
human disturbance - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... NOCTURNAL to avoid heat, deep burrows Get moisture from plants they eat Concentrated urine, dry feces ESTIVATE – hibernate to avoid extreme heat Reptiles have thick skin to reduce dehydration 39 ...
... NOCTURNAL to avoid heat, deep burrows Get moisture from plants they eat Concentrated urine, dry feces ESTIVATE – hibernate to avoid extreme heat Reptiles have thick skin to reduce dehydration 39 ...
Ecology I
... blown to them by wind. Organisms such as plants depend on wind to disperse pollen and seeds. Can also affect the pattern of a plant’s ...
... blown to them by wind. Organisms such as plants depend on wind to disperse pollen and seeds. Can also affect the pattern of a plant’s ...
Ecosystem
... ______________________________________________________________ 2. Abiotic factors are the physical nonliving components of the environment. What are the examples mentioned? ______________________________________________ ...
... ______________________________________________________________ 2. Abiotic factors are the physical nonliving components of the environment. What are the examples mentioned? ______________________________________________ ...
Abstract
... have been found, leaving the history of the first 600 million years missing. The oldest evidence for life can be traced back to between 3800 and 3500 million years and is based on chemical signatures, putative microfossils, and layered rocks known as stromatolites. Based on phylogenetic analyses it ...
... have been found, leaving the history of the first 600 million years missing. The oldest evidence for life can be traced back to between 3800 and 3500 million years and is based on chemical signatures, putative microfossils, and layered rocks known as stromatolites. Based on phylogenetic analyses it ...
Organism
... Environmental factor that cause a population to stop growing or decrease in size. Examples: weather conditions, space, food and water ...
... Environmental factor that cause a population to stop growing or decrease in size. Examples: weather conditions, space, food and water ...
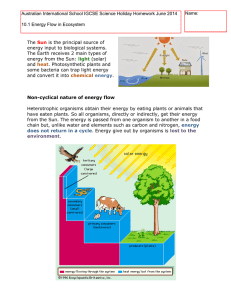
14 Ecosystem #138 Energy flow, energy loss The Sun
... The Sun is the principal source of energy input to biological systems. The Earth receives 2 main types of energy from the Sun: light (solar) and heat. Photosynthetic plants and some bacteria can trap light energy and convert it into chemical energy. ...
... The Sun is the principal source of energy input to biological systems. The Earth receives 2 main types of energy from the Sun: light (solar) and heat. Photosynthetic plants and some bacteria can trap light energy and convert it into chemical energy. ...
electrical engineering
... Living organisms need nitrogen (___), chiefly to manufacture ________________ and ________. Organisms need bacteria to convert unusable molecular nitrogen (_____) in the atmosphere into ______________________ (NH3), ____________________(NH4+), ____________________ (NO2-) and ______________________ ( ...
... Living organisms need nitrogen (___), chiefly to manufacture ________________ and ________. Organisms need bacteria to convert unusable molecular nitrogen (_____) in the atmosphere into ______________________ (NH3), ____________________(NH4+), ____________________ (NO2-) and ______________________ ( ...
Terrestrial Ecology Notes1
... The phosphorus cycle is slow and phosphorus is usually found in rock formations and ocean sediments. Phosphorus is found in fertilizers because most soil is deficient in it and plants need it. Phosphorus is usually insoluble in water and is not found in most aquatic environments. ...
... The phosphorus cycle is slow and phosphorus is usually found in rock formations and ocean sediments. Phosphorus is found in fertilizers because most soil is deficient in it and plants need it. Phosphorus is usually insoluble in water and is not found in most aquatic environments. ...
biology - People Server at UNCW
... Pre-industrial, Transitional, Industrial, and Post industrial Factors for population change used today Family planning Empowering women Economic rewards and penalties READ about China and India examples Age Structure diagrams – What do they tell? Demographic Stages of countries and graph Ecological ...
... Pre-industrial, Transitional, Industrial, and Post industrial Factors for population change used today Family planning Empowering women Economic rewards and penalties READ about China and India examples Age Structure diagrams – What do they tell? Demographic Stages of countries and graph Ecological ...
Food Webs and Ecological Pyramids
... harnessing the energy from the sun. They are called producers because they PRODUCE their own food rather than CONSUMING it by eating something else (consumers). As stated previously, energy from the sun flows into the biotic components of an ecosystem (living things) through the process of photosynt ...
... harnessing the energy from the sun. They are called producers because they PRODUCE their own food rather than CONSUMING it by eating something else (consumers). As stated previously, energy from the sun flows into the biotic components of an ecosystem (living things) through the process of photosynt ...
Energy Flow
... • As energy flows through each trophic level much is lost before it is consumed by organisms at the next level • Herbivores only eat a small fraction of plant material produced and cannot digest all of it, some will be passed unprocessed in the faeces. ...
... • As energy flows through each trophic level much is lost before it is consumed by organisms at the next level • Herbivores only eat a small fraction of plant material produced and cannot digest all of it, some will be passed unprocessed in the faeces. ...
AP Environmental Science Scoring Guidelines, 2016
... (ii) Describe one method for remediating soil affected by acid deposition. (1 point for a correct description of a method of remediation.) • Add crushed limestone / lime / marble dust / bone meal / crushed egg shells or oyster shells (e) Climate change is causing far-reaching ecosystem changes, incl ...
