Bite Me!
... and a muscle cell • Neurotransmitters from the axon send signals to the muscle • Synapses can form between two neurons, or between a neuron and another type of cell ...
... and a muscle cell • Neurotransmitters from the axon send signals to the muscle • Synapses can form between two neurons, or between a neuron and another type of cell ...
Sensory Pathways
... receptor (free nerve endings for both nociception and thermoception). Central process enters the spinal cord in the Zone of Lissauer (posterolateral funiculus) by way of the lat. div. of dorsal root and terminates in the dorsal grey horn. Thinly myelinated (Ad) fibers (for fast sharp pain) and unm ...
... receptor (free nerve endings for both nociception and thermoception). Central process enters the spinal cord in the Zone of Lissauer (posterolateral funiculus) by way of the lat. div. of dorsal root and terminates in the dorsal grey horn. Thinly myelinated (Ad) fibers (for fast sharp pain) and unm ...
Outline10 Action Potl
... - voltage-gated Na+ channels open activation gate opens in response to initial depolarization → rapid Na+ inflow → depolarization → more activation gates open (positive feedback) 2. Repolarization (falling) phase - voltage-gated Na+ channels close inactivation gate closes when depolarization reaches ...
... - voltage-gated Na+ channels open activation gate opens in response to initial depolarization → rapid Na+ inflow → depolarization → more activation gates open (positive feedback) 2. Repolarization (falling) phase - voltage-gated Na+ channels close inactivation gate closes when depolarization reaches ...
Respiratory and Nervous Systems
... receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. Depolarization occurs on the postsynaptic membrane if threshold is reached. The neurotransmitter is destroyed by an enzyme (ex. acetylcholinesterase) or reabsorbed back into the presynaptic membrane. ...
... receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. Depolarization occurs on the postsynaptic membrane if threshold is reached. The neurotransmitter is destroyed by an enzyme (ex. acetylcholinesterase) or reabsorbed back into the presynaptic membrane. ...
Brain - People
... • What if a neuron works like an antenna ? • If so the neuron-neuron interaction is coming from the electromagnetic field emitted and received by each neuron • A mean-field approach is likely to be valid, due to the close proximity of a large number of neuron and the slow decay of the electromagneti ...
... • What if a neuron works like an antenna ? • If so the neuron-neuron interaction is coming from the electromagnetic field emitted and received by each neuron • A mean-field approach is likely to be valid, due to the close proximity of a large number of neuron and the slow decay of the electromagneti ...
The Electrotonic Transformation: a Tool for Relating Neuronal Form
... membrane into discrete resistances and capacitances, we determine the elements of these equivalent T circuits directly from complex impedance functions that we derived from the impulse response of a finite cable (Tsai et al. 1994). Since each segment is treated as a cable rather than an isopotential ...
... membrane into discrete resistances and capacitances, we determine the elements of these equivalent T circuits directly from complex impedance functions that we derived from the impulse response of a finite cable (Tsai et al. 1994). Since each segment is treated as a cable rather than an isopotential ...
Eagleman Ch 3. Neurons and Synapses
... outside world are encoded by different neurons. Population coding is the idea that each stimulus is represented by a collection of neurons. ...
... outside world are encoded by different neurons. Population coding is the idea that each stimulus is represented by a collection of neurons. ...
Fill in the blanks on LB page 67-68.
... c. Norepinephrine affects brain regions concerned with emotions, dreaming, and awaking. d. Dopamine and GABA are other neurotransmitters that are present in different parts of the brain. e. Two debilitating diseases, Parkinson's and Alzheimer's, are testimony to the effects that the loss of neurotr ...
... c. Norepinephrine affects brain regions concerned with emotions, dreaming, and awaking. d. Dopamine and GABA are other neurotransmitters that are present in different parts of the brain. e. Two debilitating diseases, Parkinson's and Alzheimer's, are testimony to the effects that the loss of neurotr ...
THERIGHTBRAINPOWERPOINT
... charge of about -40mv to -90mv, typically averaging about a -70mv charge. The neuron is inactive at resting potential and contains chloride ions. An Action Potential is a brief shift in the neurons electrical charge that travels along an axon. During an action potential the charge of the neuron be ...
... charge of about -40mv to -90mv, typically averaging about a -70mv charge. The neuron is inactive at resting potential and contains chloride ions. An Action Potential is a brief shift in the neurons electrical charge that travels along an axon. During an action potential the charge of the neuron be ...
PDF
... 2000). The parameter sets used are reported in Tables 1 through 3 (see the appendix). The files used to implement voltage-dependent mechanisms, as indicated in the tables, are freely available online from the NEURON web page (http://www.neuron.yale.edu). For the cell as a whole, we tune the paramete ...
... 2000). The parameter sets used are reported in Tables 1 through 3 (see the appendix). The files used to implement voltage-dependent mechanisms, as indicated in the tables, are freely available online from the NEURON web page (http://www.neuron.yale.edu). For the cell as a whole, we tune the paramete ...
