Chapter 7
... – Chemical messenger released from presynaptic membrane – Binds to receptor on postsynaptic membrane – Causes depolarization of postsynaptic membrane ...
... – Chemical messenger released from presynaptic membrane – Binds to receptor on postsynaptic membrane – Causes depolarization of postsynaptic membrane ...
The Nervous System Ch. 12 & 13
... closer to 0 mV and will continue to +30 mV. Means we now have more + ions in the cell than outside of the cell. Voltage-gated Na+ channels only stay open for about 1 millisecond before they close. Action potentials are all-or-none, either they will occur or not at all. Once the peak of the action po ...
... closer to 0 mV and will continue to +30 mV. Means we now have more + ions in the cell than outside of the cell. Voltage-gated Na+ channels only stay open for about 1 millisecond before they close. Action potentials are all-or-none, either they will occur or not at all. Once the peak of the action po ...
Document
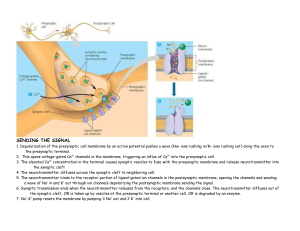
... the synaptic cleft 4. The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft to neighboring cell. 5. The neurotransmitter binds to the receptor portion of ligand–gated ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, opening the channels and sending a wave of Na+ in and K+ out through ion channels depola ...
... the synaptic cleft 4. The neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft to neighboring cell. 5. The neurotransmitter binds to the receptor portion of ligand–gated ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, opening the channels and sending a wave of Na+ in and K+ out through ion channels depola ...
Nervous System
... • This initiates an impulse in a sensory neuron • Impulse travels to the spinal cord • Impulse passes(by means of a synapse) to a connecting neuron called the relay neuron • Relay makes a synapse with one or more motor neurons that transmit the impulse to the muscles. • Causes muscles to contract an ...
... • This initiates an impulse in a sensory neuron • Impulse travels to the spinal cord • Impulse passes(by means of a synapse) to a connecting neuron called the relay neuron • Relay makes a synapse with one or more motor neurons that transmit the impulse to the muscles. • Causes muscles to contract an ...
The Nervous System
... • Bipolar: only two fibers—one dendrite and one axon • Unipolar: single fiber from the cell body which splits into dendrite and axon • Multipolar: many dendrites; one axon ...
... • Bipolar: only two fibers—one dendrite and one axon • Unipolar: single fiber from the cell body which splits into dendrite and axon • Multipolar: many dendrites; one axon ...
Nervous System ppt
... Pumps Na+ (sodium) outside & Pumps K+ (potassium) inside Membrane leaks and some K+ goes back out Resting Potential= -70mV because overall postive charge outside and negative charge inside ...
... Pumps Na+ (sodium) outside & Pumps K+ (potassium) inside Membrane leaks and some K+ goes back out Resting Potential= -70mV because overall postive charge outside and negative charge inside ...
SENSORY AND MOTOR SYSTEMS: REFLEXES
... DETECTOR(SENSORY FIBERS) • TYPE Ia NERVE FIBERS: TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT LENGTH AND VELOCITY TO THE CNS • TYPE II NERVE FIBERS:TRANSMIT ...
... DETECTOR(SENSORY FIBERS) • TYPE Ia NERVE FIBERS: TRANSMIT INFORMATION ABOUT LENGTH AND VELOCITY TO THE CNS • TYPE II NERVE FIBERS:TRANSMIT ...
The Nervous System
... • Sympathetic nerves stimulate the body in times of stress and crisis. They increase heart rate and forcefulness, dilate (relax airways so more oxygen can enter. Increase bp, stimulate adrenal glands to secrete epinephrine (adrenaline) , and inhibit intestinal contractions ...
... • Sympathetic nerves stimulate the body in times of stress and crisis. They increase heart rate and forcefulness, dilate (relax airways so more oxygen can enter. Increase bp, stimulate adrenal glands to secrete epinephrine (adrenaline) , and inhibit intestinal contractions ...
CH 12 shortened for test three nervous tissue A and P 2016
... summation = E +I results in net effect, takes place in trigger zone temporal sum=rapid input from 1 causes LPs to reach threshold and AP spatial sum = input from many add LPs to threshold and AP produced facilitation = 1 neuron makes another more likely to fire presynaptic inhibition = 1 neuron make ...
... summation = E +I results in net effect, takes place in trigger zone temporal sum=rapid input from 1 causes LPs to reach threshold and AP spatial sum = input from many add LPs to threshold and AP produced facilitation = 1 neuron makes another more likely to fire presynaptic inhibition = 1 neuron make ...
The Nervous System
... • “All or none” phenomenon…at threshold, all gates will be opened (below threshold, no extra gates will open) and stimulus is transmitted. • Additional Na+ influx causes depolarization of membrane (action potential). • K+ channels remain closed. Cell becomes positive. ...
... • “All or none” phenomenon…at threshold, all gates will be opened (below threshold, no extra gates will open) and stimulus is transmitted. • Additional Na+ influx causes depolarization of membrane (action potential). • K+ channels remain closed. Cell becomes positive. ...
Nervous System
... • Myelin sheaths surround and insulate the axon of many types of neurons; “myelinated” axons ...
... • Myelin sheaths surround and insulate the axon of many types of neurons; “myelinated” axons ...
