Nervous Sys Learning targets
... 1. List the basic functions of the nervous system 2. draw a concept map to show the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system 3. List the types of neuroglia and cite their functions ...
... 1. List the basic functions of the nervous system 2. draw a concept map to show the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system 3. List the types of neuroglia and cite their functions ...
2015-2016_1Semester_Exam1_050116
... extrapyramidal commands, the basal ganglia system hires the extrapyramidal (?) system. The striatum and the pallidum surround an important passageway of the brain called internal capsule. In the knee region of this structure, the vulnerable descending corticobulbar tract. exist. In its posterior win ...
... extrapyramidal commands, the basal ganglia system hires the extrapyramidal (?) system. The striatum and the pallidum surround an important passageway of the brain called internal capsule. In the knee region of this structure, the vulnerable descending corticobulbar tract. exist. In its posterior win ...
Chp 9: Nervous tissue chp 11: autonomic nervous system chp 12
... decrease and increase the membrane potential and eventually restore it to its resting state Ability of muscle fibers and neurons to convert stimuli into action potential is called electrical excitability. Stimulus in cell’s environment changes resting membrane potential; if stimulus causes cell to d ...
... decrease and increase the membrane potential and eventually restore it to its resting state Ability of muscle fibers and neurons to convert stimuli into action potential is called electrical excitability. Stimulus in cell’s environment changes resting membrane potential; if stimulus causes cell to d ...
Supplementary Information 1 (doc 48K)
... shuttle plasmid (pCR 2.1, Invitrogen). Plasmids were transformed into DH5α competent cells and grown in LB broth (Invitrogen). DNA miniprep (Qiagen) was performed to obtain DNA and sent for sequencing (University of Miami Oncogenomics Core Facility). BLAT search was performed against the mouse genom ...
... shuttle plasmid (pCR 2.1, Invitrogen). Plasmids were transformed into DH5α competent cells and grown in LB broth (Invitrogen). DNA miniprep (Qiagen) was performed to obtain DNA and sent for sequencing (University of Miami Oncogenomics Core Facility). BLAT search was performed against the mouse genom ...
1. What type of joint do the capitulum of the humerus
... neural cell membrane is due to: a) actions of the Sodium/Potassium pump b) sodium leakage channels c) selective permeability of the membrane to potassium d) both a and c e) all of the above 44. Which of the following statements regarding graded potentials (as compared to action potentials) is not tr ...
... neural cell membrane is due to: a) actions of the Sodium/Potassium pump b) sodium leakage channels c) selective permeability of the membrane to potassium d) both a and c e) all of the above 44. Which of the following statements regarding graded potentials (as compared to action potentials) is not tr ...
peripheral nervous system
... impulses from CNS to effectors (muscles and glands) -Interneurons (association neurons) provide more complex reflexes and associative functions (learning and memory) ...
... impulses from CNS to effectors (muscles and glands) -Interneurons (association neurons) provide more complex reflexes and associative functions (learning and memory) ...
4.BiologicalPsycholo..
... FIGURE 2.2 Electrical probes placed inside and outside an axon measure its activity. (The scale is exaggerated here. Such measurements require ultra-small electrodes, as described later in this chapter.) The inside of an axon at rest is about -60 to -70 millivolts, compared with the outside. Electro ...
... FIGURE 2.2 Electrical probes placed inside and outside an axon measure its activity. (The scale is exaggerated here. Such measurements require ultra-small electrodes, as described later in this chapter.) The inside of an axon at rest is about -60 to -70 millivolts, compared with the outside. Electro ...
File - kilbane science
... http://www.dummies.com/howto/content/understanding-the-transmission-of-nerveimpulses.html ...
... http://www.dummies.com/howto/content/understanding-the-transmission-of-nerveimpulses.html ...
Structure of the Nervous System
... •Neurons link together to form neural circuits which perform special tasks. Many of these are reflexes. •Signaling within these circuits gives rise to higher cognitive functions, such as thinking. •Since circuits are needed for even the most basic function, it has been suggested that the functional ...
... •Neurons link together to form neural circuits which perform special tasks. Many of these are reflexes. •Signaling within these circuits gives rise to higher cognitive functions, such as thinking. •Since circuits are needed for even the most basic function, it has been suggested that the functional ...
