Workshop program booklet
... its limited amount of neural resources. Such a principled framework seems particularly important for understanding complex systems, where pure descriptive models often cannot provide satisfying answers. Normative models have had great success in explaining a wide range of aspects of neural processin ...
... its limited amount of neural resources. Such a principled framework seems particularly important for understanding complex systems, where pure descriptive models often cannot provide satisfying answers. Normative models have had great success in explaining a wide range of aspects of neural processin ...
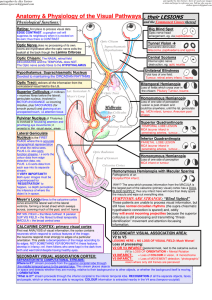
Ch 9 Sensory System
... from parts of body not actually stimulated −common with viscera pain receptors = often dull − Ex. Heart, Gallbladder, or Bladder ...
... from parts of body not actually stimulated −common with viscera pain receptors = often dull − Ex. Heart, Gallbladder, or Bladder ...
EXAM 1 Study Guide
... 2) requirements: in order for modal action pattern to develop, organism must be exposed to the sign stimulus during the critical period in the organism’s development 3) Types of stimuli: a supernormal stimulus can elicit and exaggerated response. Habituation: 1) def: Learning not to make a response ...
... 2) requirements: in order for modal action pattern to develop, organism must be exposed to the sign stimulus during the critical period in the organism’s development 3) Types of stimuli: a supernormal stimulus can elicit and exaggerated response. Habituation: 1) def: Learning not to make a response ...
Biopsychology Revision
... 1. Explain what is meant by sensory, relay and motor neurons (2 marks each) 2. With reference to neurotransmitters, explain what is meant by both excitation and inhibition (4 marks) 3. With reference to sensory, relay and motor neurons, explain the knee-jerk reflex (4 marks) 4. Explain the differenc ...
... 1. Explain what is meant by sensory, relay and motor neurons (2 marks each) 2. With reference to neurotransmitters, explain what is meant by both excitation and inhibition (4 marks) 3. With reference to sensory, relay and motor neurons, explain the knee-jerk reflex (4 marks) 4. Explain the differenc ...
File
... 5. List the four types of Neuroglial cells and their function: a. Astrocytes-their functions include the following: 1) Producing neurotransmitters 2) Maintaining potassium levels in the CNS-this aids in the production of nerve impulses. 3) These help to form the blood-brain barrier which regulates ...
... 5. List the four types of Neuroglial cells and their function: a. Astrocytes-their functions include the following: 1) Producing neurotransmitters 2) Maintaining potassium levels in the CNS-this aids in the production of nerve impulses. 3) These help to form the blood-brain barrier which regulates ...
Neuroanatomy
... processed by the brain, sent back down the spinal cord, and then back to the body with behavior instructions. The exception to this general pathway is reflexes. ...
... processed by the brain, sent back down the spinal cord, and then back to the body with behavior instructions. The exception to this general pathway is reflexes. ...
the summary and précis of the conference
... itself that gives rise to the peaks. This tells us that we really should think of ERPs as being not separate from, but rather a property of, the on-going background EEG, the continuous, spontaneous activity. The modulation of the EEG with state of arousal and attention suggest that it might reflect ...
... itself that gives rise to the peaks. This tells us that we really should think of ERPs as being not separate from, but rather a property of, the on-going background EEG, the continuous, spontaneous activity. The modulation of the EEG with state of arousal and attention suggest that it might reflect ...
Slide 1
... processed by the brain, sent back down the spinal cord, and then back to the body with behavior instructions. The exception to this general pathway is reflexes. ...
... processed by the brain, sent back down the spinal cord, and then back to the body with behavior instructions. The exception to this general pathway is reflexes. ...
The Auditory and Vestibular System
... One cycle is the distance between the waves of compression Frequency is expressed in hertz (Hz) Hearing range is 20 to 20,000 Hz. Most sensitive to frequencies ranging from 1,500 to 4,000 Hz. Decreases with age or exposure to loud sounds. There are high and low sounds that our ears cannot hear. ...
... One cycle is the distance between the waves of compression Frequency is expressed in hertz (Hz) Hearing range is 20 to 20,000 Hz. Most sensitive to frequencies ranging from 1,500 to 4,000 Hz. Decreases with age or exposure to loud sounds. There are high and low sounds that our ears cannot hear. ...
2_Vision
... Create Color? • Color does not exist in the world, only in the mind---WHOA! – color is a sensation created when light waves are transduced (I have no idea if this is the correct past tense of transduction) and then processed in our visual cortex ...
... Create Color? • Color does not exist in the world, only in the mind---WHOA! – color is a sensation created when light waves are transduced (I have no idea if this is the correct past tense of transduction) and then processed in our visual cortex ...
1 Absolute refractory period a. Time during which a second
... ARACHNOID PIA action potential jumps from node to node along the myelinated axon, 5-7X faster, uses less ATP energy BETWEEN THE SKULL AND THE DURA MATTER. converts stimuli into nerve impulses (excitability), limited mitosis A HORIZONTAL REFLECTION OF THE DURA BETWEEN THE OCCIPITAL LOBE OF THE CEREBR ...
... ARACHNOID PIA action potential jumps from node to node along the myelinated axon, 5-7X faster, uses less ATP energy BETWEEN THE SKULL AND THE DURA MATTER. converts stimuli into nerve impulses (excitability), limited mitosis A HORIZONTAL REFLECTION OF THE DURA BETWEEN THE OCCIPITAL LOBE OF THE CEREBR ...