The Nervous System
... of K, the outer environment has a high Na concentration. The neuron’s cell membrane has active Na/K gates. When an impulse comes in contact with the membrane, it turns off the gate.[polarized] Na rushes in, K leaves and the electrical impulse passes through the cell body. [wave of depolarization] Af ...
... of K, the outer environment has a high Na concentration. The neuron’s cell membrane has active Na/K gates. When an impulse comes in contact with the membrane, it turns off the gate.[polarized] Na rushes in, K leaves and the electrical impulse passes through the cell body. [wave of depolarization] Af ...
Introduction to Machine Intelligence
... Before talking to nerves and neurons it is important to know how they talk to each other. Monitor signals transmitted to a stimulus and correlate signal features with stimulus information. Most nerves communicate via Action Potentials – these are complex signals generated by ion movements across ...
... Before talking to nerves and neurons it is important to know how they talk to each other. Monitor signals transmitted to a stimulus and correlate signal features with stimulus information. Most nerves communicate via Action Potentials – these are complex signals generated by ion movements across ...
Introduction to Machine Intelligence
... Before talking to nerves and neurons it is important to know how they talk to each other. Monitor signals transmitted to a stimulus and correlate signal features with stimulus information. Most nerves communicate via Action Potentials – these are complex signals generated by ion movements across ...
... Before talking to nerves and neurons it is important to know how they talk to each other. Monitor signals transmitted to a stimulus and correlate signal features with stimulus information. Most nerves communicate via Action Potentials – these are complex signals generated by ion movements across ...
Somatosensory 2
... The sensation of pain is caused by activation of very small diameter nerve endings. When tissue is damaged, chemical substances are released that stimulate these fibers. Some stimuli that activate nociceptors: Thermal: high heat or extreme cold Mechanical: Intense mechanical stimuli Chemical: Irrita ...
... The sensation of pain is caused by activation of very small diameter nerve endings. When tissue is damaged, chemical substances are released that stimulate these fibers. Some stimuli that activate nociceptors: Thermal: high heat or extreme cold Mechanical: Intense mechanical stimuli Chemical: Irrita ...
General design of the nervous system
... Active propagation in un-myelinated axons The action potential is continually regenerated as it travels. Depolarization activates sodium channels Can only travel in one direction - get refractory period after the action potential. ...
... Active propagation in un-myelinated axons The action potential is continually regenerated as it travels. Depolarization activates sodium channels Can only travel in one direction - get refractory period after the action potential. ...
Human Body Systems - Whitehall District Schools
... • Electrical impulse due to a chemical change along the membrane of a neuron • Resting Potential: electrical potential of the neural membrane (70mV), created by Na/K pump, creates charge difference • Threshold: Minimum level of stimulus to activate a neuron, a neuron is an all or nothing response • ...
... • Electrical impulse due to a chemical change along the membrane of a neuron • Resting Potential: electrical potential of the neural membrane (70mV), created by Na/K pump, creates charge difference • Threshold: Minimum level of stimulus to activate a neuron, a neuron is an all or nothing response • ...
Chapter 48 Worksheet
... 1. Resting Potential: 2. Stimulus: 3. Depolarization: influx of Na+ in. 4. Repolarization Outline the main steps taking place in this picture: ...
... 1. Resting Potential: 2. Stimulus: 3. Depolarization: influx of Na+ in. 4. Repolarization Outline the main steps taking place in this picture: ...
013368718X_CH31_483
... Chapter 31 Vocabulary Review For Questions 1–10, match the term with its description. ...
... Chapter 31 Vocabulary Review For Questions 1–10, match the term with its description. ...
Supporting Cells - Net Start Class
... Some of the sodium channels open and Na+ rushes into the cell causing the cytoplasm to become less negative. This is known as depolarization. If enough depolarization occurs then the cell will reach a threshold potential and additional Na+ will open. If the threshold potential is reached the ...
... Some of the sodium channels open and Na+ rushes into the cell causing the cytoplasm to become less negative. This is known as depolarization. If enough depolarization occurs then the cell will reach a threshold potential and additional Na+ will open. If the threshold potential is reached the ...
NAME: AP Biology/ Ms. Gaynor (Unit #10: Animal Physiology
... 1. Draw and label the parts of a neuron including: cell body, dendrites, nucleus, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cells, and Nodes of Ranvier. Then add arrows to your drawing to show the direction of impulse. ...
... 1. Draw and label the parts of a neuron including: cell body, dendrites, nucleus, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cells, and Nodes of Ranvier. Then add arrows to your drawing to show the direction of impulse. ...
Nervous System
... Excitable cells communicate with each other by action potential (AP) for long distance and by graded potential for short distance. *Production of both types of potentials depend upon the existence of a resting membrane potential (RMP) and the presence of certain types of ion channel. *The RMP is an ...
... Excitable cells communicate with each other by action potential (AP) for long distance and by graded potential for short distance. *Production of both types of potentials depend upon the existence of a resting membrane potential (RMP) and the presence of certain types of ion channel. *The RMP is an ...
Chapter 12 - Marion ISD
... Sodium moves into cell Threshold potential point at which impulse is triggered All or none Gates stay open for a short time then close Movement to resting potential when potassium channels open (repolarization) Hyperpolarization precedes achieving resting potential again Refractory period-membrane r ...
... Sodium moves into cell Threshold potential point at which impulse is triggered All or none Gates stay open for a short time then close Movement to resting potential when potassium channels open (repolarization) Hyperpolarization precedes achieving resting potential again Refractory period-membrane r ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.