The Nervous System (Chapter 7)
... 26. What type of pump helps restore the neurons during repolarization? __________________________________ 27. The faster type of impulse propagation occurs in myelinated fibers and is called _________________________. 28. List a few of the factors that can impair the conduction of impulses. ...
... 26. What type of pump helps restore the neurons during repolarization? __________________________________ 27. The faster type of impulse propagation occurs in myelinated fibers and is called _________________________. 28. List a few of the factors that can impair the conduction of impulses. ...
NeuralCell-Neurons.stud
... Neurons differ from Other Cells 1. Neurons have specialized projections called dendrites and axons. Dendrites take information to the cell body and axons take information away from the cell body 2. Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process 3. Neurons contain some specia ...
... Neurons differ from Other Cells 1. Neurons have specialized projections called dendrites and axons. Dendrites take information to the cell body and axons take information away from the cell body 2. Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process 3. Neurons contain some specia ...
File
... Overview of the Nervous System • STRUCTURES: brain, spinal cord, & peripheral nerves • FUNCTION: Recognizes and coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environments ...
... Overview of the Nervous System • STRUCTURES: brain, spinal cord, & peripheral nerves • FUNCTION: Recognizes and coordinates the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environments ...
Neural Pathways and Transmission
... Ion channels specific for sodium open within the cell membrane, allowing sodium to move into the neuron This causes a very temporary reversal in charges, in which the interior is now positively charged, and the exterior is negatively charged Internal environment is, on average, 30 mV at this state T ...
... Ion channels specific for sodium open within the cell membrane, allowing sodium to move into the neuron This causes a very temporary reversal in charges, in which the interior is now positively charged, and the exterior is negatively charged Internal environment is, on average, 30 mV at this state T ...
暨 南 大 学 考 试 试 卷
... 13) The incorrect statement about the propagation of action potentials is that B A. An action potential elicited at any point of the membrane can excite adjacent portions of the membrane. B. It propagates to the entire membrane with certain diminishment of its amplitude. C. It propagates via the loc ...
... 13) The incorrect statement about the propagation of action potentials is that B A. An action potential elicited at any point of the membrane can excite adjacent portions of the membrane. B. It propagates to the entire membrane with certain diminishment of its amplitude. C. It propagates via the loc ...
Cell membranes - Brian Whitworth
... Lipids in a bi-layer – what is this? Proteins embedded in lipid layer (called transmembrane proteins) Proteins floating within the lipid sea (called integral proteins) Proteins associated outside the lipid bi-layer (peripheral proteins). ...
... Lipids in a bi-layer – what is this? Proteins embedded in lipid layer (called transmembrane proteins) Proteins floating within the lipid sea (called integral proteins) Proteins associated outside the lipid bi-layer (peripheral proteins). ...
File
... cell, thereby leaving a negative charge inside the cell causing the membrane to become more negative. ...
... cell, thereby leaving a negative charge inside the cell causing the membrane to become more negative. ...
ppt - UTK-EECS
... calculation. This project proved an abortion, but it brought another climax to AI research and NN research. ...
... calculation. This project proved an abortion, but it brought another climax to AI research and NN research. ...
Slide ()
... The activity of functionally distinct parietal motor neurons varies with the purpose of a grasping action. (Modified, with permission, from Fogassi et al. ...
... The activity of functionally distinct parietal motor neurons varies with the purpose of a grasping action. (Modified, with permission, from Fogassi et al. ...
RESTING MEMBRANE POTENTIALS
... The role of Ion channels The ion channels can be of 2 main types: 1. Leak channels: Include ion channels specific for Na+, K+, Cl- etc. As long as the size of the ion is appropriate, the ion will go through them. 2. Gated channels: The gates are part of the protein channel and can open or close in ...
... The role of Ion channels The ion channels can be of 2 main types: 1. Leak channels: Include ion channels specific for Na+, K+, Cl- etc. As long as the size of the ion is appropriate, the ion will go through them. 2. Gated channels: The gates are part of the protein channel and can open or close in ...
Cell Transportation - Ursuline High School
... by surface proteins and pushed’ or pulled, into the cell…. Because they are forced, the ions can flow, if necessary, against the concentration gradient.... The ions can even flow through like electrical charges on the plasma membrane. ...
... by surface proteins and pushed’ or pulled, into the cell…. Because they are forced, the ions can flow, if necessary, against the concentration gradient.... The ions can even flow through like electrical charges on the plasma membrane. ...
Nerve Cell Physiology
... 4. Voltage-gated K+ channels open in response to the depolarization, but since their kinetics are much slower, the inward Na+ current (upstroke of the action potential) dominates initially. 5. K+ conductance begins to rise as more channels open. As the rise in membrane potential approaches its peak, ...