The Nervous System
... Name the two main divisions of the nervous system Identify the CNS and PNS on a diagram of the body's Nervous System Explain the term receptor Describe the structure and function of a neuron, with reference only to cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cell, and neurotransmitter vesicle ...
... Name the two main divisions of the nervous system Identify the CNS and PNS on a diagram of the body's Nervous System Explain the term receptor Describe the structure and function of a neuron, with reference only to cell body, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cell, and neurotransmitter vesicle ...
Document
... ions to the outside. The phosphorylated form of the pump has a low affinity for Na+ ions, so they are released. • The pump binds 2 extracellular K+ ions. This causes the dephosphorylation of the pump, reverting it to its previous conformational state, transporting the K+ ions into the cell. • The un ...
... ions to the outside. The phosphorylated form of the pump has a low affinity for Na+ ions, so they are released. • The pump binds 2 extracellular K+ ions. This causes the dephosphorylation of the pump, reverting it to its previous conformational state, transporting the K+ ions into the cell. • The un ...
Chapter 2
... – Synaptic bulb (knob) – rounded area on the end of the axon terminal – Synaptic cleft (gap)– space between bulb of one cell and the dendrite of another – Receptor sites- holes is surface of dendrite; shaped to receive certain neurotransmitters – Neurotransmitters – chemicals in the synaptic vesicle ...
... – Synaptic bulb (knob) – rounded area on the end of the axon terminal – Synaptic cleft (gap)– space between bulb of one cell and the dendrite of another – Receptor sites- holes is surface of dendrite; shaped to receive certain neurotransmitters – Neurotransmitters – chemicals in the synaptic vesicle ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 4. What other cell parts are housed in this main area? nucleus, nucleolus, all other cellular organelles 5. The nerve processes that conduct the impulse/action potential away from the cell body are called ___axons___________. 6. The part of a nerve cell that receives impulses and carries them toward ...
... 4. What other cell parts are housed in this main area? nucleus, nucleolus, all other cellular organelles 5. The nerve processes that conduct the impulse/action potential away from the cell body are called ___axons___________. 6. The part of a nerve cell that receives impulses and carries them toward ...
Ch 4: Synaptic Transmission
... releases NT that bind with receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, to transmit the signal from one neuron to the next When the NT bind with the postsynaptic neuron, they have either of 2 effects 1. Depolarize the membrane ...
... releases NT that bind with receptors on the postsynaptic neuron, to transmit the signal from one neuron to the next When the NT bind with the postsynaptic neuron, they have either of 2 effects 1. Depolarize the membrane ...
Chapter 12: Nervous Tissue
... – in resting membrane, inactivation gate of sodium channel is open & activation gate is closed (Na+ can not get in) – when threshold (-55mV) is reached, both open & Na+ enters – inactivation gate closes again in few ten-thousandths of second – only a total of 20,000 Na+ actually enter the cell, but ...
... – in resting membrane, inactivation gate of sodium channel is open & activation gate is closed (Na+ can not get in) – when threshold (-55mV) is reached, both open & Na+ enters – inactivation gate closes again in few ten-thousandths of second – only a total of 20,000 Na+ actually enter the cell, but ...
File
... -- if an action potential is generated, it will originate within the axon hillock, which will then pass the signal on to the axon. -- the axon carries the action potential from the cell body/axon hillock to its bulb-like synaptic endings (located at the end of an axon). -- axons are typically long, ...
... -- if an action potential is generated, it will originate within the axon hillock, which will then pass the signal on to the axon. -- the axon carries the action potential from the cell body/axon hillock to its bulb-like synaptic endings (located at the end of an axon). -- axons are typically long, ...
Slide ()
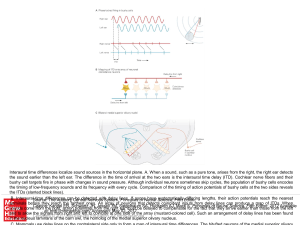
... bushy cell targets fire in phase with changes in sound pressure. Although individual neurons sometimes skip cycles, the population of bushy cells encodes the timing of low-frequency sounds and its frequency with every cycle. Comparison of the timing of action potentials of bushy cells at the two sid ...
