Lesson 7
... you’re ever going to be taken seriously as a super villain, you’ll have to change your name, Tom.” ...
... you’re ever going to be taken seriously as a super villain, you’ll have to change your name, Tom.” ...
Unit 5: Study Guide Biological Bases of Behavior (Neuroscience)
... A. Speech in the left hemisphere named after me? Gosh. B. Some said I should change my personality, but a pole through my head? Ouch! C. Reward Centers in our brains? Cool because I’m just a rat. D. You can comprehend me because of your left temporal lobe (named after me) E. Cut my corpus callosum a ...
... A. Speech in the left hemisphere named after me? Gosh. B. Some said I should change my personality, but a pole through my head? Ouch! C. Reward Centers in our brains? Cool because I’m just a rat. D. You can comprehend me because of your left temporal lobe (named after me) E. Cut my corpus callosum a ...
Heidi
... • Once complete depolarization occurs, action potential results. Na+ channels are opened all along the membrane. • After Na+ ions flood inside the membrane, K+ ions move to the outside of the membrane causing repolarization. • When K+ channels finally close, the neuron has more K+ ions on the outsid ...
... • Once complete depolarization occurs, action potential results. Na+ channels are opened all along the membrane. • After Na+ ions flood inside the membrane, K+ ions move to the outside of the membrane causing repolarization. • When K+ channels finally close, the neuron has more K+ ions on the outsid ...
C2 - The Biological Perspective
... messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons. ...
... messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons. ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... • selective permeability controls flow of substances into and out of the cell ...
... • selective permeability controls flow of substances into and out of the cell ...
What is a neuron?
... responsible for conveying information to the Central Nervous System. You can tell that these Neurons have huge cell bodies. These are some of the largest cells in the body. The larger the cell body, the further away the information is coming from.” Red arrows - Central Nuclei of Sensory Neurons UMDN ...
... responsible for conveying information to the Central Nervous System. You can tell that these Neurons have huge cell bodies. These are some of the largest cells in the body. The larger the cell body, the further away the information is coming from.” Red arrows - Central Nuclei of Sensory Neurons UMDN ...
What is a neuron?
... responsible for conveying information to the Central Nervous System. You can tell that these Neurons have huge cell bodies. These are some of the largest cells in the body. The larger the cell body, the further away the information is coming from.” Red arrows - Central Nuclei of Sensory Neurons UMDN ...
... responsible for conveying information to the Central Nervous System. You can tell that these Neurons have huge cell bodies. These are some of the largest cells in the body. The larger the cell body, the further away the information is coming from.” Red arrows - Central Nuclei of Sensory Neurons UMDN ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... - long, to reach effector - travel from sympathetic chain ganglion via gray communicating ramus into spinal nerve or other sympathetic nerves to viscera - may contact several effectors (more divergence) ...
... - long, to reach effector - travel from sympathetic chain ganglion via gray communicating ramus into spinal nerve or other sympathetic nerves to viscera - may contact several effectors (more divergence) ...
Synapse
... •It results mainly from depletion of the neurotransmitter stores the in the synaptic knobs→ because in intensive stimulation the resynthesis and reuptake mechanisms that fill these stores are unable to provide all the demands for the transmitter ...
... •It results mainly from depletion of the neurotransmitter stores the in the synaptic knobs→ because in intensive stimulation the resynthesis and reuptake mechanisms that fill these stores are unable to provide all the demands for the transmitter ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... (___________) that synapse with muscle cells b. Axon _________ allow one neuron to control many muscle cells C. The synapse between the somatic neuron and muscle cell is called the neuron____________ junction. It consists of 1. ____synaptic axon _________ that contains synaptic vesicles with _____ n ...
... (___________) that synapse with muscle cells b. Axon _________ allow one neuron to control many muscle cells C. The synapse between the somatic neuron and muscle cell is called the neuron____________ junction. It consists of 1. ____synaptic axon _________ that contains synaptic vesicles with _____ n ...
ANATOMICAL TERMS
... Sensory (afferent) division – carriers signals from various receptors to the CNS Somatic sensory division – carriers signals from receptors in the skin, muscles, bone and joints Visceral sensory division – carriers signals mainly from the viscera of the thoracic and abdominal cavities Motor (eff ...
... Sensory (afferent) division – carriers signals from various receptors to the CNS Somatic sensory division – carriers signals from receptors in the skin, muscles, bone and joints Visceral sensory division – carriers signals mainly from the viscera of the thoracic and abdominal cavities Motor (eff ...
