Modeling and Detecting Deep Brain Activity with MEG
... brain, we speculate that a greater current density might help detect MEG/EEG signals originating from the hippocampus. 4) Basal ganglia and related structures: We have considered 4 types of neuronal architecture for these structures. While the thalamus and striatum contain mainly closedfield neural ...
... brain, we speculate that a greater current density might help detect MEG/EEG signals originating from the hippocampus. 4) Basal ganglia and related structures: We have considered 4 types of neuronal architecture for these structures. While the thalamus and striatum contain mainly closedfield neural ...
Subcircuit-specific neuromodulation in the prefrontal cortex
... Shapiro, 2007, 2009). Different components of PFC function may be mediated by different PFC subregions (well reviewed in Robbins, 1996; Uylings et al., 2003; Kesner and Churchwell, 2011). Elucidating the precise cellular constituents and mechanism(s) underlying PFC function, and how it exerts top-do ...
... Shapiro, 2007, 2009). Different components of PFC function may be mediated by different PFC subregions (well reviewed in Robbins, 1996; Uylings et al., 2003; Kesner and Churchwell, 2011). Elucidating the precise cellular constituents and mechanism(s) underlying PFC function, and how it exerts top-do ...
Chapter 13 Spinal Cord
... Pain Relief - Analgesia • Aspirin and ibuprofen block formation of prostaglandins that stimulate nociceptors • Novocaine blocks conduction of nerve impulses along pain fibers • Morphine lessens the perception of pain in the brain ...
... Pain Relief - Analgesia • Aspirin and ibuprofen block formation of prostaglandins that stimulate nociceptors • Novocaine blocks conduction of nerve impulses along pain fibers • Morphine lessens the perception of pain in the brain ...
Nervous System PPT
... neocortex is required for advanced cognition may be incorrect • The anatomical basis for sophisticated information processing in birds (without a highly convoluted neocortex) appears to be the clustering of nuclei in the top or outer portion of the brain (pallium) ...
... neocortex is required for advanced cognition may be incorrect • The anatomical basis for sophisticated information processing in birds (without a highly convoluted neocortex) appears to be the clustering of nuclei in the top or outer portion of the brain (pallium) ...
49_Lecture_Presentation
... neocortex is required for advanced cognition may be incorrect • The anatomical basis for sophisticated information processing in birds (without a highly convoluted neocortex) appears to be the clustering of nuclei in the top or outer portion of the brain (pallium) ...
... neocortex is required for advanced cognition may be incorrect • The anatomical basis for sophisticated information processing in birds (without a highly convoluted neocortex) appears to be the clustering of nuclei in the top or outer portion of the brain (pallium) ...
File
... Ca2+ flows into the presynaptic neuron increasing the amount of Ca2+ in the presynaptic neuron. This Ca2+ causes vesicles containing neurotransmitters to bind to the membrane and release their neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft (space between pre and post synaptic neuron). These neurotransmit ...
... Ca2+ flows into the presynaptic neuron increasing the amount of Ca2+ in the presynaptic neuron. This Ca2+ causes vesicles containing neurotransmitters to bind to the membrane and release their neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft (space between pre and post synaptic neuron). These neurotransmit ...
Chapter 11 ppt A
... Satellite cells and Schwann cells (which form myelin) surround neurons in the PNS. ...
... Satellite cells and Schwann cells (which form myelin) surround neurons in the PNS. ...
General Physiology
... list the main subdivisions of the nervous system describe the main structure of a neuron name the glial cells and their functions describe resting membrane potential and how it is generated • describe how changes in cell ionic movements ...
... list the main subdivisions of the nervous system describe the main structure of a neuron name the glial cells and their functions describe resting membrane potential and how it is generated • describe how changes in cell ionic movements ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
The Location and Function of NMDA Receptors in Cat
... response of each cell was tested for its sensitivity to NMDA and APV (various additional trials were conducted in most cases): (1) Visual stimuli were applied continuously throughout the experiment. After collecting control responses, (2) NMDA was ejected (usually at 10-20 nA) until the cell became ...
