Study Guide 1
... 7. Describe the procedures involved in the method of limits, method of adjustment, and method of constant stimuli for measuring threshold. What errors could occur? 8. Describe the two-alternative forced choice procedure for determining absolute threshold. What errors could occur? 9. In data obtained ...
... 7. Describe the procedures involved in the method of limits, method of adjustment, and method of constant stimuli for measuring threshold. What errors could occur? 8. Describe the two-alternative forced choice procedure for determining absolute threshold. What errors could occur? 9. In data obtained ...
Introduction to Anatomy
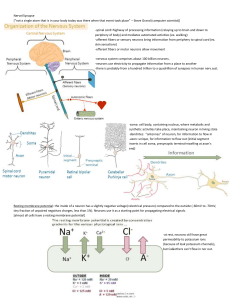
... Two Main Factors Contribute to the RMP 1. distribution of ions across the cell membrane. a. extracellular fluid is rich in Na+ and Clb. intracellular fluid is rich in K+ and anions such as organophosphates and proteins 2. relative permeability of the cell membrane to Na+ and K+ a. moderately permea ...
... Two Main Factors Contribute to the RMP 1. distribution of ions across the cell membrane. a. extracellular fluid is rich in Na+ and Clb. intracellular fluid is rich in K+ and anions such as organophosphates and proteins 2. relative permeability of the cell membrane to Na+ and K+ a. moderately permea ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the hamstring from contracting ...
... 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the hamstring from contracting ...
Power Point
... During an action potential, depolarization can change the membrane potential from –70 mV to about +30 mV. During repolarization the membrane potential returns to –70 mV. The nerve fiber cannot be stimulated again until repolarization is complete. This period is called the refractory period. If the s ...
... During an action potential, depolarization can change the membrane potential from –70 mV to about +30 mV. During repolarization the membrane potential returns to –70 mV. The nerve fiber cannot be stimulated again until repolarization is complete. This period is called the refractory period. If the s ...
Local Anesthetics
... Local anesthetics with a pKa closest to physiological pH will have a higher concentration of nonionized base that can pass through the nerve cell membrane, and generally a more rapid onset. The charged cation form more avidly binds to the Na+ channel receptors inside the cell membrane. pKa > 7.4 mor ...
... Local anesthetics with a pKa closest to physiological pH will have a higher concentration of nonionized base that can pass through the nerve cell membrane, and generally a more rapid onset. The charged cation form more avidly binds to the Na+ channel receptors inside the cell membrane. pKa > 7.4 mor ...
nervous tissue organization neurons neuroglia action potentials
... summation = Ex + In results in net effect, takes place in trigger zone temporal sum=rapid input from 1 causes LPs to reach threshold and AP spatial sum = input from many add LPs to threshold and AP produced facilitation = 1 neuron makes another more likely to fire presynaptic inhibition = 1 neuron m ...
... summation = Ex + In results in net effect, takes place in trigger zone temporal sum=rapid input from 1 causes LPs to reach threshold and AP spatial sum = input from many add LPs to threshold and AP produced facilitation = 1 neuron makes another more likely to fire presynaptic inhibition = 1 neuron m ...
Nervous System
... myelin sheath of neurons in the CNS. The sheaths deteriorate to hardened scars or plaques, in multiple regions, thus the name. The plaques interfere with nerve impulse transmission. The average age of onset is 33. The disease is unpredictable. Some people experience complete remissions, while others ...
... myelin sheath of neurons in the CNS. The sheaths deteriorate to hardened scars or plaques, in multiple regions, thus the name. The plaques interfere with nerve impulse transmission. The average age of onset is 33. The disease is unpredictable. Some people experience complete remissions, while others ...
CH 8 Nervous part 1
... Dangers of Ecstasy (MDMA) The neurotransmitter serotonin is vital in regulating many of our basic functions. Serotonin is, among other things, the feel good neurotransmitter and helps to regulate body temp. ...
... Dangers of Ecstasy (MDMA) The neurotransmitter serotonin is vital in regulating many of our basic functions. Serotonin is, among other things, the feel good neurotransmitter and helps to regulate body temp. ...
Nervous System
... There are small gaps, called nodes of Ranvier, between individual Schwann cells. Conduction velocity goes from about 5m/s without the myelin sheath to ~150m/s with it. ...
... There are small gaps, called nodes of Ranvier, between individual Schwann cells. Conduction velocity goes from about 5m/s without the myelin sheath to ~150m/s with it. ...
