File
... This sentence has one main (leading) clause and one subordinate (dependent) clause; it’s a complex sentence. We also note that the subordinate clause’s verb is subjunctive, but that alone does NOT make the clause subordinate! Our next question is: How does the clause ut lūna esset plēna relate to th ...
... This sentence has one main (leading) clause and one subordinate (dependent) clause; it’s a complex sentence. We also note that the subordinate clause’s verb is subjunctive, but that alone does NOT make the clause subordinate! Our next question is: How does the clause ut lūna esset plēna relate to th ...
A Structural Account of English Tenseless Clausal
... These verbs, as mentioned in Trask (1993: 228), are called raising verbs. The presence of these verbs leads to raising from the to-infinitive clause to the main clause. Thus, raising can be defined as the movement of the subject from the to-infinitive clause to the main clause under the conditions o ...
... These verbs, as mentioned in Trask (1993: 228), are called raising verbs. The presence of these verbs leads to raising from the to-infinitive clause to the main clause. Thus, raising can be defined as the movement of the subject from the to-infinitive clause to the main clause under the conditions o ...
the passive - englishdepartmentbaio
... They are followed by a bare infinitive in the active, but take a to-infinitive in the passive Active: Her two sisters made him clean the house Passive: He was made to clean the house by her two sisters. In the passive, let is replaced by allowed and is followed by a to-infinitive. Active: The teache ...
... They are followed by a bare infinitive in the active, but take a to-infinitive in the passive Active: Her two sisters made him clean the house Passive: He was made to clean the house by her two sisters. In the passive, let is replaced by allowed and is followed by a to-infinitive. Active: The teache ...
a brief description of english primary auxiliary verbs
... and optionally one or more auxiliary verbs. For examples, have written (one auxiliary verb), and have been written (two auxiliary verbs). There is a syntactic difference between an auxiliary verb and a main verb; that is, each has a different grammatical function within a sentence. In English, there ...
... and optionally one or more auxiliary verbs. For examples, have written (one auxiliary verb), and have been written (two auxiliary verbs). There is a syntactic difference between an auxiliary verb and a main verb; that is, each has a different grammatical function within a sentence. In English, there ...
Lección 11: Gramática
... • In Spanish, the subjunctive mood is always used in the subordinate clause when the verb in the main clause expresses the emotions of the subject, such as fear, joy, pity, hope, regret, sorrow, surprise, and anger. • Again, the subject in the subordinate clause must be different from the subject in ...
... • In Spanish, the subjunctive mood is always used in the subordinate clause when the verb in the main clause expresses the emotions of the subject, such as fear, joy, pity, hope, regret, sorrow, surprise, and anger. • Again, the subject in the subordinate clause must be different from the subject in ...
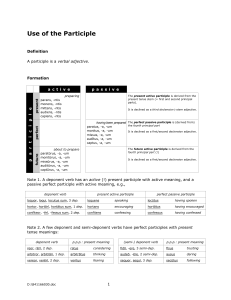
Participles
... infinitive) in the active periphrastic conjugation, e.g., paratūrus sum I am about to prepare. Note 4. A noun and a passive participle are sometimes so united that the participle and not the noun contains the main idea: ante conditam urbem before the founding of the city post nātōs hominēs since the ...
... infinitive) in the active periphrastic conjugation, e.g., paratūrus sum I am about to prepare. Note 4. A noun and a passive participle are sometimes so united that the participle and not the noun contains the main idea: ante conditam urbem before the founding of the city post nātōs hominēs since the ...
TENSE, ASPECT AND MOOD IN MESQAN MESERET ESHETU A
... i. Describe the distinction between tense and aspect. ii Identify the grammatical markers of tense, aspect and mood of the language. ii. Analyze whether Mesqan is primarily a tense or aspect language. Mesqan verbs are primarily marked for aspect, i.e. they have distinct grammatical base forms for th ...
... i. Describe the distinction between tense and aspect. ii Identify the grammatical markers of tense, aspect and mood of the language. ii. Analyze whether Mesqan is primarily a tense or aspect language. Mesqan verbs are primarily marked for aspect, i.e. they have distinct grammatical base forms for th ...
Work Book (Special English) - Madhya Pradesh Textbook Corporation
... Fill in the blanks in this story : Shravan is an orphan who came….................…..Delhi……...........................his village………….Bihar…….search……..work. His father kept a shop, but was tricked………..it……a deceitful uncle. Despair drove him……..alcohol and gambling, and he died…….a stroke soon aft ...
... Fill in the blanks in this story : Shravan is an orphan who came….................…..Delhi……...........................his village………….Bihar…….search……..work. His father kept a shop, but was tricked………..it……a deceitful uncle. Despair drove him……..alcohol and gambling, and he died…….a stroke soon aft ...
