Nervous System ppt
... Pumps Na+ (sodium) outside & Pumps K+ (potassium) inside Membrane leaks and some K+ goes back out Resting Potential= -70mV because overall postive charge outside and negative charge inside ...
... Pumps Na+ (sodium) outside & Pumps K+ (potassium) inside Membrane leaks and some K+ goes back out Resting Potential= -70mV because overall postive charge outside and negative charge inside ...
General Introduction
... • Asymmetric distribution of PAR complex and other polarity complexes • From polarity signal to polarity establishment • Cell polarization in development • Asymmetric cell division controls fly neurogenesis • PAR and Scrib complexes facilitate the partition of apical and basal membrane ...
... • Asymmetric distribution of PAR complex and other polarity complexes • From polarity signal to polarity establishment • Cell polarization in development • Asymmetric cell division controls fly neurogenesis • PAR and Scrib complexes facilitate the partition of apical and basal membrane ...
Neuron-target interaction 1. Synapse formation between presynaptic
... Neuron-target interaction 1. Synapse formation between presynaptic and postsynaptic cells synaptogenesis in neuromuscular junction (NMJ) Central synapses form in a similar manner as in NMJ. synapse elimination- A large number of synapses eliminated. Proposed model: Active axon triggers the generatio ...
... Neuron-target interaction 1. Synapse formation between presynaptic and postsynaptic cells synaptogenesis in neuromuscular junction (NMJ) Central synapses form in a similar manner as in NMJ. synapse elimination- A large number of synapses eliminated. Proposed model: Active axon triggers the generatio ...
AP Ch. 9 Nervous System Part 1 Worksheets
... 1. The skeletal muscles are controlled by the _______________________________nervous system. 2. The smooth muscles and glands are controlled by the __________________________ nervous system. 3. Neurons are composed of a network of fine threads called _________________________________ 4. The nervous ...
... 1. The skeletal muscles are controlled by the _______________________________nervous system. 2. The smooth muscles and glands are controlled by the __________________________ nervous system. 3. Neurons are composed of a network of fine threads called _________________________________ 4. The nervous ...
Chapter 4
... • Receptor proteins - recognize and bind to neurotransmitters or other chemicals • Pump proteins - exchange one type of substance for another • Polarity - intracellular fluid in more negatively charged than the extracellular fluid which has more positively charged ions; • Difference in polarity is c ...
... • Receptor proteins - recognize and bind to neurotransmitters or other chemicals • Pump proteins - exchange one type of substance for another • Polarity - intracellular fluid in more negatively charged than the extracellular fluid which has more positively charged ions; • Difference in polarity is c ...
Sound frequency (pitch, tone) measured in hertz (cycles per sec)
... Type I spiral neurons (95%) ennervate a single inner hair cell. Therefore each Type I neuron exhibits the “prefered frequency” of its hair cell. Type II small, unmyelinated spiral neurons branch to connect multiple outer hair cells, generally in the same row. ...
... Type I spiral neurons (95%) ennervate a single inner hair cell. Therefore each Type I neuron exhibits the “prefered frequency” of its hair cell. Type II small, unmyelinated spiral neurons branch to connect multiple outer hair cells, generally in the same row. ...
Abstract View A HYBRID ELECTRO-DIFFUSION MODEL FOR NEURAL SIGNALING. ;
... least-squares algorithm. We incorporate this method into MCell, a Monte-Carlo cell simulator, and present preliminary validation under several testing scenarios. We apply the method to a reactive-diffusive simulation of an action potential propagating through an unmyelinated axon, with discrete sodi ...
... least-squares algorithm. We incorporate this method into MCell, a Monte-Carlo cell simulator, and present preliminary validation under several testing scenarios. We apply the method to a reactive-diffusive simulation of an action potential propagating through an unmyelinated axon, with discrete sodi ...
Title Both ion channels and calcium signals regulate proliferation in
... Background: It has been recognized that human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are present within the bone marrow cavity and serve as a reservoir for the continuous renewal of various mesenchymal tissues. However, their cellular biology is not fully understood, especially on the reg ...
... Background: It has been recognized that human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are present within the bone marrow cavity and serve as a reservoir for the continuous renewal of various mesenchymal tissues. However, their cellular biology is not fully understood, especially on the reg ...
Nervous System I
... Even as Na+/K+ ATPases pump potassium into the cell, intracellular potassium continues to leak back out of the cell making the inside even more negative. ...
... Even as Na+/K+ ATPases pump potassium into the cell, intracellular potassium continues to leak back out of the cell making the inside even more negative. ...
Ch. 3 Exchanging Materials with the Environment
... • Hydrophilic = “Water Loving” • Typically POLAR • Mostly soluble in water • Capable of hydrogen bonds with water • Ex: Salts, Sugars . . . ...
... • Hydrophilic = “Water Loving” • Typically POLAR • Mostly soluble in water • Capable of hydrogen bonds with water • Ex: Salts, Sugars . . . ...
Presynaptic Questions
... One prohormone skips over the substance K exon and only encodes for substance P Criticize the statement: The neurotransmitter vesicles in a neuron contain only one type of NT and no other molecules. Neurons can contain more than on NT; they frequently contain a peptide and one of the other types of ...
... One prohormone skips over the substance K exon and only encodes for substance P Criticize the statement: The neurotransmitter vesicles in a neuron contain only one type of NT and no other molecules. Neurons can contain more than on NT; they frequently contain a peptide and one of the other types of ...
Nervous Systems
... A nerve signal or action potential is an electrochemical message of neurons. An all-or-none phenomenon – either the fiber is conducting an action potential or it is not. The signal is varied by changing the frequency of signal ...
