Unit 5
... species living close enough together for potential interaction between the # of species (richness) and the quantity of the species (abundance). List four properties of a community, and explain the importance of each. Competitive exclusion principle: when two species compete for exactly the same re ...
... species living close enough together for potential interaction between the # of species (richness) and the quantity of the species (abundance). List four properties of a community, and explain the importance of each. Competitive exclusion principle: when two species compete for exactly the same re ...
BI101 Winter 2016 Morré STUDY GUIDE FOR FINAL EXAM FINAL
... Understand the meaning of these terms: conservation biology, biodiversity, sustainable development. Why are they important? Why is it important to maintain biodiversity and diverse natural ecosystems? Describe three levels of biodiversity (genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity) and why it is imp ...
... Understand the meaning of these terms: conservation biology, biodiversity, sustainable development. Why are they important? Why is it important to maintain biodiversity and diverse natural ecosystems? Describe three levels of biodiversity (genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity) and why it is imp ...
Chapter 4 Matter and Energy in the Ecosystem
... ocean and rocks Oceans hold a great deal of carbon dioxide because carbon dioxide dissolves easily in water. Carbon is also stored in rocks: coal, oil and limestone are formed from the bodies of dead organisms. Because the bodies of these organisms were never completely decomposed, some of the car ...
... ocean and rocks Oceans hold a great deal of carbon dioxide because carbon dioxide dissolves easily in water. Carbon is also stored in rocks: coal, oil and limestone are formed from the bodies of dead organisms. Because the bodies of these organisms were never completely decomposed, some of the car ...
Feeding Relationships
... • Organisms that feed on the remains or wastes of other organisms. • Recycle the nutrients back into the soil • Often left out of food chain • Ex. Bacteria and fungi ...
... • Organisms that feed on the remains or wastes of other organisms. • Recycle the nutrients back into the soil • Often left out of food chain • Ex. Bacteria and fungi ...
ecology
... When succession occurs on land where nothing has grown before it is called primary succession (Example: The invasion of plants from water to land) When succession occurs in areas where there has been previous growth it is called secondary succession (Example: A fire wipes out the entire plant & anim ...
... When succession occurs on land where nothing has grown before it is called primary succession (Example: The invasion of plants from water to land) When succession occurs in areas where there has been previous growth it is called secondary succession (Example: A fire wipes out the entire plant & anim ...
Attachment H - Town of Concord MA
... Bacteria: Typically single celled microorganisms that have no chlorophyll, multiply by simple division, and occur in various forms. Some bacteria may cause disease, but many do not and are necessary for fermentation, nitrogen fixation, and decomposition of organic matter. Bathymetric Map: A map illu ...
... Bacteria: Typically single celled microorganisms that have no chlorophyll, multiply by simple division, and occur in various forms. Some bacteria may cause disease, but many do not and are necessary for fermentation, nitrogen fixation, and decomposition of organic matter. Bathymetric Map: A map illu ...
Ecology - Fall River Public Schools
... potential food available for each trophic level ◦ Biomass – the total amount of living tissue Grams of organic matter per unit area ...
... potential food available for each trophic level ◦ Biomass – the total amount of living tissue Grams of organic matter per unit area ...
Principles of Ecology
... materials in an ecosystem and return the nutrients to the soil, air, and water. The nutrients then become available for use by other organisms. Hyenas and vultures are detritivores. They feed on animals that have died. Fungi and bacteria are also detritivores. Detritivores play an important role in ...
... materials in an ecosystem and return the nutrients to the soil, air, and water. The nutrients then become available for use by other organisms. Hyenas and vultures are detritivores. They feed on animals that have died. Fungi and bacteria are also detritivores. Detritivores play an important role in ...
Habitat & Community
... • One species will be better suited • The other will be pushed out or die ...
... • One species will be better suited • The other will be pushed out or die ...
What is Biodiversity? www.syngenta.co.uk/learningzone Farmland
... products available to us. As we source our food supply from so few plant species, we are susceptible to environmental changes and crop diseases. ...
... products available to us. As we source our food supply from so few plant species, we are susceptible to environmental changes and crop diseases. ...
Ecological Succession
... • Natural, gradual changes in the types of species that live in an area; can be primary or secondary • The gradual replacement of one plant community by another through natural processes over time ...
... • Natural, gradual changes in the types of species that live in an area; can be primary or secondary • The gradual replacement of one plant community by another through natural processes over time ...
File
... • Animal Dissections. Look in the stomach of a fish, shark, or mussel. What did it have for its last meal? Was the animal living in the wild or was it from a farm? Try to identify any remains. Analyzing gut contents is used to understand the food web. For many fish species, it is nearly impossible t ...
... • Animal Dissections. Look in the stomach of a fish, shark, or mussel. What did it have for its last meal? Was the animal living in the wild or was it from a farm? Try to identify any remains. Analyzing gut contents is used to understand the food web. For many fish species, it is nearly impossible t ...
Succession
... The climax community. In Pacific Northwest forests, the climax community is known as old growth forest. Note that climax is the most correct term for all habitats when speaking of the final successional stage. ...