Melting the Iceberg
... quite a bit about is circuitry, we understand the basic response properties of its neurons, and we have a fairly clear idea of the computations that it performs. These computations are complex enough to be interesting and yet simple enough to study in detail. The property of V1 neurons that has capt ...
... quite a bit about is circuitry, we understand the basic response properties of its neurons, and we have a fairly clear idea of the computations that it performs. These computations are complex enough to be interesting and yet simple enough to study in detail. The property of V1 neurons that has capt ...
Intrinsic firing patterns of diverse neocortical neurons
... As their name implies, the neurons most commonly encountered in electrophysiological studies generate what Mountcastle and his colleagues TM were the first to call 'regular' action potentials. Most published intracellular recordings from neocortex in vivo have been from RS neurons (e.g. Refs 5, 6). ...
... As their name implies, the neurons most commonly encountered in electrophysiological studies generate what Mountcastle and his colleagues TM were the first to call 'regular' action potentials. Most published intracellular recordings from neocortex in vivo have been from RS neurons (e.g. Refs 5, 6). ...
Structure of the Brain
... - Laminae (6 total layers running parallel to the cerebral cortex) - Columns of cells run perpendicular to the laminae - Occipital lobe (located at the posterior CC. AKA primary visual cortex) - Parietal lobe (located between the occipital and central sulcus. Contains the central sulcus and the pos ...
... - Laminae (6 total layers running parallel to the cerebral cortex) - Columns of cells run perpendicular to the laminae - Occipital lobe (located at the posterior CC. AKA primary visual cortex) - Parietal lobe (located between the occipital and central sulcus. Contains the central sulcus and the pos ...
Visual pathways pathology
... put together by Alex Yartsev: Sorry if i used your images or data and forgot to reference you. Tell me who you are. [email protected] ...
... put together by Alex Yartsev: Sorry if i used your images or data and forgot to reference you. Tell me who you are. [email protected] ...
4/12 - bio.utexas.edu
... Nerves allow us to perceive the environment while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. Fig 46.1 ...
... Nerves allow us to perceive the environment while the brain integrates the incoming signals to determine an appropriate response. Fig 46.1 ...
Retina Rods retina receptors that detect black, white, and gray
... Rods retina receptors that detect black, white, and gray; needed for peripheral and twilight vision Cones function in daylight /well-lit conditions. The cones detect detail, give rise to color sensations. Optic nerve carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain. Blind spot point at which optic ...
... Rods retina receptors that detect black, white, and gray; needed for peripheral and twilight vision Cones function in daylight /well-lit conditions. The cones detect detail, give rise to color sensations. Optic nerve carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain. Blind spot point at which optic ...
Graded Potential - wquerryeducation
... • hyperpolarizes postsynaptic neuron • AP of postsynaptic neuron becomes less likely ...
... • hyperpolarizes postsynaptic neuron • AP of postsynaptic neuron becomes less likely ...
The Nervous System Ch. 12 & 13
... Impaired nerve conduction, loss of coordination, visual impairment and speech disturbances. Most common in women 20-40. Caused by autoimmunity or a viral infection. ...
... Impaired nerve conduction, loss of coordination, visual impairment and speech disturbances. Most common in women 20-40. Caused by autoimmunity or a viral infection. ...
Electrophysiological Methods for Mapping Brain Motor and Sensory
... Sensory vs. Motor Mapping Sensory Maps • Mapping a specific sensory parameter to a brain region • One input variable: Stimulus • One output measure: unit recording from region of interest • One anatomical map and one functional map • Receptive fields: naturally occurring stimulus modality to ...
... Sensory vs. Motor Mapping Sensory Maps • Mapping a specific sensory parameter to a brain region • One input variable: Stimulus • One output measure: unit recording from region of interest • One anatomical map and one functional map • Receptive fields: naturally occurring stimulus modality to ...
Nervous system Nervous system
... • Nervous tissue consists of neurons; whereas the brain and spinal cord contain all parts of neurons, nerves contain only axons. ...
... • Nervous tissue consists of neurons; whereas the brain and spinal cord contain all parts of neurons, nerves contain only axons. ...
File - biology4friends
... E.1.2 Explain the role of receptors, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram if the reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neu ...
... E.1.2 Explain the role of receptors, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram if the reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neu ...
The Brain - Science Leadership Academy
... • The cerebrum is responsible for 85% of the weight of the brain. ...
... • The cerebrum is responsible for 85% of the weight of the brain. ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... toward the receptive field increased, and that for saccades away decreased as function of local fractional income, resulting in more reliable spatial selectivity (difference between the two saccade directions) with increasing reward probability. (B) LIP neurons are modulated by limb motor planning. ...
... toward the receptive field increased, and that for saccades away decreased as function of local fractional income, resulting in more reliable spatial selectivity (difference between the two saccade directions) with increasing reward probability. (B) LIP neurons are modulated by limb motor planning. ...
Mysteries of Development
... that is, there is a large difference in its concentration from one cell to another—then cells continue to divide. As cells divide, the gradient becomes more gradual. Once it has flattened out to a particular level, cells stop dividing. There is also evidence that a cell’s sense of which direction is ...
... that is, there is a large difference in its concentration from one cell to another—then cells continue to divide. As cells divide, the gradient becomes more gradual. Once it has flattened out to a particular level, cells stop dividing. There is also evidence that a cell’s sense of which direction is ...