... 4. Voltage-gated K+ channels open in response to the depolarization, but since their kinetics are much slower, the inward Na+ current (upstroke of the action potential) dominates initially. 5. K+ conductance begins to rise as more channels open. As the rise in membrane potential approaches its peak, ...
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... inward from the extracellular fluid. 9. The calcium inside the synaptic knob initiates a series of events that causes the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the cell membrane, releasing the neurotransmitter by exocytosis. B. Synaptic Transmission 1. Released neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic ...
... inward from the extracellular fluid. 9. The calcium inside the synaptic knob initiates a series of events that causes the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the cell membrane, releasing the neurotransmitter by exocytosis. B. Synaptic Transmission 1. Released neurotransmitters diffuse across the synaptic ...
05_Boyle_compiled
... a. 10x greater Na+ outside, 20x greater K+ inside; -70 mV potential difference b. 10x greater K+ outside, 20x greater Na+ inside; -70 mV potential difference c. 20x greater Na+ outside, 10x greater K+ inside; -70 mV potential difference d. 20x greater K+ outside, 20x greater Na+ inside; -70 mV poten ...
... a. 10x greater Na+ outside, 20x greater K+ inside; -70 mV potential difference b. 10x greater K+ outside, 20x greater Na+ inside; -70 mV potential difference c. 20x greater Na+ outside, 10x greater K+ inside; -70 mV potential difference d. 20x greater K+ outside, 20x greater Na+ inside; -70 mV poten ...
Chapter 7 Membrane Structure and Function
... - Active transport moves substances against their concentration gradient and requires energy, usually in the form of ATP. - The sodium-potassium pump is one type of active transport system. B. Maintenance of Membrane Potential by Ion Pumps - Membrane potential is the voltage (electrical potential en ...
... - Active transport moves substances against their concentration gradient and requires energy, usually in the form of ATP. - The sodium-potassium pump is one type of active transport system. B. Maintenance of Membrane Potential by Ion Pumps - Membrane potential is the voltage (electrical potential en ...
Nerve Impulses ppt
... K+ moving out of the cell (closes Na+ gates) Depolarization occurs in a small area Affects adjacent gates ▪ Creates “wave” of electricity ▪ Travels length of axon ...
... K+ moving out of the cell (closes Na+ gates) Depolarization occurs in a small area Affects adjacent gates ▪ Creates “wave” of electricity ▪ Travels length of axon ...
Neurons and Nervous System
... Figure 44.7 Which Ion Channel Creates the Resting Potential? (Part 1) ...
... Figure 44.7 Which Ion Channel Creates the Resting Potential? (Part 1) ...
Document
... propagating them and synaptic transmission 14.Primarily engaged with conduction and transmission ...
... propagating them and synaptic transmission 14.Primarily engaged with conduction and transmission ...
Slide ()
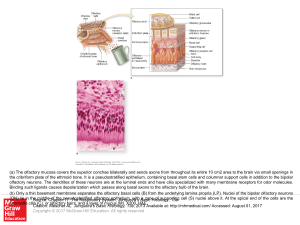
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
Ch. 10 Outline
... B. A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon C. All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength Refractory Period A. Absolute Refractory Period 1. Time when threshold stimulus does not start another action potential B. Relative Refra ...
... B. A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon C. All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength Refractory Period A. Absolute Refractory Period 1. Time when threshold stimulus does not start another action potential B. Relative Refra ...
axonal terminals
... 1. Polarization of the neuron's membrane: Sodium is on the outside, and potassium is on the inside. • When a neuron is not stimulated — it's just sitting with no impulse to carry or transmit — its membrane is polarized. • Being polarized means that the electrical charge on the outside of the membran ...
... 1. Polarization of the neuron's membrane: Sodium is on the outside, and potassium is on the inside. • When a neuron is not stimulated — it's just sitting with no impulse to carry or transmit — its membrane is polarized. • Being polarized means that the electrical charge on the outside of the membran ...
Communication within the Nervous System
... The Neural Membrane • Moves 3 Na+ outside for every 2 K+ inside ...
... The Neural Membrane • Moves 3 Na+ outside for every 2 K+ inside ...
External anatomy of the ear
... Sectional View of the Cochlear as it will appear on a microscope slide ...
... Sectional View of the Cochlear as it will appear on a microscope slide ...
Slide 1
... gestation the first brain cells, the neurons, are already forming at an astonishing rate: 250,000 every minute. ► Billions of neurons will form links with billions of other neurons and eventually there will be trillions and trillions of connections between cells. ► Every cell is precisely in its pla ...
... gestation the first brain cells, the neurons, are already forming at an astonishing rate: 250,000 every minute. ► Billions of neurons will form links with billions of other neurons and eventually there will be trillions and trillions of connections between cells. ► Every cell is precisely in its pla ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.