Homeostasis Test%28CNS%29-Tawsif Hossain
... f) Involves the sensory, inter and motor neurons only- Correct g) Requires lot of time-Incorrect- Reflex arc is very fast h) Involves voluntary control-Incorrect, is involves involuntary control. i) Composed of the central nervous system only-Incorrect, involves the peripheral nervous system as well ...
... f) Involves the sensory, inter and motor neurons only- Correct g) Requires lot of time-Incorrect- Reflex arc is very fast h) Involves voluntary control-Incorrect, is involves involuntary control. i) Composed of the central nervous system only-Incorrect, involves the peripheral nervous system as well ...
Nervous System
... The Nerve Impulse • Ungated ion channels allow ions to diffuse across the plasma membrane –These channels are always open • This diffusion does not achieve an equilibrium since sodium-potassium pumps transport these ions against their gradients ...
... The Nerve Impulse • Ungated ion channels allow ions to diffuse across the plasma membrane –These channels are always open • This diffusion does not achieve an equilibrium since sodium-potassium pumps transport these ions against their gradients ...
The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... sensory input and motor control (controls balance and equilibrium) ...
... sensory input and motor control (controls balance and equilibrium) ...
PsychSim 5 neural messages
... Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ___ Axon ...
... Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ___ Axon ...
The Nervous System
... sodium again • Potassium ions rapidly diffuse out of the neuron into the the tissue space, restoring the electrical conditions of the resting state • The neuron is now repolarized and initial sodium and potassium concentrations are restored by the Na/K pump ...
... sodium again • Potassium ions rapidly diffuse out of the neuron into the the tissue space, restoring the electrical conditions of the resting state • The neuron is now repolarized and initial sodium and potassium concentrations are restored by the Na/K pump ...
Nervous System
... membrane which sets off new action potential • Neurotransmitters are degraded by enzymes or removed by a synaptic terminal ...
... membrane which sets off new action potential • Neurotransmitters are degraded by enzymes or removed by a synaptic terminal ...
The Neural Control of Behavior
... CELL MEMBRANE: thin, porous outer covering of a neuron or other cell that separates the cell’s intracellular fluid from extracellular fluid ...
... CELL MEMBRANE: thin, porous outer covering of a neuron or other cell that separates the cell’s intracellular fluid from extracellular fluid ...
doc Nerve and synapses
... -Many types of neurotransmitters interact mainly or entirely with metabotropic receptors. These substances, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine, as well as neuropeptides like substance Y and endorphins, are often referred to as neuromodulators. They are not directly involved in the fast f ...
... -Many types of neurotransmitters interact mainly or entirely with metabotropic receptors. These substances, such as dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine, as well as neuropeptides like substance Y and endorphins, are often referred to as neuromodulators. They are not directly involved in the fast f ...
10.6: Cell Membrane Potential
... • If a neuron axon responds at all, it responds completely – with an action potential (nerve impulse) • A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon • All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength ...
... • If a neuron axon responds at all, it responds completely – with an action potential (nerve impulse) • A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon • All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength ...
The peripheral nerves
... cells, glia-like cells found along the axon. Myelin forms when a Schwann cell wraps its membrane around an axon up to 100 times. The myelin sheath envelopes the axon except at its ending and at the nodes of Ranvier The myelin has the insulating function. The loss of myelin is associated with delayed ...
... cells, glia-like cells found along the axon. Myelin forms when a Schwann cell wraps its membrane around an axon up to 100 times. The myelin sheath envelopes the axon except at its ending and at the nodes of Ranvier The myelin has the insulating function. The loss of myelin is associated with delayed ...
PsychSim - Stamford High School
... what you know about synaptic transmission, how do you think a message jumps across the synaptic gap and is passed to the next neuron? ...
... what you know about synaptic transmission, how do you think a message jumps across the synaptic gap and is passed to the next neuron? ...
nervous system ppt
... Dangers of Ecstasy (MDMA) The neurotransmitter serotonin is vital in regulating many of our basic functions. Serotonin is, among other things, the feel good neurotransmitter and helps to regulate body temp. ...
... Dangers of Ecstasy (MDMA) The neurotransmitter serotonin is vital in regulating many of our basic functions. Serotonin is, among other things, the feel good neurotransmitter and helps to regulate body temp. ...
Ch 14: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities ...
... Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities ...
chapter 48
... Astrocytes: are found within the CNS and provide structural and metabolic support as well as forming of tight junctions to help form the blood-brain barrier. They also communicate with one another via ...
... Astrocytes: are found within the CNS and provide structural and metabolic support as well as forming of tight junctions to help form the blood-brain barrier. They also communicate with one another via ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.