Chapter 2 Principles of Ecology
... determines how far apart they live and how large a population gets ...
... determines how far apart they live and how large a population gets ...
Sheet
... 4. What types of questions does science address? Which types does it not address? 5. What is the difference between a dependent and independent variable? 6. What are some economic benefits of biodiversity? 7. Name two treaties that aim to protect biodiversity. 8. What is habitat fragmentation? What ...
... 4. What types of questions does science address? Which types does it not address? 5. What is the difference between a dependent and independent variable? 6. What are some economic benefits of biodiversity? 7. Name two treaties that aim to protect biodiversity. 8. What is habitat fragmentation? What ...
Biomes_Aquatic_Ecosystems_Presentation
... • Nutrient rich soil supports a rich diversity of life, it is one of Earth's most productive ecosystems • Along the east coast of the United State, the major ecosystems found in estuaries are salt marshes • In tropical areas, the typical estuary ecosystems are ...
... • Nutrient rich soil supports a rich diversity of life, it is one of Earth's most productive ecosystems • Along the east coast of the United State, the major ecosystems found in estuaries are salt marshes • In tropical areas, the typical estuary ecosystems are ...
Feb 6 Primary Productivity: Controls, Patterns, Consequences
... LAI is a key parameter governing ecosystem processes because it determines both the area that is potentially available to absorb light and the degree to which light is attenuated through the canopy. GPP correlates closely with leaf area below an LAI of about 4, suggesting that leaf area is a critica ...
... LAI is a key parameter governing ecosystem processes because it determines both the area that is potentially available to absorb light and the degree to which light is attenuated through the canopy. GPP correlates closely with leaf area below an LAI of about 4, suggesting that leaf area is a critica ...
8th Grade First Six Weeks Vocabulary
... Overlapping food chains with different pathways for the flow of food energy in an ecosystem A pyramid that shows how much energy transfers to the next level in a food chain Organisms that transform energy from the Sun and use Carbon Dioxide and water to make food Organisms that eat producers or othe ...
... Overlapping food chains with different pathways for the flow of food energy in an ecosystem A pyramid that shows how much energy transfers to the next level in a food chain Organisms that transform energy from the Sun and use Carbon Dioxide and water to make food Organisms that eat producers or othe ...
Partnership in Fisheries -- ZMT Projects along the West African Coast
... The fisheries along the West-African coast is focused on small pelagic species of the upwelling ecosystem of the Canary current, especially off the Mauritanian and Senegalese coasts. The interplay between climate change, the potential adaptation of species, and the impact of fisheries on the coastal ...
... The fisheries along the West-African coast is focused on small pelagic species of the upwelling ecosystem of the Canary current, especially off the Mauritanian and Senegalese coasts. The interplay between climate change, the potential adaptation of species, and the impact of fisheries on the coastal ...
Part I. Aim # 48- Levels of Interaction within an
... Deer ticks are responsible for spreading Lyme disease. This organism, which feeds on the blood of warm-blooded organisms like mice, deer, and humans, is best ...
... Deer ticks are responsible for spreading Lyme disease. This organism, which feeds on the blood of warm-blooded organisms like mice, deer, and humans, is best ...
ecological succession pdf
... • Can be primary or secondary • The gradual replacement of one plant community by another through natural processes over time ...
... • Can be primary or secondary • The gradual replacement of one plant community by another through natural processes over time ...
From ecological aspect - 2010 Sophomore Composition
... species and groups of species are important in maintaining resilience(適應力) of coral reef ecosystems. In most reefs there are many species within each functional group. Many of those species do not appear to perform key functions but may be able to take over such functions if the keystone process spe ...
... species and groups of species are important in maintaining resilience(適應力) of coral reef ecosystems. In most reefs there are many species within each functional group. Many of those species do not appear to perform key functions but may be able to take over such functions if the keystone process spe ...
Primary succession
... Tropical rainforests are located near the equator where temperature is relatively warm and constant. Most areas receive 200+ cm annual rainfall, and some receive in excess of 500 cm. The soil allows high levels of leaching, thus most nutrients are tied up in biomass. Tropical rainforests hav ...
