Nervous System
... Nerve Cell Body (Soma) Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus Is the major biosynthetic center Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature) Contains an axon hillock – cone-shaped area from which ...
... Nerve Cell Body (Soma) Contains the nucleus and a nucleolus Is the major biosynthetic center Is the focal point for the outgrowth of neuronal processes Has no centrioles (hence its amitotic nature) Contains an axon hillock – cone-shaped area from which ...
Module 3 - DHS Home
... • The mixing of + and – ions (Union of Opposites) causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more Sodium-Na) while closing the original portal. • Positive Potassium (K) is pumped out AS THE PROCESS OCCURS DOWN THE AXON and now the neuron is in a state of ...
... • The mixing of + and – ions (Union of Opposites) causes an electrical charge that opens up the next portal (letting in more Sodium-Na) while closing the original portal. • Positive Potassium (K) is pumped out AS THE PROCESS OCCURS DOWN THE AXON and now the neuron is in a state of ...
Chapter 28: Nervous System
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
I. Introduction to class
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
... 3. Motor Output: Conduction of signals from brain or spinal cord to effector organs (muscles or glands). Controls the activity of muscles and glands, and allows the animal to respond to its ...
Bio 111 Lab 8: The Nervous System and the Senses
... The visible structure of the ear, the pinna, collects sound waves from the environment, and channels them down the auditory canal to the eardrum (also called tympanic membrane). Sound waves cause the ear drum to vibrate, which moves a delicate hinge mechanism made of three tiny bones: the hammer, an ...
... The visible structure of the ear, the pinna, collects sound waves from the environment, and channels them down the auditory canal to the eardrum (also called tympanic membrane). Sound waves cause the ear drum to vibrate, which moves a delicate hinge mechanism made of three tiny bones: the hammer, an ...
Nervous System - Academic Computer Center
... Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body’s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth, development and reproduction ...
... Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body’s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth, development and reproduction ...
Learning, Memory and Perception.
... they express also the selective biases imposed by the physics of our world and environment: light-dark cycles, natural images and sounds, to take only a few examples, are not randomly distributed; they have quite specific statistics—far from randomness—to which our nervous systems are adapted. This ...
... they express also the selective biases imposed by the physics of our world and environment: light-dark cycles, natural images and sounds, to take only a few examples, are not randomly distributed; they have quite specific statistics—far from randomness—to which our nervous systems are adapted. This ...
3. Explain the basic thrust of signal-detection theory. 5. Discuss the
... (a) These cells are particular about the width and orientation of a line but respond to any position in their receptive field. ...
... (a) These cells are particular about the width and orientation of a line but respond to any position in their receptive field. ...
Nervous Systems
... • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – network of nerves extending into different parts of the body – carries sensory input to the CNS and motor output away from the CNS ...
... • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) – network of nerves extending into different parts of the body – carries sensory input to the CNS and motor output away from the CNS ...
BOX 28.5 NEURAL CONTROL OF HUMAN WALKING Human
... induced by epidural electrical stimulation after a clinically complete spinal cord injury (SCI). Spontaneous involuntary rhythmic leg movements have also been reported after a clinically complete and incomplete SCI. However, even though this evidence suggests the existence of a CPG network in humans ...
... induced by epidural electrical stimulation after a clinically complete spinal cord injury (SCI). Spontaneous involuntary rhythmic leg movements have also been reported after a clinically complete and incomplete SCI. However, even though this evidence suggests the existence of a CPG network in humans ...
آلفا با دامنهي زياد
... only if the activity of the underlying neurons adds up. To add up the activity must be generated by parallel neurons. The neocortex is composed of pyramidal cells aligned in parallel. ...
... only if the activity of the underlying neurons adds up. To add up the activity must be generated by parallel neurons. The neocortex is composed of pyramidal cells aligned in parallel. ...
PDF
... the extraembryonic tissues) in embryos carrying a paternally transmitted A-repeat-deleted Xist allele. Furthermore, the normally silent paternal copy of Tsix (a negative regulator of Xist) is ectopically activated in these A-repeat-deleted embryos. The researchers suggest, therefore, that the genomi ...
... the extraembryonic tissues) in embryos carrying a paternally transmitted A-repeat-deleted Xist allele. Furthermore, the normally silent paternal copy of Tsix (a negative regulator of Xist) is ectopically activated in these A-repeat-deleted embryos. The researchers suggest, therefore, that the genomi ...
PDF
... the extraembryonic tissues) in embryos carrying a paternally transmitted A-repeat-deleted Xist allele. Furthermore, the normally silent paternal copy of Tsix (a negative regulator of Xist) is ectopically activated in these A-repeat-deleted embryos. The researchers suggest, therefore, that the genomi ...
... the extraembryonic tissues) in embryos carrying a paternally transmitted A-repeat-deleted Xist allele. Furthermore, the normally silent paternal copy of Tsix (a negative regulator of Xist) is ectopically activated in these A-repeat-deleted embryos. The researchers suggest, therefore, that the genomi ...
Answers - Mosaiced.org
... 88. towards eqm potential for Na+ (ie. becomes more positive) 89. ++++ reduction in membrane permeability to Na+. Increase in membrane permeability to K+. 90. Open. Open. 91. Period during which Na+ channels will not open in response to stimulus, however large. Therefore no action potentials can be ...
... 88. towards eqm potential for Na+ (ie. becomes more positive) 89. ++++ reduction in membrane permeability to Na+. Increase in membrane permeability to K+. 90. Open. Open. 91. Period during which Na+ channels will not open in response to stimulus, however large. Therefore no action potentials can be ...
11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... neurotransmitter, and spatial summation, which occurs when the postsynaptic cell is stimulated at the same time by multiple terminals. ...
... neurotransmitter, and spatial summation, which occurs when the postsynaptic cell is stimulated at the same time by multiple terminals. ...
Neuroplasticity - Bakersfield College
... Totipotent – earliest cells have the ability to become any type of body cell Multipotent – with development, neural plate cells are limited to becoming one of the range of mature nervous system cells ...
... Totipotent – earliest cells have the ability to become any type of body cell Multipotent – with development, neural plate cells are limited to becoming one of the range of mature nervous system cells ...
Chapter 32 The Nervous System, Cells of the Nervous System
... (not conducting an impulse) Cell membrane is polarized (charged). Resting potential = -70 mV (millivolts) ...
... (not conducting an impulse) Cell membrane is polarized (charged). Resting potential = -70 mV (millivolts) ...
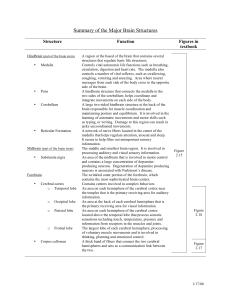
Summary of the Major Brain Structures
... integrate movements on each side of the body. A large two-sided hindbrain structure at the back of the brain responsible for muscle coordination and maintaining posture and equilibrium. It is involved in the learning of automatic movements and motor skills such as typing, or writing. Damage to this ...
... integrate movements on each side of the body. A large two-sided hindbrain structure at the back of the brain responsible for muscle coordination and maintaining posture and equilibrium. It is involved in the learning of automatic movements and motor skills such as typing, or writing. Damage to this ...
Somatic nervous system
... muscle fiber could either be excitatory or inhibitory. For vertebrates, however, the response of a muscle fiber to a neurotransmitter (always acetylcholine (ACh)) can only be excitatory. ...
... muscle fiber could either be excitatory or inhibitory. For vertebrates, however, the response of a muscle fiber to a neurotransmitter (always acetylcholine (ACh)) can only be excitatory. ...