Development of the Cerebral Cortex: VIII. Apoptosis: Neuronal Hari
... release active fragments (Fig. 1). It is interesting that some caspases activate other members of their family. A wave of active proteases is produced in response to a signal. For apoptosis to occur, the cell’s chromatin must come apart. DNA mechanisms that normally detect and rapidly repair DNA dam ...
... release active fragments (Fig. 1). It is interesting that some caspases activate other members of their family. A wave of active proteases is produced in response to a signal. For apoptosis to occur, the cell’s chromatin must come apart. DNA mechanisms that normally detect and rapidly repair DNA dam ...
6419982_1441921514
... In order for two cells to be electrically coupled, they must be approximately equal in size and they must be joined by areas of contact with low electrical resistance. In this way, impulses can be regenerated from one cell to the next without interruption. ...
... In order for two cells to be electrically coupled, they must be approximately equal in size and they must be joined by areas of contact with low electrical resistance. In this way, impulses can be regenerated from one cell to the next without interruption. ...
What is the Nervous System?
... Neurons – individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information. Parts of the Neuron: ...
... Neurons – individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information. Parts of the Neuron: ...
Lecture
... Representation with neurons and populations of neurons II. Do we really have a certain nerve cell for recognising the concatenation of features representing our grandmother(s)? Population (ensemble) code: Perception depends on the combined output of a group (ensemble) of cells not on the ouput of an ...
... Representation with neurons and populations of neurons II. Do we really have a certain nerve cell for recognising the concatenation of features representing our grandmother(s)? Population (ensemble) code: Perception depends on the combined output of a group (ensemble) of cells not on the ouput of an ...
II. ORGANIZATION OF THE HUMAN NERVOUS
... Cell Body – Contains the _nucleus______. Site of _metabolic_____ activity. Receives impulse from _dendrite______. Axon – Transmits impulses _away from the cell body______ to next cell. Usually a long, single fiber with many small tips called _axon terminals_________. Schwann Cells – Wrap aroun ...
... Cell Body – Contains the _nucleus______. Site of _metabolic_____ activity. Receives impulse from _dendrite______. Axon – Transmits impulses _away from the cell body______ to next cell. Usually a long, single fiber with many small tips called _axon terminals_________. Schwann Cells – Wrap aroun ...
Human PSC-Derived Mixed Neurons
... Storage of frozen cell products in the vapor phase of a liquid nitrogen storage tank is recommended. Storage in the liquid phase can result in cross-contamination if the vial breaks or is not sealed properly. Storage in the liquid phase also increases the potential for liquid nitrogen to penetrate t ...
... Storage of frozen cell products in the vapor phase of a liquid nitrogen storage tank is recommended. Storage in the liquid phase can result in cross-contamination if the vial breaks or is not sealed properly. Storage in the liquid phase also increases the potential for liquid nitrogen to penetrate t ...
BIO201 Crimando Vocab 6 BIO201 Nervous System I Vocabulary
... Value of the resting membrane potential on a “resting” neuron: ____________________ Cation more concentrated in extracellular fluid (ECF): ____________________ Cation more concentrated in intracellular fluid (ICF): ____________________ Ion channel that opens in response to chemical binding: _______ ...
... Value of the resting membrane potential on a “resting” neuron: ____________________ Cation more concentrated in extracellular fluid (ECF): ____________________ Cation more concentrated in intracellular fluid (ICF): ____________________ Ion channel that opens in response to chemical binding: _______ ...
neurons
... The cell body contains the nucleus, which provides energy for the neuron to carry out its functions. The cell body also contains genetic material and other structures that are found in virtually all the cells in the body. Extending out from the cell body are many short, branching fibers, called dend ...
... The cell body contains the nucleus, which provides energy for the neuron to carry out its functions. The cell body also contains genetic material and other structures that are found in virtually all the cells in the body. Extending out from the cell body are many short, branching fibers, called dend ...
The Action Potential
... The depolarization phase of action potential is abrupt and very rapid: in takes place in less than one milisecond. Soon after reaching the maximum peak of depolarization ( which inverts the membrane potential to some +10 to+ 20 mV), it begins to return to normal, that is, towards its value at rest. ...
... The depolarization phase of action potential is abrupt and very rapid: in takes place in less than one milisecond. Soon after reaching the maximum peak of depolarization ( which inverts the membrane potential to some +10 to+ 20 mV), it begins to return to normal, that is, towards its value at rest. ...
biology lecture notes chapter 2
... One neuron “talks” to another neuron at a SYNAPSE. Action potentials cause PRESYNAPTIC VESICLES in the AXON TERMINAL (also called terminal buttons or synaptic knobs) to release NEUROTRANSMITTERS (chemicals stored in the Axon Terminal inside synaptic vesicles that enable neurons to communicate) int ...
... One neuron “talks” to another neuron at a SYNAPSE. Action potentials cause PRESYNAPTIC VESICLES in the AXON TERMINAL (also called terminal buttons or synaptic knobs) to release NEUROTRANSMITTERS (chemicals stored in the Axon Terminal inside synaptic vesicles that enable neurons to communicate) int ...
Divisions of the Nervous System
... – controls subconscious actions: contractions of smooth muscle and cardiac muscle and ...
... – controls subconscious actions: contractions of smooth muscle and cardiac muscle and ...
