Brain lateralisation: a question of spatial frequency?
... To be registered by electrodes on the scalp many neurons would need to fire at the same time, which is unlikely given that action potentials lasts around 1msec No dipole created ...
... To be registered by electrodes on the scalp many neurons would need to fire at the same time, which is unlikely given that action potentials lasts around 1msec No dipole created ...
cell membrane ppt - Valhalla High School
... Cell Membrane • Permeability of the cell membrane – 1. Semi permeable/selectively permeable only certain substances can pass across the membrane. – 2. Factors that determine whether a molecule can pass through a membrane or not: • a. size • b. type (polar, non-polar) ...
... Cell Membrane • Permeability of the cell membrane – 1. Semi permeable/selectively permeable only certain substances can pass across the membrane. – 2. Factors that determine whether a molecule can pass through a membrane or not: • a. size • b. type (polar, non-polar) ...
the nervous system
... Define local circuits and explain how an impulse travels by “self - propagation” and compare conduction in myelinated fibers (“saltatory conduction”) with that in non - myelinated nerve fibers. ...
... Define local circuits and explain how an impulse travels by “self - propagation” and compare conduction in myelinated fibers (“saltatory conduction”) with that in non - myelinated nerve fibers. ...
Nervous System Review ANSWERS File
... A. Movement of a sodium ion all the way from dendrite to axon tip B. Movement of a potassium ion all the way form dendrite to axon tip C. Movement of an electron all the way from dendrite to axon tip D. A change in the difference in positive and negative ions on the surfaces of the neuron membrane, ...
... A. Movement of a sodium ion all the way from dendrite to axon tip B. Movement of a potassium ion all the way form dendrite to axon tip C. Movement of an electron all the way from dendrite to axon tip D. A change in the difference in positive and negative ions on the surfaces of the neuron membrane, ...
The Nervous System - Hartland High School
... 23. What is depolarization? Cell becomes permeable to Na+ or sodium ions and they rush into cell changing the polarity of neuron. The inside becomes more positive and the outside of the cell more negative. 24. What is an action potential? What is another name for it? Electrical current generated by ...
... 23. What is depolarization? Cell becomes permeable to Na+ or sodium ions and they rush into cell changing the polarity of neuron. The inside becomes more positive and the outside of the cell more negative. 24. What is an action potential? What is another name for it? Electrical current generated by ...
Nervous System PPT
... – left = right side of body – right = left side of body • The right side of your brain perceives and controls the left side of your body • Left side of brain perceives and controls right side of your ...
... – left = right side of body – right = left side of body • The right side of your brain perceives and controls the left side of your body • Left side of brain perceives and controls right side of your ...
Science Media Centre Fact Sheet Nanoparticles in medicine
... enough to cross the cell membrane could interact with DNA and cause damage, and potentially diseases such as cancer; ...
... enough to cross the cell membrane could interact with DNA and cause damage, and potentially diseases such as cancer; ...
File
... ________ The nerve cell that carriers impulses from a sense receptor to the brain and spinal cord. ________ The nerve cell that connects sensory and motor neurons. ________ The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or a gland. 3. There are three structural clas ...
... ________ The nerve cell that carriers impulses from a sense receptor to the brain and spinal cord. ________ The nerve cell that connects sensory and motor neurons. ________ The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or a gland. 3. There are three structural clas ...
Postdoctoral Researchers – Stem Cell Biology (2)
... The Regenerative Medicine Institute (REMEDI) is a Science Foundation Ireland-funded biomedical research centre with a primary goal of studying stem cell biology and translating these findings to new regenerative therapies for human disease. REMEDI is a partnership of scientists, clinicians, and engi ...
... The Regenerative Medicine Institute (REMEDI) is a Science Foundation Ireland-funded biomedical research centre with a primary goal of studying stem cell biology and translating these findings to new regenerative therapies for human disease. REMEDI is a partnership of scientists, clinicians, and engi ...
CLASS #1: 9 Jan 2001
... by post-synaptic neuron; ● glial uptake; ● enzyme deactivation. D. Actions at post-synaptic membrane: If receptors in post-synaptic membrane recognize the transmitter (=ligand-gated channels), the membrane’s conformation changes, causing a change in ion movement across the post-synaptic membrane and ...
... by post-synaptic neuron; ● glial uptake; ● enzyme deactivation. D. Actions at post-synaptic membrane: If receptors in post-synaptic membrane recognize the transmitter (=ligand-gated channels), the membrane’s conformation changes, causing a change in ion movement across the post-synaptic membrane and ...
Bump attractors and the homogeneity assumption
... • Visual synaptic bombardment leads to changes in conductance. This in turn increases fluctuations in membrane potential and these fluctuations modify the firing rate. • Firing rate decreases because of shunted membrane potential fluctuations, and increases because of shorter membrane time constants ...
... • Visual synaptic bombardment leads to changes in conductance. This in turn increases fluctuations in membrane potential and these fluctuations modify the firing rate. • Firing rate decreases because of shunted membrane potential fluctuations, and increases because of shorter membrane time constants ...