... The climax community. In Pacific Northwest forests, the climax community is known as old growth forest. Note that climax is the most correct term for all habitats when speaking of the final successional stage. ...
IUCN-Green to Blue Economy
... increasing energy efficiency, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, waste and pollution, and conserving water and other natural resources.” (Pew Charitable Trusts) “Industries that provide products or services related to renewable energy, increased energy efficiency, clean transportation and fuels, agr ...
... increasing energy efficiency, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, waste and pollution, and conserving water and other natural resources.” (Pew Charitable Trusts) “Industries that provide products or services related to renewable energy, increased energy efficiency, clean transportation and fuels, agr ...
Ecology of plant–animal interactions: pollination, seed dispersal and
... the mechanism by which plants circumvent and minimize the adverse effects of nectar robbing on their fitness. He also gave a hands-on training on the plant– pollinator network analysis in the R platform. Plants are able to activate defence mechanisms against various forms of insect attacks. Insects ...
... the mechanism by which plants circumvent and minimize the adverse effects of nectar robbing on their fitness. He also gave a hands-on training on the plant– pollinator network analysis in the R platform. Plants are able to activate defence mechanisms against various forms of insect attacks. Insects ...
ecosystems - Four Winds Nature Institute
... to live side by side. We’ll experience the nature of competition when we hide away nuts, and compare our success rate to squirrels when we attempt to retrieve our hidden caches. STAYING WARM: Ecosystems are very different places in the winter, with less solar energy, shorter days, and little or no ...
... to live side by side. We’ll experience the nature of competition when we hide away nuts, and compare our success rate to squirrels when we attempt to retrieve our hidden caches. STAYING WARM: Ecosystems are very different places in the winter, with less solar energy, shorter days, and little or no ...
Forest Patterns and Processes
... easily worked, whereas if the soil pH is either extremely acid or extremely alkaline, clays tend to become sticky and hard to cultivate. A pH determination (soil test) will tell whether your soil will produce good plant growth or whether it will need to be treated to adjust the pH level. For most pl ...
... easily worked, whereas if the soil pH is either extremely acid or extremely alkaline, clays tend to become sticky and hard to cultivate. A pH determination (soil test) will tell whether your soil will produce good plant growth or whether it will need to be treated to adjust the pH level. For most pl ...
Study Guide Test #2 Ecology
... 11. Autotrophs are also known as _________________________. 12. Heterotrophs are also known as ________________________. 13. What are the 10 major biomes and 1 characteristic of each? (refer to your homework questions from textbook page 105) ...
... 11. Autotrophs are also known as _________________________. 12. Heterotrophs are also known as ________________________. 13. What are the 10 major biomes and 1 characteristic of each? (refer to your homework questions from textbook page 105) ...
Ch. 4 Ecology
... factors. Define key ecological concepts • Left side – make a list of biotic and abiotic factors that might impact a rainforest ecosystem. Read the story a hike through the rainforest. Pick one living thing from the story and describe it’s niche, and habitat, describe what other organisms it might be ...
... factors. Define key ecological concepts • Left side – make a list of biotic and abiotic factors that might impact a rainforest ecosystem. Read the story a hike through the rainforest. Pick one living thing from the story and describe it’s niche, and habitat, describe what other organisms it might be ...
Document
... - Unlike the one-way flow of energy, matter is recycled within and between ecosystems. Water continuously flows between the oceans, the atmosphere, and land – sometimes outside organisms and sometimes inside organisms. Every organism needs nutrients to build tissues and carry out life functions. Lik ...
... - Unlike the one-way flow of energy, matter is recycled within and between ecosystems. Water continuously flows between the oceans, the atmosphere, and land – sometimes outside organisms and sometimes inside organisms. Every organism needs nutrients to build tissues and carry out life functions. Lik ...
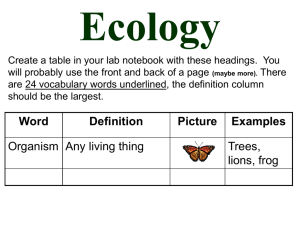
Ecology
... - Unlike the one-way flow of energy, matter is recycled within and between ecosystems. Water continuously flows between the oceans, the atmosphere, and land – sometimes outside organisms and sometimes inside organisms. Every organism needs nutrients to build tissues and carry out life functions. Lik ...
... - Unlike the one-way flow of energy, matter is recycled within and between ecosystems. Water continuously flows between the oceans, the atmosphere, and land – sometimes outside organisms and sometimes inside organisms. Every organism needs nutrients to build tissues and carry out life functions. Lik ...
Energy flow and the nutrient cycling in an ecosystem
... into simple compounds : these compounds are absorbed as nutrients b y the green plants again : they enable the nutrients to be used continuousl y in a cyclic form in the ecos ystem : they are most abundant in the soil or water bottom where the dead bodies of plant and animals accumulate : when the t ...
... into simple compounds : these compounds are absorbed as nutrients b y the green plants again : they enable the nutrients to be used continuousl y in a cyclic form in the ecos ystem : they are most abundant in the soil or water bottom where the dead bodies of plant and animals accumulate : when the t ...