... bushy cell targets fire in phase with changes in sound pressure. Although individual neurons sometimes skip cycles, the population of bushy cells encodes the timing of low-frequency sounds and its frequency with every cycle. Comparison of the timing of action potentials of bushy cells at the two sid ...
Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport
... molecule to pass through the membrane. Gated channels have a binding site that is specific for a given molecule or ion. A stimulus causes the "gate" to open or shut. The stimulus may be chemical or electrical signals, temperature, or mechanical force, depending on the type of gated channel. For exam ...
... molecule to pass through the membrane. Gated channels have a binding site that is specific for a given molecule or ion. A stimulus causes the "gate" to open or shut. The stimulus may be chemical or electrical signals, temperature, or mechanical force, depending on the type of gated channel. For exam ...
Biology 118 - Exam 2
... 36. The “background” firing rate of action potentials (#/min.) in the CNS will ____ if the blood plasma drops below normal, to pH = 7.25. a. increase b. be impossible c. decrease * d. remain constant 37. A neurotransmitter that opens Cl- channels in a neuron will produce _________. a. no change in t ...
... 36. The “background” firing rate of action potentials (#/min.) in the CNS will ____ if the blood plasma drops below normal, to pH = 7.25. a. increase b. be impossible c. decrease * d. remain constant 37. A neurotransmitter that opens Cl- channels in a neuron will produce _________. a. no change in t ...
Biology of Humans 2/e
... The signal passes across the synaptic cleft as a chemical called neurotransmitter which is released from vesicles by exocytosis. Neurotransmitter is a chemical that is secreted into a synaptic cleft by a neuron that affects another neuron or an effector by binding with receptors on it. The sending c ...
... The signal passes across the synaptic cleft as a chemical called neurotransmitter which is released from vesicles by exocytosis. Neurotransmitter is a chemical that is secreted into a synaptic cleft by a neuron that affects another neuron or an effector by binding with receptors on it. The sending c ...
Activity Overview - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
... The brain, like all organs of the body, is made up of cells. The brain is made of many types of cells. In Activity 1C, students learned about three types of cells found in the nervous system. These cells are – neurons, glial cells, and microglial cells (a specialized type of macrophage cell). In thi ...
Cell Membranes
... of movement is always with the concentration gradient, never against the gradient. B. The carrier molecule is nonspecific to the molecule that is transported. The direction of movement is always with the concentration gradient, never against the gradient. C. The carrier molecule is nonspecific to th ...
... of movement is always with the concentration gradient, never against the gradient. B. The carrier molecule is nonspecific to the molecule that is transported. The direction of movement is always with the concentration gradient, never against the gradient. C. The carrier molecule is nonspecific to th ...
Neurotechnique Targeted Whole-Cell Recordings in the Mammalian
... close contact. However, seal formation between the targeted neuron and the patch pipette was almost never successful under strong illumination. One possible reason for the failure of seal formation could be photodamage of the targeted neuron or photo-chemical interactions between the laser and the i ...
... close contact. However, seal formation between the targeted neuron and the patch pipette was almost never successful under strong illumination. One possible reason for the failure of seal formation could be photodamage of the targeted neuron or photo-chemical interactions between the laser and the i ...
Hair cells
... Axon nerve endings respond to stimuli...Axon nerve endings are not dendrites!!! And they can be afferent or efferent -Exteroceptors -Interoceptors 1. Mechanoreceptors are stimulated by mechanical forces such as pressure 2. Chemoreceptors detect chemicals or chemical changes 3. Energy-detecting recep ...
... Axon nerve endings respond to stimuli...Axon nerve endings are not dendrites!!! And they can be afferent or efferent -Exteroceptors -Interoceptors 1. Mechanoreceptors are stimulated by mechanical forces such as pressure 2. Chemoreceptors detect chemicals or chemical changes 3. Energy-detecting recep ...
20-NervousSystem
... of the brain that results in dementia Parkinson’s disease – degeneration of the dopaminereleasing neurons of the substantia nigra Huntington’s disease – a fatal hereditary disorder caused by accumulation of the protein huntingtin that leads to degeneration of the basal nuclei ...
... of the brain that results in dementia Parkinson’s disease – degeneration of the dopaminereleasing neurons of the substantia nigra Huntington’s disease – a fatal hereditary disorder caused by accumulation of the protein huntingtin that leads to degeneration of the basal nuclei ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.