PDF
... different types of CN neurons and for all recorded cells are presented in Fig. 3. The large majority of cells (18 of 23; 78%) responded with latencies ranging from 3 to 9 ms, whereas ®ve neurons exhibited IPSPs with latencies of 13.5 ms or longer. Our previous studies of central vestibular networks, ...
... different types of CN neurons and for all recorded cells are presented in Fig. 3. The large majority of cells (18 of 23; 78%) responded with latencies ranging from 3 to 9 ms, whereas ®ve neurons exhibited IPSPs with latencies of 13.5 ms or longer. Our previous studies of central vestibular networks, ...
pg 6 - Advanced Targeting Systems
... RNA substrates to assay adenine-specific RNA N-glycosidases, one of which is saporin (Cat. #PR-01). The RNA substrates are annealed to a ruthenylated oligodeoxynucleotide, allowing the capture of ruthenium chelate on magnetic beads. The N-glycosidase activity can then be detected by enzymelinked che ...
... RNA substrates to assay adenine-specific RNA N-glycosidases, one of which is saporin (Cat. #PR-01). The RNA substrates are annealed to a ruthenylated oligodeoxynucleotide, allowing the capture of ruthenium chelate on magnetic beads. The N-glycosidase activity can then be detected by enzymelinked che ...
Chapter 3
... • Motor cortex is just posterior • Followed by Central Sulcus • Function: • Motor nerves from left motor cortex control right side of the body • Broca’s area very important in speech production • Until 1960s, pre-frontal lobotomy was surgery that intended to minimize dysfunction and calm moods of me ...
... • Motor cortex is just posterior • Followed by Central Sulcus • Function: • Motor nerves from left motor cortex control right side of the body • Broca’s area very important in speech production • Until 1960s, pre-frontal lobotomy was surgery that intended to minimize dysfunction and calm moods of me ...
Chapter 5b
... – Positively charged sodium – Positively charged potassium – Negatively charged chloride ions – Other negatively charged proteins. ...
... – Positively charged sodium – Positively charged potassium – Negatively charged chloride ions – Other negatively charged proteins. ...
A Brief History of the Discovery of the Neuron Based on the History
... functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are discrete cells which are not continuous with other cells. The neuron is composed of 3 parts – the dendrites, axon and cell body. Information flows along the neuron in one direction (from the dendrites to the axon, via the cell body). ...
... functional unit of the nervous system. Neurons are discrete cells which are not continuous with other cells. The neuron is composed of 3 parts – the dendrites, axon and cell body. Information flows along the neuron in one direction (from the dendrites to the axon, via the cell body). ...
Nervous System
... The preganglionic (first) neuron has a lightly myelinated axon. The ganglionic (second) unmyelinated neuron extends to an effector organ via the postganglionic axon ...
... The preganglionic (first) neuron has a lightly myelinated axon. The ganglionic (second) unmyelinated neuron extends to an effector organ via the postganglionic axon ...
Ch 8 Nervous System Test 1. In a neuron, short, branching
... 4. Gaps between segments of oligodendrocytes or between individual Schwann cells are called a. ganglia. b. microglia. c. nodes of Ranvier. d. ependymal cells. e. nerve tracts. 5. White matter of the central nervous system a. is formed by nerve cell bodies and their dendrites. b. is formed by bundles ...
... 4. Gaps between segments of oligodendrocytes or between individual Schwann cells are called a. ganglia. b. microglia. c. nodes of Ranvier. d. ependymal cells. e. nerve tracts. 5. White matter of the central nervous system a. is formed by nerve cell bodies and their dendrites. b. is formed by bundles ...
Laboratory 9: Pons to Midbrain MCB 163 Fall 2005 Slide #108 1
... The pontine nuclei are the gateway from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellar cortex (cerebropontocerebellar, anyone?). These fibers arise largely in prefrontal, premotor, and many other cortical areas. Their target is the cerebrocerebellum (the lateral hemispheres). The structures are much bigger i ...
... The pontine nuclei are the gateway from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellar cortex (cerebropontocerebellar, anyone?). These fibers arise largely in prefrontal, premotor, and many other cortical areas. Their target is the cerebrocerebellum (the lateral hemispheres). The structures are much bigger i ...
Sparse Neural Systems: The Ersatz Brain gets Thin
... well in sparse systems. Let us our Network of Networks approximation and see if we can do better. Network of Networks: the basic computing units are not neurons, but small (104 neurons) attractor networks. Basic Network of Networks ...
... well in sparse systems. Let us our Network of Networks approximation and see if we can do better. Network of Networks: the basic computing units are not neurons, but small (104 neurons) attractor networks. Basic Network of Networks ...
Review for Quiz 2 Fixed Action Pattern Types of neurons Anatomy of
... Define and know examples of the following types of rhythms Ultradian Infradian Circadian Circannual Exogenous vs. Endogenous rhythms Free running rhythms Entrainment & Zeitgeiber What is the SCN and where ...
... Define and know examples of the following types of rhythms Ultradian Infradian Circadian Circannual Exogenous vs. Endogenous rhythms Free running rhythms Entrainment & Zeitgeiber What is the SCN and where ...
Name________________________ Midterm #1 Biology 3330, Fall
... 2) (6pts) A transformation in the representation of visual information occurs between the ...
... 2) (6pts) A transformation in the representation of visual information occurs between the ...
Central Nervous System
... VITAL CENTERS (CV and Vasomotor center) Cardiovascular center (rate/force of heart) diameter = _______________ Respiratory center: adjust basic rhythm of breathing Reflex: vomit, cough, sneeze, swallow Reticular formation: gray matter from spine to thalamus Keeps ____________________________________ ...