Nervous System Formative Study Guide File
... a. Motor neurons Motor neurons are efferent nerves (also called effector neurons), that carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles to produce (effect) movement. b. Sensory neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that transmit sensory information (sight, sound, feeling, etc.). They are activat ...
... a. Motor neurons Motor neurons are efferent nerves (also called effector neurons), that carry signals from the spinal cord to the muscles to produce (effect) movement. b. Sensory neurons Sensory neurons are nerve cells that transmit sensory information (sight, sound, feeling, etc.). They are activat ...
General Psychology Chapter 2 - Sarah Rach
... • Plasticity – its ability to modify itself after some types of damage • Some neural tissue can reorganize in response to damage • Most plastic when we are young children • If a blind person uses one finger to read Braille, the brain area dedicated to that finger expands as the sense of touch invade ...
... • Plasticity – its ability to modify itself after some types of damage • Some neural tissue can reorganize in response to damage • Most plastic when we are young children • If a blind person uses one finger to read Braille, the brain area dedicated to that finger expands as the sense of touch invade ...
BGYB30 Mammalian Physiology • Today: • Next Lecture:
... Question from 2002 final exam • Identify three major groups of transmembrane proteins discussed in class, indicate how they function, and give examples of how they act to stimulate and inhibit cellular physiology. ...
... Question from 2002 final exam • Identify three major groups of transmembrane proteins discussed in class, indicate how they function, and give examples of how they act to stimulate and inhibit cellular physiology. ...
Nervous Systems
... 2) Signal intensity of stimulus • All signals similar in size (all-or-none response) ...
... 2) Signal intensity of stimulus • All signals similar in size (all-or-none response) ...
Reflexes
... -sensory neurons monitor the degree (type Ia fibers and type II fibers) and rate of stretch (type Ia fibers) of the intrafusal muscle fibers -the whole production (receptor cells and sensory neuron endings) is called a muscle spindle -when the muscle is stretched, sensory neurons send impulses and “ ...
... -sensory neurons monitor the degree (type Ia fibers and type II fibers) and rate of stretch (type Ia fibers) of the intrafusal muscle fibers -the whole production (receptor cells and sensory neuron endings) is called a muscle spindle -when the muscle is stretched, sensory neurons send impulses and “ ...
Document
... The nervous system is one of the 2 control systems in our body. The nervous system is designed for fast action. It coordinates fast or rapid activities, such as muscle movement. Signaling is by electrical impulses, these are rapid, specific and produce an almost immediate response. ...
... The nervous system is one of the 2 control systems in our body. The nervous system is designed for fast action. It coordinates fast or rapid activities, such as muscle movement. Signaling is by electrical impulses, these are rapid, specific and produce an almost immediate response. ...
Chapter 17:
... All neurons provide an all-or-none response: - in response to a stimulus, they either activate (fire) and provide a certain level of response, or don’t fire at all A neuron will only fire if it is stimulated with an intensity of at least threshold level Every action potential for a neuron is identic ...
... All neurons provide an all-or-none response: - in response to a stimulus, they either activate (fire) and provide a certain level of response, or don’t fire at all A neuron will only fire if it is stimulated with an intensity of at least threshold level Every action potential for a neuron is identic ...
neural_networks
... vote has some positive value (= 1 in simplest model). If tally is large enough, postsynaptic neuron declares ‘yes’ and it fires If the tally is not large enough, the postsynaptic neuron says ‘no’ and does not fire. ...
... vote has some positive value (= 1 in simplest model). If tally is large enough, postsynaptic neuron declares ‘yes’ and it fires If the tally is not large enough, the postsynaptic neuron says ‘no’ and does not fire. ...
What are Neurons
... Interneurons are responsible for communicating information between different neurons in the body. ...
... Interneurons are responsible for communicating information between different neurons in the body. ...
Ch. 3 S. 1
... • ___________________ nervous system – consists of the brain and the spinal cord. • ____________________________ nervous system – made up of nerve cells that send messages between the central nervous system and all the parts of the ____________. Neurons Nerve cells, called __________________, run th ...
... • ___________________ nervous system – consists of the brain and the spinal cord. • ____________________________ nervous system – made up of nerve cells that send messages between the central nervous system and all the parts of the ____________. Neurons Nerve cells, called __________________, run th ...
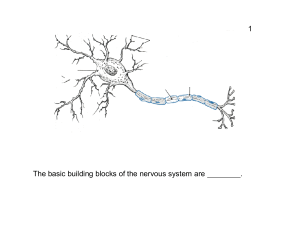
The basic building blocks of the nervous system are . 1
... The peripheral nervous system is connect to your brain and your brainstem, which is also known as ...
... The peripheral nervous system is connect to your brain and your brainstem, which is also known as ...