting conditions. – Na+ channels cannot be opened, as it can’t be depolarised again. WHY? – AP travel in one ...
Chapter II - Angelfire
... After a few moment, the neuron will gradually undergo recovery and the neuron is now in its PARTIAL REFRACTORY PERIOD o In this state, the neuron has partially recovered and recovery continues until it becomes normal again o During this time, a neuron may fire an impulse IF the second stimulus is ...
... After a few moment, the neuron will gradually undergo recovery and the neuron is now in its PARTIAL REFRACTORY PERIOD o In this state, the neuron has partially recovered and recovery continues until it becomes normal again o During this time, a neuron may fire an impulse IF the second stimulus is ...
Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... – sodium moves into the cell – potassium moves outside the cell. ...
... – sodium moves into the cell – potassium moves outside the cell. ...
Learning by localized plastic adaptation in recurrent neural networks
... where ωi j is the synaptic strength and ηi ∈ [0, 1] stands for the amount of releasable neurotransmitter, which for simplicity is the same for all synapses. All neurons are excitatory. After each firing ηi decreases by a fixed amount ∆η = 0.2, which guarantees that the network activity will decay in ...
... where ωi j is the synaptic strength and ηi ∈ [0, 1] stands for the amount of releasable neurotransmitter, which for simplicity is the same for all synapses. All neurons are excitatory. After each firing ηi decreases by a fixed amount ∆η = 0.2, which guarantees that the network activity will decay in ...
01Integrated Normal Cells of CNS
... Based on number of processes 2. Bipolar Neuron (spindle-shaped neuron): Has two processes (one arising from each pole of the cell body). One of them is the dendrite and the other is the axon, e.g. retina & ...
... Based on number of processes 2. Bipolar Neuron (spindle-shaped neuron): Has two processes (one arising from each pole of the cell body). One of them is the dendrite and the other is the axon, e.g. retina & ...