UNIT 3
... A cell that is not being stimulated to send an impulse is in a resting state. Factors that contribute to resting membrane potential include unequal distribution of ions across the plasma membrane (high concentration of sodium ions outside the cell and a high concentration of potassium inside), or a ...
... A cell that is not being stimulated to send an impulse is in a resting state. Factors that contribute to resting membrane potential include unequal distribution of ions across the plasma membrane (high concentration of sodium ions outside the cell and a high concentration of potassium inside), or a ...
The Nervous System
... LO 3.45 The student is able to describe how nervous systems transmit information. LO 3.46 The student is able to describe how the vertebrate brain integrates information to produce a response. LO 3.47 The student is able to create a visual representation of complex nervous systems to describe/explai ...
... LO 3.45 The student is able to describe how nervous systems transmit information. LO 3.46 The student is able to describe how the vertebrate brain integrates information to produce a response. LO 3.47 The student is able to create a visual representation of complex nervous systems to describe/explai ...
Passive Conduction - Cable Theory
... the electrical constants of the dendrites. The first measurements were made some time after equivalent experiments were carried out on squid axons. The dendrites are much smaller in stature; therefore, more refined measurement techniques were necessary. Eventually measurements of rc , rm , and cm we ...
... the electrical constants of the dendrites. The first measurements were made some time after equivalent experiments were carried out on squid axons. The dendrites are much smaller in stature; therefore, more refined measurement techniques were necessary. Eventually measurements of rc , rm , and cm we ...
BGYB30 Mammalian Physiology • Today: • Next Lecture:
... I use fruit flies as a model system to study the molecular mechanisms used in neural function and development ...
... I use fruit flies as a model system to study the molecular mechanisms used in neural function and development ...
Cell Communication
... One signal-activated receptor activates another protein, which activates another molecule, etc., etc. These act as relay molecules Often the message is transferred using protein kinases, which transfer phosphate groups from ATP molecules to proteins ...
... One signal-activated receptor activates another protein, which activates another molecule, etc., etc. These act as relay molecules Often the message is transferred using protein kinases, which transfer phosphate groups from ATP molecules to proteins ...
Powerpoint version
... diffusion of Na+ in K+ would diffuse until it is balanced by its electrical gradient EK+ = –90 mV ...
... diffusion of Na+ in K+ would diffuse until it is balanced by its electrical gradient EK+ = –90 mV ...
Slides - gserianne.com
... • absolute - time when threshold stimulus does not start another action potential (Na+ channels inactivated) • relative – time when stronger threshold stimulus can start another action potential (Na+ channels restored, K+ channels begin ...
... • absolute - time when threshold stimulus does not start another action potential (Na+ channels inactivated) • relative – time when stronger threshold stimulus can start another action potential (Na+ channels restored, K+ channels begin ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous System – Homework – Part I
... your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contrast dendrites and axons. 4. Discuss how the following relate to each other: presynaptic cell, postsynaptic cell, synapse, neurotransmitter. 5. Des ...
... your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contrast dendrites and axons. 4. Discuss how the following relate to each other: presynaptic cell, postsynaptic cell, synapse, neurotransmitter. 5. Des ...
Neurons
... nervous system that is also known as a nerve cell. Neurons are responsible for sending impulse messages to other neural cells. Impulse messages in a neuron are sent via the release of neurotransmitters. The neuron's cell body is called the soma. The neuron cell consists of 3 main sections a soma, ax ...
... nervous system that is also known as a nerve cell. Neurons are responsible for sending impulse messages to other neural cells. Impulse messages in a neuron are sent via the release of neurotransmitters. The neuron's cell body is called the soma. The neuron cell consists of 3 main sections a soma, ax ...
No Slide Title
... Muscle contraction mechanisms: recruitment : activation of an increasing number of motor units within a muscle on contraction ...
... Muscle contraction mechanisms: recruitment : activation of an increasing number of motor units within a muscle on contraction ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
here
... 4. What are three types of information that neurons must process? What does each type allow us to do? ...
... 4. What are three types of information that neurons must process? What does each type allow us to do? ...
