NervousSystem2
... boutons, is subject to excitatory and inhibitory stimulation. When conditions of time and proximity of excitation result in threshold stimulation, it “fires” and carries impulses (the excitatory state) to all of its synapses. If it is an excitatory interneuron, every one of these synapses will be e ...
... boutons, is subject to excitatory and inhibitory stimulation. When conditions of time and proximity of excitation result in threshold stimulation, it “fires” and carries impulses (the excitatory state) to all of its synapses. If it is an excitatory interneuron, every one of these synapses will be e ...
Chapter 2 - davis.k12.ut.us
... D) action potential. E) refractory period. 8. Increasing excitatory signals above the threshold for neural activation will not affect the intensity of an action potential. This indicates that a neuron's reaction is A) inhibited by the myelin sheath. B) delayed by the refractory period. C) an all-or- ...
... D) action potential. E) refractory period. 8. Increasing excitatory signals above the threshold for neural activation will not affect the intensity of an action potential. This indicates that a neuron's reaction is A) inhibited by the myelin sheath. B) delayed by the refractory period. C) an all-or- ...
The Nervous System - Ridgewood High School
... When you pull the handle, water floods the bowl. This event takes a couple of seconds and you cannot stop it in the middle. Once the bowl empties, the flush is complete. Now the upper tank is empty. If you try pulling the handle at this point, nothing happens (absolute refractory). Wait for the uppe ...
... When you pull the handle, water floods the bowl. This event takes a couple of seconds and you cannot stop it in the middle. Once the bowl empties, the flush is complete. Now the upper tank is empty. If you try pulling the handle at this point, nothing happens (absolute refractory). Wait for the uppe ...
Media:oreilly_genpsych_ch2_neuron
... E = driving potential (pull down for inhibition, up for excitation) Vm = the “flag” – reflects net balance between two sides ...
... E = driving potential (pull down for inhibition, up for excitation) Vm = the “flag” – reflects net balance between two sides ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... • With inputs to dendrites, the inside becomes more positive • If resting potential rises above the sensory threshold, an action potential starts to travel from cell body down the axon • Figure shows resting axon being approached by an action potential ...
... • With inputs to dendrites, the inside becomes more positive • If resting potential rises above the sensory threshold, an action potential starts to travel from cell body down the axon • Figure shows resting axon being approached by an action potential ...
HISTOLOGY REVISIT: NEURONS AND NEUROGLIA LEARNING
... Afferent processes of neurons Have primary secondary and tertiary branches. Contains all the components of perikayon except golgi apparatus Nissal substance restricted to main stem Outer surface shows numerous small spines or knobbed out growths called gemmules these are sites of synaptic contacts. ...
... Afferent processes of neurons Have primary secondary and tertiary branches. Contains all the components of perikayon except golgi apparatus Nissal substance restricted to main stem Outer surface shows numerous small spines or knobbed out growths called gemmules these are sites of synaptic contacts. ...
Ch 3 Biopsychology & the Foundations of Neuroscience
... organisms adapt over time to their unique environments. O 4.Because the human brain is born already programmed for language, we can say that innate behavioral tendency. language is a(n) ________ The Nervous & Endocrine form the body's two O 5 .____________________ communication systems. ...
... organisms adapt over time to their unique environments. O 4.Because the human brain is born already programmed for language, we can say that innate behavioral tendency. language is a(n) ________ The Nervous & Endocrine form the body's two O 5 .____________________ communication systems. ...
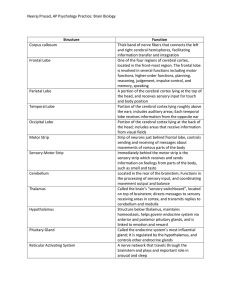
Neeraj Prasad, AP Psychology Practice: Brain Biology Structure
... A portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head, and receives sensory input for touch and body position Portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes auditory areas; Each temporal lobe receives information from the opposite ear Portion of the cerebral cortex lyi ...
... A portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head, and receives sensory input for touch and body position Portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; includes auditory areas; Each temporal lobe receives information from the opposite ear Portion of the cerebral cortex lyi ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Messages are gathered by the dendrites & cell body Transmitted along the axon in the form of a ...
... Messages are gathered by the dendrites & cell body Transmitted along the axon in the form of a ...
Powerpoint template for scientific posters (Swarthmore
... Many studies have shown the existence of large-scale plasticity in the visual, somatosensory, and auditory cortices of the brain. In addition, other research has focused on achieving a better grasp of multisensory interactions. However, these areas of neurophysiological monitoring have a great deal ...
... Many studies have shown the existence of large-scale plasticity in the visual, somatosensory, and auditory cortices of the brain. In addition, other research has focused on achieving a better grasp of multisensory interactions. However, these areas of neurophysiological monitoring have a great deal ...
The body`s information system is built from billions of interconnected
... lobes are the frontal lobe (forehead), parietal lobe (top to rear head), occipital lobe (back head) and temporal lobe (side of head). Structure of the Cortex Frontal lobe: Receives and coordinates messages from other 3 lobes; governs motor control, speech production, and higher functions such as thi ...
... lobes are the frontal lobe (forehead), parietal lobe (top to rear head), occipital lobe (back head) and temporal lobe (side of head). Structure of the Cortex Frontal lobe: Receives and coordinates messages from other 3 lobes; governs motor control, speech production, and higher functions such as thi ...