6_4_PeptideTransmMetaboReceptor_HalaszO
... behaviour and pair bonding. More precisely/locally, they can regulate gene expression, local blood flow and synaptogenesis (among others). ...
... behaviour and pair bonding. More precisely/locally, they can regulate gene expression, local blood flow and synaptogenesis (among others). ...
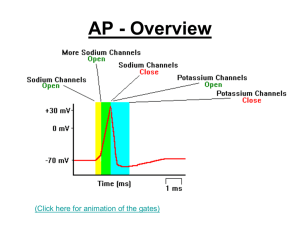
AP – All or nothing
... • During the action potential, the membrane is depolarised. • Following the impulse K+ ions move out of the membrane, this is repolarisation • The membrane briefly becomes hyperpolarised (more negative on the inside than usual) • The Na+ / K+ channels close ...
... • During the action potential, the membrane is depolarised. • Following the impulse K+ ions move out of the membrane, this is repolarisation • The membrane briefly becomes hyperpolarised (more negative on the inside than usual) • The Na+ / K+ channels close ...
Neural Tissue
... – Axons and dendrites of PNS neurons that are associated with a neurolemma may undergo repair if the cell body remains intact, if the schwann cells are functions, and if scar tissue formation does not occur too rapidly – Axons in the CNS are myelinated by oligodendrocytes that do not form neurolemma ...
... – Axons and dendrites of PNS neurons that are associated with a neurolemma may undergo repair if the cell body remains intact, if the schwann cells are functions, and if scar tissue formation does not occur too rapidly – Axons in the CNS are myelinated by oligodendrocytes that do not form neurolemma ...
view - Scan. Vet. Press
... synaptic input from many neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus. The neurons connected to a particular cortical cell have circular receptive fields that are linearly arranged and of the same type. This gives the cortical cell an oblong receptive field, with parallel regions where illumination eit ...
... synaptic input from many neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus. The neurons connected to a particular cortical cell have circular receptive fields that are linearly arranged and of the same type. This gives the cortical cell an oblong receptive field, with parallel regions where illumination eit ...
Objective ACD3.1 Discuss, with examples, changes that occur in
... 1. Describe the histological changes in the patient’s cells compared to normal. Your answer should discuss both the cytoplasm and nuclei. Cytoplasm: The myocardial cells are larger than normal, with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm [i.e., picks up the pink eosin stain]. (As mentioned previously, the ...
... 1. Describe the histological changes in the patient’s cells compared to normal. Your answer should discuss both the cytoplasm and nuclei. Cytoplasm: The myocardial cells are larger than normal, with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm [i.e., picks up the pink eosin stain]. (As mentioned previously, the ...
Answers to Questions — neurons
... 3. Hyponatremia occurs when people have very low amounts of sodium in their body. How might the nervous system be affected if the person had this condition? Sodium is important in generating action potentials, thus low amounts of sodium would make it so neurons are less able to transmit signals. In ...
... 3. Hyponatremia occurs when people have very low amounts of sodium in their body. How might the nervous system be affected if the person had this condition? Sodium is important in generating action potentials, thus low amounts of sodium would make it so neurons are less able to transmit signals. In ...
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... • Cell has ions for thousands of action potentials • Eventually must run Sodium-Potassium pump (burn ATP) to reset high [K+] inside and high [Na+] outside – Death = no ATP, but stored ions can generate action ...
... • Cell has ions for thousands of action potentials • Eventually must run Sodium-Potassium pump (burn ATP) to reset high [K+] inside and high [Na+] outside – Death = no ATP, but stored ions can generate action ...
I. Introduction to class
... Small peptides that decrease pain perception by CNS. Natural painkillers produced in times of stress (childbirth). Also decrease urine output, depress respiration, and cause euphoria and other emotional effects on brain. Heroin and morphine mimic action of endorphin. ...
... Small peptides that decrease pain perception by CNS. Natural painkillers produced in times of stress (childbirth). Also decrease urine output, depress respiration, and cause euphoria and other emotional effects on brain. Heroin and morphine mimic action of endorphin. ...
Chapter 28: Nervous System
... Small peptides that decrease pain perception by CNS. Natural painkillers produced in times of stress (childbirth). Also decrease urine output, depress respiration, and cause euphoria and other emotional effects on brain. Heroin and morphine mimic action of endorphin. ...
... Small peptides that decrease pain perception by CNS. Natural painkillers produced in times of stress (childbirth). Also decrease urine output, depress respiration, and cause euphoria and other emotional effects on brain. Heroin and morphine mimic action of endorphin. ...
Name: Date: Grade / Section: _____ Neurons Questions Notes 1
... ● ____________ or ________ cells are the special cells that carry information through your nervous system ● The message a neuron carries is called a _______ ___________ ● A neuron has 3 main parts: ...
... ● ____________ or ________ cells are the special cells that carry information through your nervous system ● The message a neuron carries is called a _______ ___________ ● A neuron has 3 main parts: ...
Chapter 11: Nervous System
... Voltage-gated channels – open and close in response to membrane potential Mechanically gated channels – open and close in response to physical deformation of receptors ...
... Voltage-gated channels – open and close in response to membrane potential Mechanically gated channels – open and close in response to physical deformation of receptors ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.