The Participle
... The indefinite forms, both active and passive, are used to express an action or a state simultaneous with that expressed by the predicate of the sentence. She leaned against the gate pretending to read the morning paper. The perfect forms, both active and passive, express an action or a state which ...
... The indefinite forms, both active and passive, are used to express an action or a state simultaneous with that expressed by the predicate of the sentence. She leaned against the gate pretending to read the morning paper. The perfect forms, both active and passive, express an action or a state which ...
The Acquisition of English Locative Constructions by Native
... consistent verb semantics-syntax correspondences, and knowing these regularities can help an L2 learner assign correct syntactic structures to verbs. For example, if a learner understands that mental verbs such as “think,” “know,” and “hope” take a sentential argument, then he or she can use this me ...
... consistent verb semantics-syntax correspondences, and knowing these regularities can help an L2 learner assign correct syntactic structures to verbs. For example, if a learner understands that mental verbs such as “think,” “know,” and “hope” take a sentential argument, then he or she can use this me ...
Тема 6 THE PASSIVE VOICE The voice is one of the categories of
... His last film is much talked about. His jokes are always laughed at. Notice that the prepositional passive construction is not used with such verbs as: to explain, to point out, to announce, to dedicate, to devote, to say, to suggest, to propose; They take two objects, direct and prepositional in ac ...
... His last film is much talked about. His jokes are always laughed at. Notice that the prepositional passive construction is not used with such verbs as: to explain, to point out, to announce, to dedicate, to devote, to say, to suggest, to propose; They take two objects, direct and prepositional in ac ...
Summary of New Testament Greek Structure
... Classical Greek had a velar nasal sound [ŋ], which only occurred before velar phonemes (γ, κ, χ, ξ), and was always spelled γ. The orthography implies that this sound was an allophone of γ, rather than of ν. Linguistically this is possible; however, the linguistic evidence also makes it possible to ...
... Classical Greek had a velar nasal sound [ŋ], which only occurred before velar phonemes (γ, κ, χ, ξ), and was always spelled γ. The orthography implies that this sound was an allophone of γ, rather than of ν. Linguistically this is possible; however, the linguistic evidence also makes it possible to ...
The Indo-Uralic verb
... The Proto-Uralic pronouns 1sg. *mi, 2sg. *ti (later *mu, *tu with the suffix *-u ‘self’), 1pl. *me, 2pl. *te (later *me-i, *te-i with the plural ending *-i) are attested in the corresponding personal endings *-mi, *-ti, *-me, *-te (cf. Collinder 1960: 243, 308, Raun 1988: 562), which can be identifi ...
... The Proto-Uralic pronouns 1sg. *mi, 2sg. *ti (later *mu, *tu with the suffix *-u ‘self’), 1pl. *me, 2pl. *te (later *me-i, *te-i with the plural ending *-i) are attested in the corresponding personal endings *-mi, *-ti, *-me, *-te (cf. Collinder 1960: 243, 308, Raun 1988: 562), which can be identifi ...
On the Argument Structure of Verbs with Bi
... a solution which does not look attractive to us. Alternatively, these verbs could basically be result verbs, which, however, can be coerced into mono-eventive (manner) verbs. Below, we will investigate this second hypothesis and show that this cannot explain the behavior of defeasible causatives. Th ...
... a solution which does not look attractive to us. Alternatively, these verbs could basically be result verbs, which, however, can be coerced into mono-eventive (manner) verbs. Below, we will investigate this second hypothesis and show that this cannot explain the behavior of defeasible causatives. Th ...
Tense in Basque - Create and Use Your home.uchicago.edu Account
... realization of Asp. In fact, as I argue in §5, there is evidence that neither of the participial suffixes described so far are the realization of Asp. As I show there, these suffixes are better described as fulfilling certain morphosyntactic requirements imposed on non-finite verbal forms.This part ...
... realization of Asp. In fact, as I argue in §5, there is evidence that neither of the participial suffixes described so far are the realization of Asp. As I show there, these suffixes are better described as fulfilling certain morphosyntactic requirements imposed on non-finite verbal forms.This part ...
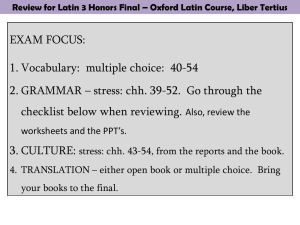
Final Review PowerPoint
... All forms of the infinitives per conjugation (see list on page 149) Alternate future infinitive of sum: fore = futūrus/a/um esse (page 149 & 164) Note the infinitives of deponent verbs and, as always, their passive forms, but active meanings (page 149) Verbs which introduce indirect statemen ...
