Neurophysiological Aspects of Song Pattern Recognition and Sound
... in songs. It must be the auditory receptors which transmit information about these gaps to the CNS, despite their inter-spike intervals often being larger than the detected gaps. Spike numbers of receptor responses to models with different gaps (Fig. 3A) do not differ in a range, where behavior show ...
... in songs. It must be the auditory receptors which transmit information about these gaps to the CNS, despite their inter-spike intervals often being larger than the detected gaps. Spike numbers of receptor responses to models with different gaps (Fig. 3A) do not differ in a range, where behavior show ...
L7-Brainstem Student..
... • (3) It has centers for Brainstem Reflexes , such as cough reflex , gag reflex , swallowing , and vomiting ; + visual & auditory orientation reflexes (required for head movements. through Superior & Inferior Colliculi ) • (4) Contributes to maintenance of body balance through the vestibular nucle ...
... • (3) It has centers for Brainstem Reflexes , such as cough reflex , gag reflex , swallowing , and vomiting ; + visual & auditory orientation reflexes (required for head movements. through Superior & Inferior Colliculi ) • (4) Contributes to maintenance of body balance through the vestibular nucle ...
Cerebral Cortex Lect
... Motor area: somatotopically organized around the cruciate sulcus. The motor area drives voluntary movement and it is the primary source of pyramidal tract fibers to cranial nerve nuclei and spinal cord (corticospinal tracts). Somatotopic organization = organization based on regional organization of ...
... Motor area: somatotopically organized around the cruciate sulcus. The motor area drives voluntary movement and it is the primary source of pyramidal tract fibers to cranial nerve nuclei and spinal cord (corticospinal tracts). Somatotopic organization = organization based on regional organization of ...
Modeling and interpretation of extracellular potentials
... Forward modelling of spikes What does an action potential look like as seen by an extracellular electrode? [neuron model from Mainen & Sejnowski, 1996] From Henze et al (2000): ...
... Forward modelling of spikes What does an action potential look like as seen by an extracellular electrode? [neuron model from Mainen & Sejnowski, 1996] From Henze et al (2000): ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-31
... o Descending motor axons from cortex and red nucleus (in midbrain) o Ascending sensory axons from body AND face Cranial nerves – V, VI, VII, VIII Cerebellar Peduncles axons linking the cerebellum & brainstem Inferior Input (ICP) – unconscious proprioception info (what you are doing) o Info fro ...
... o Descending motor axons from cortex and red nucleus (in midbrain) o Ascending sensory axons from body AND face Cranial nerves – V, VI, VII, VIII Cerebellar Peduncles axons linking the cerebellum & brainstem Inferior Input (ICP) – unconscious proprioception info (what you are doing) o Info fro ...
Encoding of Rules by Neurons in the Human Dorsolateral Prefrontal
... was applied to filter out the majority of the low-voltage background activity. Classification of action potentials was performed using template matching and principal component analysis. Putative neurons were required to separate clearly from any channel noise, to demonstrate waveform morphology consi ...
... was applied to filter out the majority of the low-voltage background activity. Classification of action potentials was performed using template matching and principal component analysis. Putative neurons were required to separate clearly from any channel noise, to demonstrate waveform morphology consi ...
Buzsaki and Draguhn (2004), Neuronal Oscillations in Cortical
... network is independent of the temporal fluctuation of sensory signals. The oscillationrelated fluctuation of the membrane potentials in the participating neurons continuously and predictably biases the open-time probability of a multitude of voltage-gated channels (9). This design is an energy-effic ...
... network is independent of the temporal fluctuation of sensory signals. The oscillationrelated fluctuation of the membrane potentials in the participating neurons continuously and predictably biases the open-time probability of a multitude of voltage-gated channels (9). This design is an energy-effic ...
Ch33 nervous system reading essentials
... covered in a myelin sheath, which is a lipid layer that protects the axon. Sodium and potassium cannot diffuse through the myelin sheath. The myelin sheath, however, has many gaps called nodes. The ions reach the cell’s plasma membrane at the nodes. The action potential jumps from node to node, incr ...