Simulation of myelinated neuron with focus on conduction speed
... Myelin sheath is a protective coat around the axon of a neuron and acts as an insulator to the electrical signal that is conducted down the axon as a neuron fires. This increases the conduction speed of action potential and thus is a critical factor in maintaining the proper communication within the ...
... Myelin sheath is a protective coat around the axon of a neuron and acts as an insulator to the electrical signal that is conducted down the axon as a neuron fires. This increases the conduction speed of action potential and thus is a critical factor in maintaining the proper communication within the ...
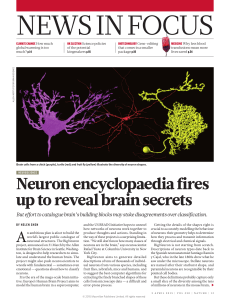
Neuron encyclopaedia fires up to reveal brain secrets
... are willing to pay loss and damages to countries that bear the brunt of the impacts,” she says. “Vulnerable countries have no other leverage within this political process.” The history of the 2 °C goal extends back four decades. At the time, researchers argued that it would be wise to keep Earth’s a ...
... are willing to pay loss and damages to countries that bear the brunt of the impacts,” she says. “Vulnerable countries have no other leverage within this political process.” The history of the 2 °C goal extends back four decades. At the time, researchers argued that it would be wise to keep Earth’s a ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 11-07
... o When receptors synapse in spinal cord, many receptors converge; therefore, spinal cord neuron receptive fields are much more complex Adapation – reduction in sensation with repeated stimulation; some receptors adapt whereas other do not o Slowly adapting receptors respond through the stimulus du ...
... o When receptors synapse in spinal cord, many receptors converge; therefore, spinal cord neuron receptive fields are much more complex Adapation – reduction in sensation with repeated stimulation; some receptors adapt whereas other do not o Slowly adapting receptors respond through the stimulus du ...
BOX 2.2 CAJAL: ICONOCLAST TO ICON Santiago Ramón y Cajal
... Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852–1934) is considered by many people to be the founder of modern neuroscience— a peer of Darwin and Pasteur in nineteenth-century biology. He was born in the tiny Spanish village of Petilla de Aragon on May 1, 1852, and as related in his delightful autobiography, he was so ...
... Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852–1934) is considered by many people to be the founder of modern neuroscience— a peer of Darwin and Pasteur in nineteenth-century biology. He was born in the tiny Spanish village of Petilla de Aragon on May 1, 1852, and as related in his delightful autobiography, he was so ...
PowerPoint
... interact with each other: Activity: certain activity patterns are produced by a given network in response to input signals Connectivity: synaptic weights are modified in response to neuronal signals in the activity patterns ...
... interact with each other: Activity: certain activity patterns are produced by a given network in response to input signals Connectivity: synaptic weights are modified in response to neuronal signals in the activity patterns ...
chapter1
... • Poisson + refractory period accounts for much data but – Does not account difference in vitro and in vivo: neurons are not Poisson generators – Accuracy of timing (between trials) often higher than Poisson – Variance of ISI often higher than Poisson – Bursting behavior ...
... • Poisson + refractory period accounts for much data but – Does not account difference in vitro and in vivo: neurons are not Poisson generators – Accuracy of timing (between trials) often higher than Poisson – Variance of ISI often higher than Poisson – Bursting behavior ...
The Nervous System
... Synaptic gap/synaptic cleft: the tiny gap at the synapse in which neurotransmitters cross. Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. When released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving ...
... Synaptic gap/synaptic cleft: the tiny gap at the synapse in which neurotransmitters cross. Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. When released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving ...
Visual categorization shapes feature selectivity in the primate
... Red circles : Neurons with statistically significant selectivity for diagnostic dimension only Blue circles : Neurons with significant selectivity for diagnostic and non-diagnostic feature Black triangles : Neurons with no significant selectivity Red star : Example neuron depicted in previous figure ...
... Red circles : Neurons with statistically significant selectivity for diagnostic dimension only Blue circles : Neurons with significant selectivity for diagnostic and non-diagnostic feature Black triangles : Neurons with no significant selectivity Red star : Example neuron depicted in previous figure ...
PET (positron emission tomography): measures the different levels
... Synaptic gap/synaptic cleft: the tiny gap at the synapse in which neurotransmitters cross. Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. When released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving ...
... Synaptic gap/synaptic cleft: the tiny gap at the synapse in which neurotransmitters cross. Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. When released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving ...
Nervous System
... Always the same regardless of stimulus The underlying functional feature of the nervous system ...
... Always the same regardless of stimulus The underlying functional feature of the nervous system ...
The First Open International Symposium
... Then, how is the spatial gradient detected in klinotaxis? Because worms sense chemicals at one point at the anterior end of the body, comparison between two sensors is unlikely. By stimulating the sensory neuron by using chanelrhodopsin in synchrony with head swing, it was suggested that spatial gra ...
... Then, how is the spatial gradient detected in klinotaxis? Because worms sense chemicals at one point at the anterior end of the body, comparison between two sensors is unlikely. By stimulating the sensory neuron by using chanelrhodopsin in synchrony with head swing, it was suggested that spatial gra ...