EOC concept review mod 2015 -ls jc
... insects or mice on land or small krill in the ocean--and the biggest predators get that toxin built up in their bodies over time as they feed. * DDT, a pesticide, is a famous example from the 19501970’s that nearly made The American Eagle extinct. 3) Organisms live in populations of their (one) spec ...
... insects or mice on land or small krill in the ocean--and the biggest predators get that toxin built up in their bodies over time as they feed. * DDT, a pesticide, is a famous example from the 19501970’s that nearly made The American Eagle extinct. 3) Organisms live in populations of their (one) spec ...
Ecosystem - WordPress.com
... The most stable ecosystems (greatest biodiversity) have such complex food webs that the removal of one producer or consumer does not have a great negative affect on the other food chains in the web. ...
... The most stable ecosystems (greatest biodiversity) have such complex food webs that the removal of one producer or consumer does not have a great negative affect on the other food chains in the web. ...
Science-vocabulary-new-text-2009
... replaced or that takes thousands of years to be replaced (ex.: oil, coal, redwood tree) ore – rock that contains metal or other useful minerals renewable resource – a natural resource that can be replaced by nature (plants and most trees, water, sunlight, wind) pollution – the addition of harmful ma ...
... replaced or that takes thousands of years to be replaced (ex.: oil, coal, redwood tree) ore – rock that contains metal or other useful minerals renewable resource – a natural resource that can be replaced by nature (plants and most trees, water, sunlight, wind) pollution – the addition of harmful ma ...
Background Factsheet: Microbes
... Synechococcus is the main source of primary production in oligotrophic, pelagic marine waters. They can cause destructive blooms, producing neurotoxins. Their growth is generally limited however by the concentration of nutrients and trace metals such as iron and phosphorus. Cyanobacteria as a whole ...
... Synechococcus is the main source of primary production in oligotrophic, pelagic marine waters. They can cause destructive blooms, producing neurotoxins. Their growth is generally limited however by the concentration of nutrients and trace metals such as iron and phosphorus. Cyanobacteria as a whole ...
all notes from this document will be shown in class
... Environmental Science a Global Perspective Environmental Problems (intro overheads of local animals) ...
... Environmental Science a Global Perspective Environmental Problems (intro overheads of local animals) ...
Yr 11 - Biodiversity Biology Term 3 - TCC-Yr11
... • Food chain series of steps in an ecosystem in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten • Food web network of complex interactions formed by the feeding relationships among the various organisms in an ecosystem • Food pyramid the loss of energy from one trophic level up to the nex ...
... • Food chain series of steps in an ecosystem in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten • Food web network of complex interactions formed by the feeding relationships among the various organisms in an ecosystem • Food pyramid the loss of energy from one trophic level up to the nex ...
Ecosystem - WordPress.com
... 1. Producers: These are green plants (autotrophs) having chlorophyll. They manufacture energy-rich food materials with the help of carbon dioxide, water, sunlight through the process of photosynthesis. Eg: Green plants, photosynthetic bacteria, chemosynthetic bacteria. 2. Consumers: All living organ ...
... 1. Producers: These are green plants (autotrophs) having chlorophyll. They manufacture energy-rich food materials with the help of carbon dioxide, water, sunlight through the process of photosynthesis. Eg: Green plants, photosynthetic bacteria, chemosynthetic bacteria. 2. Consumers: All living organ ...
Aquatics Glossary
... A wildlife management term for the equilibrium expressed by the availability of habitat components and the number of animals in a given area. In general ecological usage, carrying capacity is the dynamic equilibrium established between any life form and its environment. It is frequently expressed as ...
... A wildlife management term for the equilibrium expressed by the availability of habitat components and the number of animals in a given area. In general ecological usage, carrying capacity is the dynamic equilibrium established between any life form and its environment. It is frequently expressed as ...
The earth rotates on an imaginary line called a(n)
... place for gas exchange, and carrying food up the stem c. anchoring the soil, storing food, and taking in minerals and water d. holding the flower up, preventing erosion, and anchoring the soil What substance enters the leaf through the stomata? ...
... place for gas exchange, and carrying food up the stem c. anchoring the soil, storing food, and taking in minerals and water d. holding the flower up, preventing erosion, and anchoring the soil What substance enters the leaf through the stomata? ...
Chapter 4: Ecosystems: Components, Energy Flow, Matter Cycling
... measures the different forms of life and lifesustaining processes found in ecosystems. There are several types: Genetic diversity: genetic make-up Species diversity: number of different species in a given habitat Ecological diversity: diversity of biological communities ...
... measures the different forms of life and lifesustaining processes found in ecosystems. There are several types: Genetic diversity: genetic make-up Species diversity: number of different species in a given habitat Ecological diversity: diversity of biological communities ...