... All forms of the infinitives per conjugation (see list on page 149) Alternate future infinitive of sum: fore = futūrus/a/um esse (page 149 & 164) Note the infinitives of deponent verbs and, as always, their passive forms, but active meanings (page 149) Verbs which introduce indirect statemen ...
A temporal semantics for Malayalam Conjunctive Participle
... The name Conjunctive/Adverbial Participle comes from the two ways these constructions can be translated, either as participle adjuncts serving an adverbial type function, (3), or as conjoined sentences, (2). While they are sometimes translated using conjunction, they are different than ‘genuinely’ c ...
... The name Conjunctive/Adverbial Participle comes from the two ways these constructions can be translated, either as participle adjuncts serving an adverbial type function, (3), or as conjoined sentences, (2). While they are sometimes translated using conjunction, they are different than ‘genuinely’ c ...
Working with VERBALS: Participles / infinitives / gerunds
... More exercises for verbals: participles / infinitives / gerunds Identify the underlined part of speech. After completing the entire exercise, click on the "Are You Prepared?" button at the bottom of this page to see the answers. 1. The thief arrested for the robbery shot at the security guard. a. g ...
... More exercises for verbals: participles / infinitives / gerunds Identify the underlined part of speech. After completing the entire exercise, click on the "Are You Prepared?" button at the bottom of this page to see the answers. 1. The thief arrested for the robbery shot at the security guard. a. g ...
Irregular Verbs
... can accompany auxiliary verbs including the three main ones: do, be, and have. Sometimes actions or conditions occur only one time and then they’re over. It’s at times like these that some of the same verbs that are used as auxiliary verbs are instead used as action or linking verbs. In this example ...
... can accompany auxiliary verbs including the three main ones: do, be, and have. Sometimes actions or conditions occur only one time and then they’re over. It’s at times like these that some of the same verbs that are used as auxiliary verbs are instead used as action or linking verbs. In this example ...
Abstract
... while the perfective aspect allows for four tenses: - perfectum (obljubil sem, 'I have promised'(PF)), - plusquamperfectum (obljubil sem bil, 'I had promised'(PF)), - futurum exactum (obljubil bom 'I will promise’(PF)), - aorist (obljubim, 'I promise’(PF)). One thing is certain for Skrabec (1887:VII ...
... while the perfective aspect allows for four tenses: - perfectum (obljubil sem, 'I have promised'(PF)), - plusquamperfectum (obljubil sem bil, 'I had promised'(PF)), - futurum exactum (obljubil bom 'I will promise’(PF)), - aorist (obljubim, 'I promise’(PF)). One thing is certain for Skrabec (1887:VII ...
El Primer Paso
... ______ the difference between SABER and CONOCER ______ expressions followed by infinitives to express what needs to be done ______ the preterite of regular –AR, -ER, -IR verbs ______ the preterite of HACER and IR ...
... ______ the difference between SABER and CONOCER ______ expressions followed by infinitives to express what needs to be done ______ the preterite of regular –AR, -ER, -IR verbs ______ the preterite of HACER and IR ...
Grace Theological Journal 5.2 (1984) 163
... attributive or predicate. This does not mean that such functions are not present; it only means that they cannot be determined by position. No attempt is made in this study to ascertain the function of these participles. The statistical chart will show that the N P pattern is more common; the P N pa ...
... attributive or predicate. This does not mean that such functions are not present; it only means that they cannot be determined by position. No attempt is made in this study to ascertain the function of these participles. The statistical chart will show that the N P pattern is more common; the P N pa ...
The Classification of Participles: A Statistical Study
... attributive or predicate. This does not mean that such functions are not present; it only means that they cannot be determined by position. No attempt is made in this study to ascertain the function of these participles. The statistical chart will show that the N P pattern is more common; the P N pa ...
... attributive or predicate. This does not mean that such functions are not present; it only means that they cannot be determined by position. No attempt is made in this study to ascertain the function of these participles. The statistical chart will show that the N P pattern is more common; the P N pa ...
Language reference
... If I had sold my shares in May, I would have made a good profit. 6 When the past situation is negative, the effect is sometimes to congratulate ourselves or others for the actions they took. This can also happen with past situations that are not grammatically negative, but which are seen as undesirab ...
... If I had sold my shares in May, I would have made a good profit. 6 When the past situation is negative, the effect is sometimes to congratulate ourselves or others for the actions they took. This can also happen with past situations that are not grammatically negative, but which are seen as undesirab ...
1. Taxonomic categories
... narisovat' `to draw ' are accomplishments; but where does
the corresponding Ipfvs belong? Vendler's classification has no room for them.
Problem 2 was elegantly posed by M. Flier: delimitatives (pospat' `sleep for
a while', pokurit' `smoke for a while') are not accomplishments ...
... narisovat'