... A nerve signal or action potential is an electrochemical message of neurons. An all-or-none phenomenon – either the fiber is conducting an action potential or it is not. The signal is varied by changing the frequency of signal ...
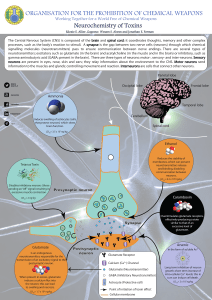
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... linear and nonlinear filters. Classifiers require no basic understanding of the relation between neural activity and behavior, relying instead on consistent patterns within and between variables and include self organizing feature maps, back-propagation, and maximum-likelihood methods. Filter techni ...
... linear and nonlinear filters. Classifiers require no basic understanding of the relation between neural activity and behavior, relying instead on consistent patterns within and between variables and include self organizing feature maps, back-propagation, and maximum-likelihood methods. Filter techni ...
Hasan_PressRelease_2008 - Max Planck Institute for Medical
... able to confirm this finding: targeted electrical recordings of neuronal activity after the triggering of stimulus showed that the colour change actually coincides with the firing of the action potentials. Hasan’s method sheds light on which nerve cells will talk to each other and in which time peri ...
... able to confirm this finding: targeted electrical recordings of neuronal activity after the triggering of stimulus showed that the colour change actually coincides with the firing of the action potentials. Hasan’s method sheds light on which nerve cells will talk to each other and in which time peri ...
My Reaction Test Score = Neural Transmission
... reflexes. The signal would travel at near the speed of light. Response time would be nearly instantaneous. The signals do have an electrical nature and messages can be initiated by electrical shocks. Rather than moving along a wire like electricity, the signals in your nervous system move by changin ...
... reflexes. The signal would travel at near the speed of light. Response time would be nearly instantaneous. The signals do have an electrical nature and messages can be initiated by electrical shocks. Rather than moving along a wire like electricity, the signals in your nervous system move by changin ...
METABOLIC-REDOX ADAPTATIONS OF NEURONS AND
... Energy and redox conservation in the brain requires metabolic cooperation between distinct cell types. We have identified mechanisms and factors that maintain cell specific programs to allow this metabolic-redox collaboration. Neurons show a high dependence on mitochondrial oxidative metabolism for ...
... Energy and redox conservation in the brain requires metabolic cooperation between distinct cell types. We have identified mechanisms and factors that maintain cell specific programs to allow this metabolic-redox collaboration. Neurons show a high dependence on mitochondrial oxidative metabolism for ...
The Nervous System - chemistrywithmrsmorton
... Neuron Function 1. Irritability: ability to respond to stimulus & convert to nerve impulse 2. Conductivity: transmit impulse to other neurons, muscles, or glands ...
... Neuron Function 1. Irritability: ability to respond to stimulus & convert to nerve impulse 2. Conductivity: transmit impulse to other neurons, muscles, or glands ...
MCB 130L Lecture 4 - Department of Molecular & Cell Biology
... required for cell morphology & motility Tubulin forms microtubule “tracks” that enable chromosomes & vesicles to move within cells ...
... required for cell morphology & motility Tubulin forms microtubule “tracks” that enable chromosomes & vesicles to move within cells ...
1 MCB3210F NAME EXAM 1A SECTION CELLS, TISSUES
... A) at the resting membrane potential of neurons, potassium is at equilibrium B) at -94 mV, the chemical force for potassium movement is zero C) at -94 mV, the electrical force for potassium movement is zero D) at -94 mV, the chemical force for potassium movement is opposed exactly by the electrical ...
... A) at the resting membrane potential of neurons, potassium is at equilibrium B) at -94 mV, the chemical force for potassium movement is zero C) at -94 mV, the electrical force for potassium movement is zero D) at -94 mV, the chemical force for potassium movement is opposed exactly by the electrical ...
Biology 621 - Chapter 12 Midterm Exam Review
... 24. ____ neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 25. What are the two major division of the peripheral nervous system? ____&___ 26 Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord.____ 27.The __ is the basic functional unit of the nervous system. 28.____ neu ...
... 24. ____ neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 25. What are the two major division of the peripheral nervous system? ____&___ 26 Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord.____ 27.The __ is the basic functional unit of the nervous system. 28.____ neu ...
Title: Nervous System
... Binding of a signal molecule – into an intracellular response that modifies the behavior of target cell a) Phase I – binding of first messenger (transmitter) to the receptor (T+R) b) Phase II – transduction of a signal into the intracellular compartment. T+R complex interacts with a specific G-prote ...
... Binding of a signal molecule – into an intracellular response that modifies the behavior of target cell a) Phase I – binding of first messenger (transmitter) to the receptor (T+R) b) Phase II – transduction of a signal into the intracellular compartment. T+R complex interacts with a specific G-prote ...
Exam
... A) at the resting membrane potential of neurons, potassium is at equilibrium B) at -94 mV, the chemical force for potassium movement is zero C) at -94 mV, the electrical force for potassium movement is zero D) at -94 mV, the chemical force for potassium movement is opposed exactly by the electrical ...
... A) at the resting membrane potential of neurons, potassium is at equilibrium B) at -94 mV, the chemical force for potassium movement is zero C) at -94 mV, the electrical force for potassium movement is zero D) at -94 mV, the chemical force for potassium movement is opposed exactly by the electrical ...
Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial
... Neurons are usually described as having one, and only one, axon—a fiber that emerges from the cell body and projects to target cells. That single axon can branch repeatedly to communicate with many target cells. It is the axon that propagates the nerve impulse, which is communicated to one or more c ...
... Neurons are usually described as having one, and only one, axon—a fiber that emerges from the cell body and projects to target cells. That single axon can branch repeatedly to communicate with many target cells. It is the axon that propagates the nerve impulse, which is communicated to one or more c ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.