... VITAL CENTERS (CV and Vasomotor center) Cardiovascular center (rate/force of heart) diameter = _______________ Respiratory center: adjust basic rhythm of breathing Reflex: vomit, cough, sneeze, swallow Reticular formation: gray matter from spine to thalamus Keeps ____________________________________ ...
The Visual System: From Eye to Cortex - U
... vertebrates, most mammals have two eyes on the front of their heads, rather than one on each side; this cuts down the field of view, but it insures that most of what is seen is seen through both eyes ...
... vertebrates, most mammals have two eyes on the front of their heads, rather than one on each side; this cuts down the field of view, but it insures that most of what is seen is seen through both eyes ...
Vocal communication between male Xenopus laevis
... dyes have strong affinities for components of the cell body such as the Nissl substance or cytoplasmic RNA (Nissl stains include cresyl violet and neutral red). Slide 17 This is a transverse section through a song bird forebrain that has been stained with cresyl violet. Each individual purple dot i ...
... dyes have strong affinities for components of the cell body such as the Nissl substance or cytoplasmic RNA (Nissl stains include cresyl violet and neutral red). Slide 17 This is a transverse section through a song bird forebrain that has been stained with cresyl violet. Each individual purple dot i ...
Chapter 18: Senses - Johnston Community College
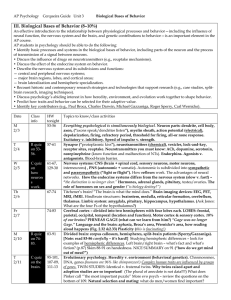
... Sensation occurs when nerve impulses reach the cerebral cortex. Perception is an interpretation of the meaning of sensations. The sensation that results depends on the part of the brain receiving the impulses. Receptors may integrate signals before sending nerve impulses. Sensory adaptation occurs w ...
... Sensation occurs when nerve impulses reach the cerebral cortex. Perception is an interpretation of the meaning of sensations. The sensation that results depends on the part of the brain receiving the impulses. Receptors may integrate signals before sending nerve impulses. Sensory adaptation occurs w ...
Webquests_files/Nervous System SWQ
... Use the following website to play an interactive game. Click on Probe the Brain Activity. http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/brain/# 12. How many body parts do the section of the brain included control? ...
... Use the following website to play an interactive game. Click on Probe the Brain Activity. http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/brain/# 12. How many body parts do the section of the brain included control? ...
here - TurkoTek
... ---has four lobes, Frontal, Temporal, Parietal, Occipital --- Parietal- process sensory input from body surface; on the lobes, there is a Sensory Homunclus- little map of the body, but is strange looking. Not proportional to size but to density of sensory intervation. --- Frontal- Controls voluntary ...
... ---has four lobes, Frontal, Temporal, Parietal, Occipital --- Parietal- process sensory input from body surface; on the lobes, there is a Sensory Homunclus- little map of the body, but is strange looking. Not proportional to size but to density of sensory intervation. --- Frontal- Controls voluntary ...
At the crossroads of metabolism and reproduction in the brain
... Through elegant gene deletion-replacement experiments, Donato et al. (2011) showed that expressing functional leptin receptors exclusively in a little-studied part of the brain – the hypothalamic ventral premammillary nucleus (PMv) – is sufficient to mediate the hormone’s powerful stimulatory effect ...
... Through elegant gene deletion-replacement experiments, Donato et al. (2011) showed that expressing functional leptin receptors exclusively in a little-studied part of the brain – the hypothalamic ventral premammillary nucleus (PMv) – is sufficient to mediate the hormone’s powerful stimulatory effect ...
Document
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
CNS
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
... • the dorsal tract brings sensory information into the spinal cord and the ventral tract carries motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles, organs and glands. • the brain and spinal cord are protected by protective membrane, the meninges and surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. The Brain • ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... the lacrimal fluid into the conjunctival sac of the superior eyelid. There, the blinking motion of the eyelids “washes” the lacrimal fluid over the eyes. The lacrimal fluid drains through the lacrimal puncta into the lacrimal canaliculi. A lacrimal sac temporarily stores the fluid. The nasolacrimal ...
... the lacrimal fluid into the conjunctival sac of the superior eyelid. There, the blinking motion of the eyelids “washes” the lacrimal fluid over the eyes. The lacrimal fluid drains through the lacrimal puncta into the lacrimal canaliculi. A lacrimal sac temporarily stores the fluid. The nasolacrimal ...
Visual organ
... covers the entire lens and prevents wandering cells from penetrating it. Subcapsular epithelium. The height of this low cuboidal epithelium beneath the capsule on the anterior lens surface increases to columnar near the lens equator, where cell division occurs Lens fibers are long, narrow, hexagonal ...
... covers the entire lens and prevents wandering cells from penetrating it. Subcapsular epithelium. The height of this low cuboidal epithelium beneath the capsule on the anterior lens surface increases to columnar near the lens equator, where cell division occurs Lens fibers are long, narrow, hexagonal ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... the lacrimal fluid into the conjunctival sac of the superior eyelid. There, the blinking motion of the eyelids “washes” the lacrimal fluid over the eyes. The lacrimal fluid drains through the lacrimal puncta into the lacrimal canaliculi. A lacrimal sac temporarily stores the fluid. The nasolacrimal ...
... the lacrimal fluid into the conjunctival sac of the superior eyelid. There, the blinking motion of the eyelids “washes” the lacrimal fluid over the eyes. The lacrimal fluid drains through the lacrimal puncta into the lacrimal canaliculi. A lacrimal sac temporarily stores the fluid. The nasolacrimal ...
Unit 3 Cerqueira guide
... AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: • Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. • Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake m ...
... AP students in psychology should be able to do the following: • Identify basic processes and systems in the biological bases of behavior, including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. • Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake m ...