Midterm 1 - studyfruit
... ● Always one nerve, but either three signals at different points at same time (parallel) or three signals at same point one after another (in sequence) ■ IPSP ● (inhibitory post synaptic potential) ● Analogous to above, NT can open channels that cause cell membrane potential to drop, thus inhibiting ...
... ● Always one nerve, but either three signals at different points at same time (parallel) or three signals at same point one after another (in sequence) ■ IPSP ● (inhibitory post synaptic potential) ● Analogous to above, NT can open channels that cause cell membrane potential to drop, thus inhibiting ...
Nervous System Worksheet
... A. Nerves of the eyes that allow us to see what is above, below and to the sides of a focused object (peripheral vision). B. The collective name for nerve tissue outside of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). C. The nerves of the fingers, toes, nose-tip and other areas around the per ...
... A. Nerves of the eyes that allow us to see what is above, below and to the sides of a focused object (peripheral vision). B. The collective name for nerve tissue outside of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). C. The nerves of the fingers, toes, nose-tip and other areas around the per ...
Time Zones
... 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes are found in segments of them! 7. This is the mechanism that allows evolution to occur. It inv ...
... 3. Name the main function of the Myelin Sheath? 4. Name the 3 types of Neurons: 5. One word to describe all of a human’s cell nuclei (in regards to genetics)? 6. These long threads make a chromosome. Genes are found in segments of them! 7. This is the mechanism that allows evolution to occur. It inv ...
File
... and metabolism within nerve cells Neurons: Cells responsible for conducting electrochemical messages throughout the body ...
... and metabolism within nerve cells Neurons: Cells responsible for conducting electrochemical messages throughout the body ...
Nervous System Notes
... knob, causing release of calcium ions to diffuse into the knob Increased calcium concentrations trigger the release of neurotransmitters via exocytosis Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptor molecules causing ion channels to open This causes postsynaptic poten ...
... knob, causing release of calcium ions to diffuse into the knob Increased calcium concentrations trigger the release of neurotransmitters via exocytosis Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to receptor molecules causing ion channels to open This causes postsynaptic poten ...
Human Body Systems
... Part II: Relaying the Message (Partners) You will create a flow map of how the nervous system and body interact from the time of seeing a cockroach to your reaction (stepping on it, running, picking it up) Please read the full instructions – you need to use linking words and pictures! ...
... Part II: Relaying the Message (Partners) You will create a flow map of how the nervous system and body interact from the time of seeing a cockroach to your reaction (stepping on it, running, picking it up) Please read the full instructions – you need to use linking words and pictures! ...
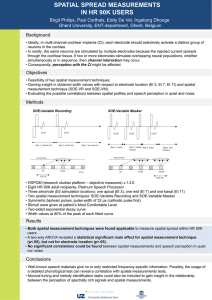
Spatial Spread Measurements in HR 90K users
... • Ideally, in multi-channel cochlear implants (CI), each electrode should selectively activate a distinct group of neurons in the cochlea. • In reality, the same neurons are stimulated by multiple electrodes because the injected current spreads through the cochlear tissue. If two or more electrodes ...
... • Ideally, in multi-channel cochlear implants (CI), each electrode should selectively activate a distinct group of neurons in the cochlea. • In reality, the same neurons are stimulated by multiple electrodes because the injected current spreads through the cochlear tissue. If two or more electrodes ...
Chapter 11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... ______6. A major subdivision of the nervous system that serves as the communication lines, linking all parts of the body to the CNS. 3. This exercise emphasizes the difference between neurons and neuroglia. Indicate which cell type is identified by the following descriptions. A. Neurons B. Neuroglia ...
... ______6. A major subdivision of the nervous system that serves as the communication lines, linking all parts of the body to the CNS. 3. This exercise emphasizes the difference between neurons and neuroglia. Indicate which cell type is identified by the following descriptions. A. Neurons B. Neuroglia ...
M.learning.hccs.edu
... A) 1 intracellular sodium ion for 2 extracellular potassium ions. B) 2 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. C) 3 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. D) 3 intracellular sodium ions for 2 extracellular potassium ions. E) 3 extracellular sodium ions for ...
... A) 1 intracellular sodium ion for 2 extracellular potassium ions. B) 2 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. C) 3 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. D) 3 intracellular sodium ions for 2 extracellular potassium ions. E) 3 extracellular sodium ions for ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.