... Tropical rainforests are located near the equator where temperature is relatively warm and constant. Most areas receive 200+ cm annual rainfall, and some receive in excess of 500 cm. The soil allows high levels of leaching, thus most nutrients are tied up in biomass. Tropical rainforests hav ...
Ecological Succession
... thousand years ago. • Mosses, shrubs, and small trees cover the concrete of a demolished building. ...
... thousand years ago. • Mosses, shrubs, and small trees cover the concrete of a demolished building. ...
2012 Training Handout - Overview
... Competition has negative effect on both organisms competing for a resource Because resources are limited in nature there will always be competition for them Competition is the driving force of evolution, those that win leave more offspring Types of competition: Intraspecific - competition ...
... Competition has negative effect on both organisms competing for a resource Because resources are limited in nature there will always be competition for them Competition is the driving force of evolution, those that win leave more offspring Types of competition: Intraspecific - competition ...
Four Winds Nature Institute
... animals busily feeding upon leaves or hiding in them from their predators. The signs of leafeaters, or leaf-hiders, are easy to find. Peer into any bush or tree and you are sure to see leaves that are chewed, rolled, folded, or sewn up with silk. Snails, aphids and caterpillars feed upon this bounti ...
... animals busily feeding upon leaves or hiding in them from their predators. The signs of leafeaters, or leaf-hiders, are easy to find. Peer into any bush or tree and you are sure to see leaves that are chewed, rolled, folded, or sewn up with silk. Snails, aphids and caterpillars feed upon this bounti ...
Succession
... • If grass were no longer cut on a lawn, what would it look like in a year? • Five years? • In 90 years? ...
... • If grass were no longer cut on a lawn, what would it look like in a year? • Five years? • In 90 years? ...
41 Animal Nutrition
... B. Behavior and habitat selection 1. How do plants choose their habitats? 2. What factor restricts the range of the anopheline mosquito? C. Biotic factors 1. What living factors can limit distribution of a plant or animal? 2. How do sea urchins effect the distribution of seaweed? D. Abiotic factors ...
... B. Behavior and habitat selection 1. How do plants choose their habitats? 2. What factor restricts the range of the anopheline mosquito? C. Biotic factors 1. What living factors can limit distribution of a plant or animal? 2. How do sea urchins effect the distribution of seaweed? D. Abiotic factors ...
ANSWERS Biology Interim Study Guide
... 11. What happens to the energy that is not passed on to the next trophic level or used for life processes? Decreases It is eliminated (gotten rid of) as _____heat____________. ...
... 11. What happens to the energy that is not passed on to the next trophic level or used for life processes? Decreases It is eliminated (gotten rid of) as _____heat____________. ...
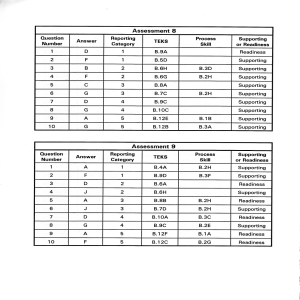
Assessment 8 Assessment I
... A biology class conducts a field investigation to study a stream ecosystem. Wearing boots, long pants, and long-sleeved shirts, the students arrive at the investigation site and discover that beavers have built a dam across the stream, creating a pond. The beavers are using the dam to create their h ...
... A biology class conducts a field investigation to study a stream ecosystem. Wearing boots, long pants, and long-sleeved shirts, the students arrive at the investigation site and discover that beavers have built a dam across the stream, creating a pond. The beavers are using the dam to create their h ...
Mitten Crab
... • The ecosystem after mitten crabs came is different. They now have lost some species as the crabs are killing them. They also have a lot more erosion due to the face that they are burrowing in the riverbanks. ...
... • The ecosystem after mitten crabs came is different. They now have lost some species as the crabs are killing them. They also have a lot more erosion due to the face that they are burrowing in the riverbanks. ...