... covered in a myelin sheath, which is a lipid layer that protects the axon. Sodium and potassium cannot diffuse through the myelin sheath. The myelin sheath, however, has many gaps called nodes. The ions reach the cell’s plasma membrane at the nodes. The action potential jumps from node to node, incr ...
Core concepts - University of Arizona
... brain. (For Braille readers, nerves in the fingers send similar information from the skin up through the spinal cord to the brain.) About one fourth of the brain is involved in visual processing, more than any other sense. The precise process of reading, like many brain functions, is a topic of inte ...
... brain. (For Braille readers, nerves in the fingers send similar information from the skin up through the spinal cord to the brain.) About one fourth of the brain is involved in visual processing, more than any other sense. The precise process of reading, like many brain functions, is a topic of inte ...
Psychology - Bideford College Sixth Form
... written or typed onto the assignment. This can be printed off in school or at home. If you have any questions that arise over the summer, please email me. See you in September! Ms Thurley [email protected] The Neuron Neurons are the building blocks of our nervous system. A bundle of neu ...
... written or typed onto the assignment. This can be printed off in school or at home. If you have any questions that arise over the summer, please email me. See you in September! Ms Thurley [email protected] The Neuron Neurons are the building blocks of our nervous system. A bundle of neu ...
How Do We See the World?
... Let us return to D. B. to make another point about sensory experiences. D. B. was not consciously aware of the presence of a light in his blind area, yet he could indicate where the light was. Clearly, the brain must process visual information in multiple ways. Some ways allow us to consciously anal ...
... Let us return to D. B. to make another point about sensory experiences. D. B. was not consciously aware of the presence of a light in his blind area, yet he could indicate where the light was. Clearly, the brain must process visual information in multiple ways. Some ways allow us to consciously anal ...
Consciousness Operates Beyond the Timescale
... from simple, "extraverted" neurons in the amphibian pallium, via pyramid-like neurons in the reptilian cortex to the fully developed neocortical elements designated by Cajal as psychic cells. Typical mammalian pyramidal neurons have the following eight features in common: (1) spiny dendrites, (2) a ...
... from simple, "extraverted" neurons in the amphibian pallium, via pyramid-like neurons in the reptilian cortex to the fully developed neocortical elements designated by Cajal as psychic cells. Typical mammalian pyramidal neurons have the following eight features in common: (1) spiny dendrites, (2) a ...
nervous system - Doctor Jade Main
... reestablished, membrane cannot respond to stimuli • Refractory Period • if second stimulus is applied <0.001 second after the first, will not trigger an impulse • membrane cannot respond • all voltage regulated Na channels are open or inactivated • Absolute Refractory period • Relative refractory pe ...
... reestablished, membrane cannot respond to stimuli • Refractory Period • if second stimulus is applied <0.001 second after the first, will not trigger an impulse • membrane cannot respond • all voltage regulated Na channels are open or inactivated • Absolute Refractory period • Relative refractory pe ...
An Introduction to Artificial Neural Networks
... After each data pair is presented, the error the network produces guides the adjustment of its weights. Training continues until the error falls within an acceptable tolerance. ...
... After each data pair is presented, the error the network produces guides the adjustment of its weights. Training continues until the error falls within an acceptable tolerance. ...
Chemosensory Systems
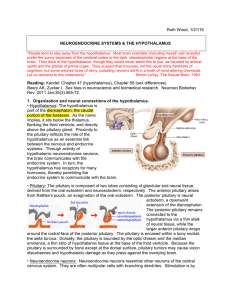
... taste qualities. 5. A secondary cortical taste area in the orbito-frontal cortex integrates taste, olfactory and visual aspects of foods. Some of its neurons respond less and less as a taste stimulus is repeatedly sampled, showing “stimulus-specific satiety.” Pathways to amygdala and hypothalamus [l ...