Ch 3 Review
... The Action Potential The axon membrane is pierced by tiny molecular channels called ion channels These channels are blocked when the neuron is at its resting potential. ...
... The Action Potential The axon membrane is pierced by tiny molecular channels called ion channels These channels are blocked when the neuron is at its resting potential. ...
Nerve Hormone WebQuest 2015
... 36. Slide the cursor over the brain and observe the areas highlighted and their function – describe two areas and the specific function of the cerebrum. a. b. 37. Which side of the brain controls the movements on the left side of the body? 38. What do you think is more important, the number of neur ...
... 36. Slide the cursor over the brain and observe the areas highlighted and their function – describe two areas and the specific function of the cerebrum. a. b. 37. Which side of the brain controls the movements on the left side of the body? 38. What do you think is more important, the number of neur ...
Failure in recycling cellular membrane may be a
... Cao, a member of the De Camilli lab, recreated the patients' mutation in mice, which developed movement problems and epilepsy similar to the neurological problems found in Parkinson's. Synaptojanin 1 plays a key role in the reformation of packets of neurotransmitters within the cell after neurotrans ...
... Cao, a member of the De Camilli lab, recreated the patients' mutation in mice, which developed movement problems and epilepsy similar to the neurological problems found in Parkinson's. Synaptojanin 1 plays a key role in the reformation of packets of neurotransmitters within the cell after neurotrans ...
Biopsychology and the Foundations of Neuroscience Chapter 3
... the axon. These spaces are important because they keep the action potential going through the long axon. ◦ Without the spaces, the charge might lose its intensity before reaching the end of the cell. Think of the nodes as the turbo button in a race car ...
... the axon. These spaces are important because they keep the action potential going through the long axon. ◦ Without the spaces, the charge might lose its intensity before reaching the end of the cell. Think of the nodes as the turbo button in a race car ...
Slide ()
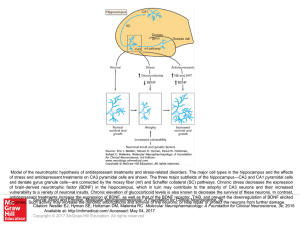
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission
... terminals. When the electrical signal reaches the terminal, it cannot cross the synaptic space, or synaptic cleft, to reach the postsynaptic neuron. Instead, that electrical signal triggers chemical changes that can cross the synapse and affect the postsynaptic cell. When the electrical impulse reac ...
... terminals. When the electrical signal reaches the terminal, it cannot cross the synaptic space, or synaptic cleft, to reach the postsynaptic neuron. Instead, that electrical signal triggers chemical changes that can cross the synapse and affect the postsynaptic cell. When the electrical impulse reac ...
Vertebrate Zoology BIOL 322/Nervous System Ch 33 and Brain
... - dfference of 70mV (70mV less on the inside) ...
... - dfference of 70mV (70mV less on the inside) ...
The Nervous System
... Divergence – Impulse that leaves one neuron and goes to several other output neurons. Amplifies an impulse so it can move to many ...
... Divergence – Impulse that leaves one neuron and goes to several other output neurons. Amplifies an impulse so it can move to many ...
Chapter 48 Nervous System
... 1. Na+ entering the cell creates an electrical current that depolarizes the next neighboring region of the membrane. 2. In case of the action potential, the depolarization is strong enough to reach the threshold in the neighboring regions, re-initiating the action potential there. 3. The membrane i ...
... 1. Na+ entering the cell creates an electrical current that depolarizes the next neighboring region of the membrane. 2. In case of the action potential, the depolarization is strong enough to reach the threshold in the neighboring regions, re-initiating the action potential there. 3. The membrane i ...
Chapter 7: the Nervous System
... • Cells of the central nervous system have a very limited ability to regenerate themselves • The cells themselves are soft and easily damaged (your brain has the consistency of tofu) • The blood-brain barrier refers to the fact that capillaries in the brain are less permeable than those in other par ...
... • Cells of the central nervous system have a very limited ability to regenerate themselves • The cells themselves are soft and easily damaged (your brain has the consistency of tofu) • The blood-brain barrier refers to the fact that capillaries in the brain are less permeable than those in other par ...
My Big List Thing
... o Peripheral nervous system (PNS): nervous system outside of brain and spinal cord; majority of neurons are here Neurite: extension of cell body of neuron; can be axon or dendrite; typically used re: immature neurons due to difficulty in determining which is being observed Neuropilin: receptors in n ...
... o Peripheral nervous system (PNS): nervous system outside of brain and spinal cord; majority of neurons are here Neurite: extension of cell body of neuron; can be axon or dendrite; typically used re: immature neurons due to difficulty in determining which is being observed Neuropilin: receptors in n ...
Neuroscience - HuskiesScience
... • When the cell is at rest (i.e., not doing anything), it has a charge of -70 mV. This is called the resting potential. • Because of the cell properties, many forces are acting on the cell. • 1. Diffusion - substances tend to move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. • 2. ...
... • When the cell is at rest (i.e., not doing anything), it has a charge of -70 mV. This is called the resting potential. • Because of the cell properties, many forces are acting on the cell. • 1. Diffusion - substances tend to move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. • 2. ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.