* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download electrical engineering
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
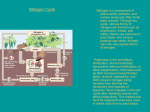
ST/EST 404 THE EARTH & SPACE CHAPTER 8 NOTES CHAPTER 8 The Biosphere (pp. 254 – 279) 1 What is the biosphere? The Earth is wrapped in _______________ overlapping layers: 1. _________________________ (solid layer) 2. _________________________ (layer of water) 3. _________________________ (layer of air) 4. _________________________ (layer of LIFE!) The biosphere corresponds to the entire system of living ____________________ and their __________________. The biosphere is the layer around the Earth containing all _______________ _______________. 2 Biogeochemical cycles In order to survive, living organisms needs to take in large amounts of certain essential elements, namely, ___________________, ____________________, _____________________, ______________________, _____________________, and ______________________. They are found in ____________ and ____________, in the atmosphere and in ________________ and ___________________ tissues and they are constantly circulating within the biosphere in biogeochemical cycles. Bio = ___________________ processes (respiration and photosynthesis) Geo = ____________________ processes (erosion and sedimentation) Chemical = _________________ processes (combustion and synthesis) A biogeochemical cycle is the continuous ______________________ of an element from one ______________________ to another. 1 ST/EST 404 THE EARTH & SPACE CHAPTER 8 NOTES Read “Solution to Pollution” on p. 255 What revolutionary technique is being used in Saskatchewan to remove CO2 that is being pumped into the atmosphere in North Dakota? ______________________________________________________________________________ What is the CO2 being use for? ______________________________________________________________________________ 2.1 THE CARBON CYCLE Carbon (___) is the main element making up all biological molecules (____________, ___________, and _____________________). It is also found in _________ and methane (________) which are found in the atmosphere. How is carbon recycled within the biosphere? 1. _________________________: _____________ ______________ + water _______________ + oxygen (CO2) (C6H12O6) 2. ________________________: animals eat ______________ and other ______________ to get the carbon they need. 3. ________________________: When organisms exhale, they release _______. _______________ + oxygen _____________ ______________ + water (C6H12O6) (CO2) 4. _______________________of waste: Any carbon that is not used for respiration is returned to the biosphere as waste (_____________and ___________ ______________) which is broken down by _______________________ which release ________ and ___________________ in the process. 2 ST/EST 404 THE EARTH & SPACE CHAPTER 8 NOTES 5. __________________ fires: Carbon stored in the ______________ and ____________ of trees is released as _________. 6. __________________ and ____________________: Carbon dioxide dissolved in the water reacts with _________________ and then with __________________ to form _______________ ____________________ which is used to make __________________ and ____________________ of marine organisms. 7. ______________________ ______________: Shells and skeletons of marine organisms accumulate as sediment on the ocean floor forming rock which can eventually return to the surface with the movement of _________________ __________________. 8. ____________________ _____________________: CO2 from certain types of melted rock is released into the atmosphere when a _________________ erupts. 9. ____________________ _________________: Dead organisms (mainly plant matter) get buried in the ocean floor and compacted by sediment converting them into _________________ ________________ (takes millions of years). 10. ___________________________ of fossil fuels: When fossil fuels (coal, oil and gas) are burned (automobiles, thermal power plants) _______________ _______________ is released into the atmosphere. 3 http://www.marietta.edu/~biol/102/ccycle.gif ST/EST 404 THE EARTH & SPACE CHAPTER 8 NOTES 2.2 THE NITROGEN CYCLE Living organisms need nitrogen (___), chiefly to manufacture ________________ and ________. Organisms need bacteria to convert unusable molecular nitrogen (_____) in the atmosphere into ______________________ (NH3), ____________________(NH4+), ____________________ (NO2-) and ______________________ (NO3-). 1. Nitrogen ____________________: nitrogen-fixing bacteria take nitrogen form the __________________ and convert it into __________________. Some ammonia is converted into _____________________. 2. ___________________________: Bacteria oxidize ___________________ to form _____________. Other bacteria oxidize _________________ into _________________. 3. Nitrogen absorption by_________________ and ___________________: Plants draw _________________ and _________________ from soil and water. Herbivores get their nitrogen by eating the _________________ and carnivores get their nitrogen by eating the _____________________ or other animals. 4. _______________________ of waste: Certain bacteria and fungi break down the nitrogen in plant and animal _________________. They produce _________________ which dissolves and forms ___________________. 5. ________________________: Certain bacteria convert ___________________ into molecular ________________, which returns to the _________________________. Many natural factors can alter the nitrogen cycle: But human activities have a much greater impact: Farming: Fertilizers rich in _________________, ___________________ and ______________________ are applied to the fields. Factories: nitrogen compounds are discharged in _______________________. Too much nitrogen can alter ___________ __________________ which interfere with _____________ growth. 4 ST/EST 404 THE EARTH & SPACE CHAPTER 8 NOTES 2.3 THE PHOSPHORUS CYCLE (EST only) Phosphorus is important to living things because it is a basic component of ___________ and many animals need to form _____________, ________________ and _______________. How is phosphorus recycled within the biosphere? 