... taste qualities. 5. A secondary cortical taste area in the orbito-frontal cortex integrates taste, olfactory and visual aspects of foods. Some of its neurons respond less and less as a taste stimulus is repeatedly sampled, showing “stimulus-specific satiety.” Pathways to amygdala and hypothalamus [l ...
NERVOUS and ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS TEST PREVIEW
... 12. How does alcohol act on the brain? 13. How does a nerve impulse travel from one neuron to the next? 14. How does a nerve impulse travel through a single neuron? 15. What does the central nervous system include? 16. What does the peripheral nervous include? 17. Explain what happens during a refle ...
... 12. How does alcohol act on the brain? 13. How does a nerve impulse travel from one neuron to the next? 14. How does a nerve impulse travel through a single neuron? 15. What does the central nervous system include? 16. What does the peripheral nervous include? 17. Explain what happens during a refle ...
Development of glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses
... L1 immunoglobulin family, along the PC soma-AIS axis, and such gradient requires ankyrinG, a membrane adaptor protein that recruits neurofascin (Ango et al. 2004). Interestingly, another member of the same family of adhesion molecules, CHL1, is localized along Bergmann glia fibers and stellate cells ...
... L1 immunoglobulin family, along the PC soma-AIS axis, and such gradient requires ankyrinG, a membrane adaptor protein that recruits neurofascin (Ango et al. 2004). Interestingly, another member of the same family of adhesion molecules, CHL1, is localized along Bergmann glia fibers and stellate cells ...
Physiology of Proprioception in Balance
... Receptor Potential of the Pacinian Corpuscle For joint position and vibration sensation (Also Ruffini’s Endings) •The receptor potential produced by compression induces a local circuit of current flow that spreads along nerve fiber. •The frequency of repetitive action potentials transmitted from sen ...
... Receptor Potential of the Pacinian Corpuscle For joint position and vibration sensation (Also Ruffini’s Endings) •The receptor potential produced by compression induces a local circuit of current flow that spreads along nerve fiber. •The frequency of repetitive action potentials transmitted from sen ...
NSCI 525 RWood 1-22-15
... Animal studies suggest that there is a critical period during early development when steroid exposure increases the size of the sexually dimorphic nuclei. If there is no steroid hormone in the brain during this early period, the nuclei remain permanently smaller (female). Interestingly, in most case ...
... Animal studies suggest that there is a critical period during early development when steroid exposure increases the size of the sexually dimorphic nuclei. If there is no steroid hormone in the brain during this early period, the nuclei remain permanently smaller (female). Interestingly, in most case ...
Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the
... 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out signals of their own and are considered the basic building blocks of the brain’s anatomy are called neurons b. Cells that aid in the transferring ...
... 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out signals of their own and are considered the basic building blocks of the brain’s anatomy are called neurons b. Cells that aid in the transferring ...
Lower motor neuron
... • The neurons in the red nucleus are activated monosynaptically by projections from the cortex • In humans most of the efferent fibers emerging from the red nucleus terminate in the inferior olive • Ends on interneurons that, in turn, project to the dorsal aspect of ventral (motor) horn cells • F ...
... • The neurons in the red nucleus are activated monosynaptically by projections from the cortex • In humans most of the efferent fibers emerging from the red nucleus terminate in the inferior olive • Ends on interneurons that, in turn, project to the dorsal aspect of ventral (motor) horn cells • F ...
How Antidepressants Work - Rainsville Family Practice
... is missing. This process may take weeks or months to completely restore a normal amount of seratonin. This is the reason we recommend taking SSRI’s for six months before stopping them. While some people seem to benefit from continued use after six months, it is hoped that most patients will have ret ...
... is missing. This process may take weeks or months to completely restore a normal amount of seratonin. This is the reason we recommend taking SSRI’s for six months before stopping them. While some people seem to benefit from continued use after six months, it is hoped that most patients will have ret ...