Definition • An experimental science to describe physiological
... • High concentrations of salts in soil solutions or aquatic environments may depress their water potential to such an extent that plants cannot obtain sufficient water to germinate or grow • Some desert plants growing in saline soils can accumulate salt concentrations of 20–50% dry weight in their l ...
... • High concentrations of salts in soil solutions or aquatic environments may depress their water potential to such an extent that plants cannot obtain sufficient water to germinate or grow • Some desert plants growing in saline soils can accumulate salt concentrations of 20–50% dry weight in their l ...
Envirothon Current Issue Study Guide Notes
... provides extensive knowledge of existing and possible states, transitions, thresholds or other barriers to change, opportunities for management intervention, and what changes can occur through mismanagement range site became ecological site due to more knowledge gained in US site descriptions ...
... provides extensive knowledge of existing and possible states, transitions, thresholds or other barriers to change, opportunities for management intervention, and what changes can occur through mismanagement range site became ecological site due to more knowledge gained in US site descriptions ...
Ch. 13 Notes-Sections 1 to 4
... • An organism may have multiple feeding relationships in an ecosystem. • A food web emphasizes complicated feeding relationships and energy flow in an ecosystem. ...
... • An organism may have multiple feeding relationships in an ecosystem. • A food web emphasizes complicated feeding relationships and energy flow in an ecosystem. ...
Biogeochemical Cycles
... • Where does all this carbon come from? – Buried in sedimentary rocks – Fossil fuels – Oceans (bicarbonate and carbonate ions) – Terrestrial systems (biomass) • Believed now to be a sink which means what to us? ...
... • Where does all this carbon come from? – Buried in sedimentary rocks – Fossil fuels – Oceans (bicarbonate and carbonate ions) – Terrestrial systems (biomass) • Believed now to be a sink which means what to us? ...
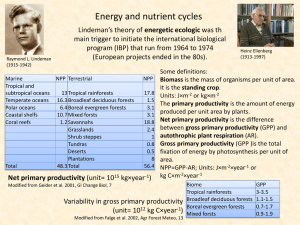
Productivity Review and Calculations
... The gain in energy/biomass per unit area per unit time remaining after allowing for respiration losses which is passed onto the herbivores. ...
... The gain in energy/biomass per unit area per unit time remaining after allowing for respiration losses which is passed onto the herbivores. ...
Powerpoint
... intermediate -15o/oo isotope values. This complicated interpretation of the isotope results (model B), creating a “mixing muddle” with no unique solution, i.e., source contributions of 50/0/50 and 0/100/0 were both logically possible. To resolve this muddle, we turned to observational studies, compa ...
... intermediate -15o/oo isotope values. This complicated interpretation of the isotope results (model B), creating a “mixing muddle” with no unique solution, i.e., source contributions of 50/0/50 and 0/100/0 were both logically possible. To resolve this muddle, we turned to observational studies, compa ...
Ecology Unit Review Questions
... How is the density of a population calculated? You will be asked to be able to calculate the population density of a specific population. What factors affect population growth or decline? Don’t forget to define words like immigration vs. emigration. Understand exponential and logistic growth curves. ...
... How is the density of a population calculated? You will be asked to be able to calculate the population density of a specific population. What factors affect population growth or decline? Don’t forget to define words like immigration vs. emigration. Understand exponential and logistic growth curves. ...
Forest Management
... • Haiti’s electricity sector only covered 10% of its population in 2006 • Wood became and continues to be the principal energy source in Haiti - accounting for 70% of energy consumption • Deforestation leads to erosion – an estimated 6,000 hectares of soil lost each year to erosion (1 ha = 10,000 m2 ...
... • Haiti’s electricity sector only covered 10% of its population in 2006 • Wood became and continues to be the principal energy source in Haiti - accounting for 70% of energy consumption • Deforestation leads to erosion – an estimated 6,000 hectares of soil lost each year to erosion (1 ha = 10,000 m2 ...
Chapter22and23StudyGuide-1
... ____ 15. Population density is defined as a. an approximation of a number, based on reasonable assumptions. b. the number of individuals of a population in a specific area. c. the number of individuals moving into a population. d. the smallest level of ecological organization. ____ 16. Counting the ...
... ____ 15. Population density is defined as a. an approximation of a number, based on reasonable assumptions. b. the number of individuals of a population in a specific area. c. the number of individuals moving into a population. d. the smallest level of ecological organization. ____ 16. Counting the ...
Species Interactions: Competition
... 1. Hairston, et al. first observe that in contemporary communities fossil fuels are accumulating at a negligible rate compared to the amount of photosynthesis occurring world-wide. If decomposing plant material is not accumulated, then it is being used up. Decomposers, as a trophic level, are limite ...
... 1. Hairston, et al. first observe that in contemporary communities fossil fuels are accumulating at a negligible rate compared to the amount of photosynthesis occurring world-wide. If decomposing plant material is not accumulated, then it is being used up. Decomposers, as a trophic level, are limite ...