... (ii) Describe one method for remediating soil affected by acid deposition. (1 point for a correct description of a method of remediation.) • Add crushed limestone / lime / marble dust / bone meal / crushed egg shells or oyster shells (e) Climate change is causing far-reaching ecosystem changes, incl ...
How can we use this knowledge?
... the removal or increase of particular species • Food web models are good management tools • No MPA anywhere has restored an ecosystem to its mature ...
... the removal or increase of particular species • Food web models are good management tools • No MPA anywhere has restored an ecosystem to its mature ...
Ecology
... • Abiotic factors reduce populations by floods, fires, storms and severe climate fluctuations • These agents kill young or other members of a population regardless of the size of population ...
... • Abiotic factors reduce populations by floods, fires, storms and severe climate fluctuations • These agents kill young or other members of a population regardless of the size of population ...
pyramid of energy
... LEVEL. Food Chains- The transfer of food energy from the source in the plants through a series of organisms with repeated stages of eating and being eaten is known as the FOOD CHAIN. Food chain can be a simple form as in: Plants herbivores a food chain could be : Phytoplankton ...
... LEVEL. Food Chains- The transfer of food energy from the source in the plants through a series of organisms with repeated stages of eating and being eaten is known as the FOOD CHAIN. Food chain can be a simple form as in: Plants herbivores a food chain could be : Phytoplankton ...
Organism Relationships
... • A network of food chains by which energy and nutrients are passed on from one living organism to another. • Multiple pathways • The arrows represent energy being transferred. • Energy is greatest at the bottom of the food web. ...
... • A network of food chains by which energy and nutrients are passed on from one living organism to another. • Multiple pathways • The arrows represent energy being transferred. • Energy is greatest at the bottom of the food web. ...
UNIT A Notes Bio20
... producers. Most of the chemical energy made by the plant is used by the plant for life functions (movement, growth, repair, transport, reproduction, exchange of materials with the environment, response to stimuli). Some of the chemical energy is stored for future use (usually as starch). Chemosynthe ...
... producers. Most of the chemical energy made by the plant is used by the plant for life functions (movement, growth, repair, transport, reproduction, exchange of materials with the environment, response to stimuli). Some of the chemical energy is stored for future use (usually as starch). Chemosynthe ...
Chapter 4 AND 5 Practice - North Salem Schools Teachers Module
... consumers than producers. D) It contains complex food webs that have more heterotrophs than autotrophs. ...
... consumers than producers. D) It contains complex food webs that have more heterotrophs than autotrophs. ...
Exam practice answers 3
... support a single head of cattle. Illegal logging of tropical hardwood trees, together with roads cut through the forest to provide access, have also degraded vast areas of rainforest. On a more localised scale, open-cast mining for minerals such as iron ore and bauxite, has not only destroyed the fo ...
... support a single head of cattle. Illegal logging of tropical hardwood trees, together with roads cut through the forest to provide access, have also degraded vast areas of rainforest. On a more localised scale, open-cast mining for minerals such as iron ore and bauxite, has not only destroyed the fo ...
Document
... DGVMs are designed to reproduce and quantify ecosystem processes. Based on plant functions or species specific parameter sets, the energy, carbon, nitrogen and water cycles of different ecosystems are assessed. These models have been proven to be important tools to investigate ecosystem fluxes as th ...
... DGVMs are designed to reproduce and quantify ecosystem processes. Based on plant functions or species specific parameter sets, the energy, carbon, nitrogen and water cycles of different ecosystems are assessed. These models have been proven to be important tools to investigate ecosystem fluxes as th ...
Ch16_EcosystemsStudentNotes[1] - Mrs-Lamberts-Biology
... shrubs later take over from pioneer plants. • As the amount of_____ increases, spruce and hemlock____ become plentiful. Movement of Energy Through Ecosystems Primary Energy Source • The rate at which organic material is produced by _______________________organisms in an ecosystem is called primary _ ...
... shrubs later take over from pioneer plants. • As the amount of_____ increases, spruce and hemlock____ become plentiful. Movement of Energy Through Ecosystems Primary Energy Source • The rate at which organic material is produced by _______________________organisms in an ecosystem is called primary _ ...
The Value of Endangered Species: the Importance of Conserving
... area is termed its “biological diversity.” The term biological diversity is often used interchangeably (sometimes confusingly) with two other terms, “genetic diversity” and “ecological diversity.” Genetic diversity (amount of genetic variability among individuals of the same species) and ecological ...
... area is termed its “biological diversity.” The term biological diversity is often used interchangeably (sometimes confusingly) with two other terms, “genetic diversity” and “ecological diversity.” Genetic diversity (amount of genetic variability among individuals of the same species) and ecological ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... humans occur. Malaria may cause anemia and jaundice (yellow coloring of the skin and eyes) because of the loss of red blood ...
... humans occur. Malaria may cause anemia and jaundice (yellow coloring of the skin and eyes) because of the loss of red blood ...




















![Ch16_EcosystemsStudentNotes[1] - Mrs-Lamberts-Biology](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009688549_1-67efd9bcb8e6f5acdcf17bfaf22d0643-300x300.png)