1. ________________________: Wind and rain wear away small amounts of phosphorus from _______________, usually in the form of ________________________. 2. _______________________ by living organisms: _________________ rapidly absorb phosphates from the ______________. _________________ get their phosphate by eating plants, and carnivores get their phosphorus by eating ______________ and other_______________. 3. ___________________________ of waste: Digested phosphates are returned to the soil by animals in the form of _____________ and _______________. Phosphate are also released when ___________________ break down dead ___________________ and __________________. 4. Proliferation of __________________ and ________________________: Phosphates from _______________ and from animal and decomposer ________________________ go into the ocean. Once in the ocean, the phosphorus either promotes the growth of ________________ or settles out at the bottom with other sediment and, over millions of years, forms __________________. Human activities are ______________________ the natural phosphorus cycle. Those activities include: Over-use of phosphorus-rich______________________ on farmland Use of phosphorus-laden _________________. The phosphorus in these substances makes its way into our ________________, _________________ and coastal _________________ where it accelerates _________________ growth. Overpopulation of algae causes __________________________ - a drop in deep water oxygen concentration. What would that do to the aquatic life? 5 ST/EST 404 THE EARTH & SPACE CHAPTER 8 NOTES 3 Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive ______________________, _________________________, and ____________________________. 3.1 FACTORS DETERMINING BIOME DISTRIBUTION Terrestrial Biomes Latitude Aquatic Biomes Altitude Turbidity (water clarity) Direction and strength of current Soil type Presence of _________ and __________ Nutrients (type, amount, etc.) Proximity to bodies of _______________ Water ____________________________ These factors determine which __________________ and _________________ species live in a certain biome. Ex. Some fish require _______________ water to thrive, while others need salt water. The following section will describe all the different types of biomes (ecosystems) on the Earth. There are two types of biomes: __________________________ and ______________________. All the information about the biomes will be summarized in a table on the following two pages. 6 ST/EST 404 THE EARTH & SPACE CHAPTER 8 NOTES 3.2 TERRESTRIAL BIOMES Terrestrial Biome Location Characteristics Threats TROPICAL FORESTS Either side of the equator (between the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn) 20 C – 34 C Seasonal (Africa) or evergreen/ rainforest (South America & Asia) Home to 50-80% plants and animal species Regulates the Earth’s climate Clear-cutting for farmland and timber BOREAL FORESTS Below Arctic circle: Mainly conifers Acidic soil Nutrient poor soil Canada Northern Russia o o TEMPERATE FORESTS Southern Canada USA Europe Australia Avg. temp. = 8-10oC Coniferous & deciduous trees Nutrient rich soil GRASSLANDS & SHRUBLANDS (A.K.A Prairies) Everywhere EXCEPT Europe & Arctic regions ARCTIC TUNDRA North of the Boreal forest Max. temp. = 10oC Grasses, stunted bushes. moss, lichen Permafrost Caribou, arctic foxes, lemmings, migratory birds DESERTS Areas of low precipitation and extreme temperatures (Asia, Africa, Antarctic) 25 cm of precip/yr -89oCT 52oC Little plant life ALPINE BIOMES High altitudes Submontane zone Montane zone Subalpine zone Alpine zone Nival zone Rocky Mountains (US & CAN) Andes (S. America) Logging for paper products and timber for construction Fire, insects and disease Urbanization & farming (Montreal and Toronto used to be temperate forests) Low rainfall (no trees) Can survive fires, drought and mowing Temperate grasslands: Hot summers, cold winters Savannas: Hot all year Derived grasslands: Farms Below 1300 m 1300-1800 m 1800-2400 m 2400 m 3000 m Climate change, global warming (Arctic is warming up twice as fast as the rest of the Earth) Deciduous tress Conifers Sparse conifers Bushes and grass Snowcaps Himalayas (Asia) 7 ST/EST 404 THE EARTH & SPACE CHAPTER 8 NOTES 3.3 AQUATIC BIOMES FRESHWATER BIOMES Aquatic Biome Definition Characteristics Threats LAKES Bodies of water surrounded by land and fed by rivers Home to microorganisms, plants, plankton, fish, amphibians, reptiles & birds Shoreline acts as buffer, filtering the surface run-off Farming and industrial activities, urbanization pollutes them RIVERS Permanent or seasonal drainage channels for surface water Home to grasses & moss Agriculture and industrial activities deteriorate water quality WETLANDS Areas that are permanently or temporarily covered with fresh or salt water Habitat for many plants and animals Acts as a huge sponge that absorbs rainwater and reduces the risk of flooding MARSHES: stagnant water w/o trees SWAMPS: stagnant or moving water w/ trees or shrubs PEAT BOGS: poorly drained soil carpeted with moss MARINE (SALTWATER) BIOMES Aquatic Biome Definition Characteristics ESTUARIES Zone between maritime and river environments Threats Fresh water mixes with salt water Home to oysters, sponges, belugas Great for whale watching (whales feed there) OCEANS AND SEAS Habitats are subdivided by depth Surface: phytoplankton Open water: crustaceans, fish, jellyfish, mollusks, birds Ocean floor/Seabed: benthos = mollusks, crustaceans, deep-water fish which feed off dead organisms scattered over the ocean floor Fishing 8 ST/EST 404 THE EARTH & SPACE CHAPTER 8 NOTES CORAL REEFS Most found in tropical seas Habitat (food and shelter) for hundreds of thousands of marine species (biodiversity!!!) Formed of calcium carbonate which the coral produces Major source of economic, social and cultural importance 20% have been destroyed Pollution, over-fishing, global warming, increased sedimentation END OF CHAPTER 8 NOTES 9