Disturbance and Succesion Worksheet - Ecosystem
... The more common type, it occurs on a surface where an ecosystem was disturbed but still contains soil and life in the soil. After most forest fires, plants are killed but their seeds remain in the soil and begin to grow very quickly. The first species to colonize an area after a disturbance are call ...
... The more common type, it occurs on a surface where an ecosystem was disturbed but still contains soil and life in the soil. After most forest fires, plants are killed but their seeds remain in the soil and begin to grow very quickly. The first species to colonize an area after a disturbance are call ...
energy or whatever
... Answer: the levels that organisms are on: primary producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and so on. 7. What are the differences between assimilation efficiency, net production efficiency, and ecological efficiency? ...
... Answer: the levels that organisms are on: primary producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and so on. 7. What are the differences between assimilation efficiency, net production efficiency, and ecological efficiency? ...
Science
... 1. Different levels can occur such as 1’ (primary), 2’ (secondary), 3’ (tertiary), etc 2. 1’ feeds on producers, 2’ feeds on 1’, 3’ feeds on 2’ etc. 3. They must eat other organisms to obtain energy and matter. C. Decomposers or Detritovores (feed on dead, organic matter - detritus) 1. The decompose ...
... 1. Different levels can occur such as 1’ (primary), 2’ (secondary), 3’ (tertiary), etc 2. 1’ feeds on producers, 2’ feeds on 1’, 3’ feeds on 2’ etc. 3. They must eat other organisms to obtain energy and matter. C. Decomposers or Detritovores (feed on dead, organic matter - detritus) 1. The decompose ...
Environment and Ecology - Hawk Mountain Sanctuary
... How do changes in the environment affect the ability of living things to meet their basic needs? How do the living and nonliving parts of ecosystems interact and change over time? How do organisms survive in their environment? How do the characteristics of organisms affect their ability to survive w ...
... How do changes in the environment affect the ability of living things to meet their basic needs? How do the living and nonliving parts of ecosystems interact and change over time? How do organisms survive in their environment? How do the characteristics of organisms affect their ability to survive w ...
Topic 1
... Describe an example of change in the environment (food, ecosystem) that might select some individuals in a species for survival over others. Explain. Describe an example where variability within a species has helped a species to survive an environmental change. Suppose a population of sparrows migra ...
... Describe an example of change in the environment (food, ecosystem) that might select some individuals in a species for survival over others. Explain. Describe an example where variability within a species has helped a species to survive an environmental change. Suppose a population of sparrows migra ...
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic components are regarded as linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. As ecosystems are defined by the network of interactions among organisms, and between organisms and their environment, they can be of any size but usually encompass specific, limited spaces (although some scientists say that the entire planet is an ecosystem).Energy, water, nitrogen and soil minerals are other essential abiotic components of an ecosystem. The energy that flows through ecosystems is obtained primarily from the sun. It generally enters the system through photosynthesis, a process that also captures carbon from the atmosphere. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and other microbes.Ecosystems are controlled both by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, the parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem and the way things work within it, but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. Other external factors include time and potential biota. Ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances and are in the process of recovering from some past disturbance. Ecosystems in similar environments that are located in different parts of the world can have very different characteristics simply because they contain different species. The introduction of non-native species can cause substantial shifts in ecosystem function. Internal factors not only control ecosystem processes but are also controlled by them and are often subject to feedback loops. While the resource inputs are generally controlled by external processes like climate and parent material, the availability of these resources within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors like decomposition, root competition or shading. Other internal factors include disturbance, succession and the types of species present. Although humans exist and operate within ecosystems, their cumulative effects are large enough to influence external factors like climate.Biodiversity affects ecosystem function, as do the processes of disturbance and succession. Ecosystems provide a variety of goods and services upon which people depend; the principles of ecosystem management suggest that rather than managing individual species, natural resources should be managed at the level of the ecosystem itself. Classifying ecosystems into ecologically homogeneous units is an important step towards effective ecosystem management, but there is no single, agreed-upon way to do this.