Chapter 40
... parts of the brain perform different functions. 4. Increase number of association neurons and complex synaptic contacts that allow better integration of incoming messages, provide a greater range and precision of responses. 5. Cephalization with a concentration of sense organs toward the anterior en ...
... parts of the brain perform different functions. 4. Increase number of association neurons and complex synaptic contacts that allow better integration of incoming messages, provide a greater range and precision of responses. 5. Cephalization with a concentration of sense organs toward the anterior en ...
Senses presentation
... received by receptor. • Receptors transduce (change) different forms of energy into nerve impulses • Nerve impulses are conducted to the brain – Stimulus must initiate and action potential in the cerebral cortex – The brain interprets these impulses as sound or sight even though the impulses themsel ...
... received by receptor. • Receptors transduce (change) different forms of energy into nerve impulses • Nerve impulses are conducted to the brain – Stimulus must initiate and action potential in the cerebral cortex – The brain interprets these impulses as sound or sight even though the impulses themsel ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... Neurons can also be classified by the direction that they send information: ・Sensory (or afferent) neurons: send information from sensory receptors (e.g., in skin, eyes, nose, tongue, ears) TOWARD the central nervous system. ・Motor (or efferent) neurons: send information AWAY from the central nervou ...
... Neurons can also be classified by the direction that they send information: ・Sensory (or afferent) neurons: send information from sensory receptors (e.g., in skin, eyes, nose, tongue, ears) TOWARD the central nervous system. ・Motor (or efferent) neurons: send information AWAY from the central nervou ...
The Reflex Arc
... I. Reflex – involuntary response to a stimulus. A. Stimulus – any change in the environment that causes a response (reaction). Ex: light, temperature, pressure. B. Response – the action or movement resulting from a stimulus. ...
... I. Reflex – involuntary response to a stimulus. A. Stimulus – any change in the environment that causes a response (reaction). Ex: light, temperature, pressure. B. Response – the action or movement resulting from a stimulus. ...
The First Open International Symposium
... Then, how is the spatial gradient detected in klinotaxis? Because worms sense chemicals at one point at the anterior end of the body, comparison between two sensors is unlikely. By stimulating the sensory neuron by using chanelrhodopsin in synchrony with head swing, it was suggested that spatial gra ...
... Then, how is the spatial gradient detected in klinotaxis? Because worms sense chemicals at one point at the anterior end of the body, comparison between two sensors is unlikely. By stimulating the sensory neuron by using chanelrhodopsin in synchrony with head swing, it was suggested that spatial gra ...
Strategies for drug delivery through the blood
... • Protects the brain from “foreign substances” in the blood that my injure the brain • Protects the brain from hormones and neurotransmitters in the rest of the body • Maintains a constant environment for the brain ...
... • Protects the brain from “foreign substances” in the blood that my injure the brain • Protects the brain from hormones and neurotransmitters in the rest of the body • Maintains a constant environment for the brain ...
AP Biology Animal Form and Function
... effectors (target cells) that produce some kind of response. For example, motor neurons may stimulate muscles, sweat glands (to cool the body) or cells in the stomach (to secrete gastrin in response to the smell of food). ...
... effectors (target cells) that produce some kind of response. For example, motor neurons may stimulate muscles, sweat glands (to cool the body) or cells in the stomach (to secrete gastrin in response to the smell of food). ...
Guided notes 2 Histology - Liberty Union High School District
... Schwann cells layer around the axon and squeeze the cytoplasm out of themselves leave layers of__________________ ___________________surrounding the axion. This layer is called the ______________________________________. This is discontinuous…so there are spaces with no sheath. These areas are calle ...
... Schwann cells layer around the axon and squeeze the cytoplasm out of themselves leave layers of__________________ ___________________surrounding the axion. This layer is called the ______________________________________. This is discontinuous…so there are spaces with no sheath. These areas are calle ...
Human Nervous System
... - transmit impulses from the receptors to the spinal cord and brain interneurons - relay impulses between sensory and motor neurons or between other interneurons motor neurons - transmit impulses from the spinal cord to the effectors ...
... - transmit impulses from the receptors to the spinal cord and brain interneurons - relay impulses between sensory and motor neurons or between other interneurons motor neurons - transmit impulses from the spinal cord to the effectors ...
CHAPTER 28 Nervous Systems
... An action potential is a nerve signal – It is an electrical change in the plasma membrane voltage from the resting potential to a maximum level and back to the resting potential ...
... An action potential is a nerve signal – It is an electrical change in the plasma membrane voltage from the resting potential to a maximum level and back to the resting potential ...
Specific and Nonspecific Plasticity of the Primary
... • MGBm neurons of the guinea pig show a BF shift for conditioning. Does this mean that they evoke the cortical BF shift? It had not been examined whether electric stimulation of the MGBm of the guinea pig evoked the cortical BF shift. ...
... • MGBm neurons of the guinea pig show a BF shift for conditioning. Does this mean that they evoke the cortical BF shift? It had not been examined whether electric stimulation of the MGBm of the guinea pig evoked the cortical BF shift. ...
Chapter Two Part Three - K-Dub
... Input: Sensory cortex (Left hemisphere section receives input from the body’s right side) ...
... Input: Sensory cortex (Left hemisphere section receives input from the body’s right side) ...