... response of each cell was tested for its sensitivity to NMDA and APV (various additional trials were conducted in most cases): (1) Visual stimuli were applied continuously throughout the experiment. After collecting control responses, (2) NMDA was ejected (usually at 10-20 nA) until the cell became ...
Marieb_ch7a
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
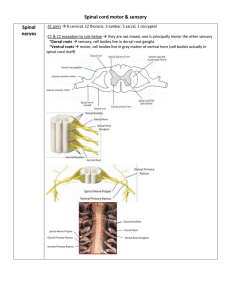
Changes in spinal cord
... -itch histamine; unmyelinated C fibers -anterolateral pathway -primary neuron in DRG -first synapse in dorsal horn of spinal cord at level it enters -receptors in peripheral tissue (bare nerve endings) input to soma in DRG; enter cord via dorsal horn; SYNAPSE at or near level of entry to dorsal ...
... -itch histamine; unmyelinated C fibers -anterolateral pathway -primary neuron in DRG -first synapse in dorsal horn of spinal cord at level it enters -receptors in peripheral tissue (bare nerve endings) input to soma in DRG; enter cord via dorsal horn; SYNAPSE at or near level of entry to dorsal ...
14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... The largest part of the brain is the cerebrum, which controls the higher mental functions such as thought, memory and conscious movement. The cerebrum is divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres, and covered by a surface layer of gray matter or neural cortex (cerebral cortex). The surface is ...
... The largest part of the brain is the cerebrum, which controls the higher mental functions such as thought, memory and conscious movement. The cerebrum is divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres, and covered by a surface layer of gray matter or neural cortex (cerebral cortex). The surface is ...
Chapter 13 - apsubiology.org
... sensory neurons respond strongly to one type of stimulus and weakly or not at all to other types some respond accidentally to other types of stimuli – rubbing one’s eyes mechanically stimulates the eyes’ light receptors in the retina ...
... sensory neurons respond strongly to one type of stimulus and weakly or not at all to other types some respond accidentally to other types of stimuli – rubbing one’s eyes mechanically stimulates the eyes’ light receptors in the retina ...
A soft-wired hypothalamus
... treatment of either positive (obesity) or negative (cachexia) energy balance. Indeed, other hypothalamic systems have also been closely synaptic inputs24. Both neuronal systems are directly targeted by leptin tied to this regulatory mechanism (for review, see refs. 3,4). These and can also be affect ...
... treatment of either positive (obesity) or negative (cachexia) energy balance. Indeed, other hypothalamic systems have also been closely synaptic inputs24. Both neuronal systems are directly targeted by leptin tied to this regulatory mechanism (for review, see refs. 3,4). These and can also be affect ...
Subconscious Stimulus Recognition and Processing During
... cortex during sleep. Recently, Issa and Wang (2008), studying marmoset monkeys during natural sleep and waking, recorded cortical unit responses to acoustic stimulation. Single units in both the primary and secondary auditory cortex decreased or increased their responses during sleep compared to wak ...
... cortex during sleep. Recently, Issa and Wang (2008), studying marmoset monkeys during natural sleep and waking, recorded cortical unit responses to acoustic stimulation. Single units in both the primary and secondary auditory cortex decreased or increased their responses during sleep compared to wak ...
14132.full - Explore Bristol Research
... The possibility that electrical stimulation within the IO may have excited ascending fibers that lie outside or course through the IO was minimized by positioning the IO stimulating electrode at a depth where the minimum current was required to evoke an antidromic spike (see Fig. 1b). In support of ...
... The possibility that electrical stimulation within the IO may have excited ascending fibers that lie outside or course through the IO was minimized by positioning the IO stimulating electrode at a depth where the minimum current was required to evoke an antidromic spike (see Fig. 1b). In support of ...
Synaptic reverberation underlying mnemonic persistent activity
... excitatory connections in a recurrent network are sufficiently strong. It is only recently, beginning with the work by Amit and colleagues, that attractor network models have been implemented with realistic models of cortical neurons and synapses22–27. Figure 2 illustrates the biophysics of an attra ...
... excitatory connections in a recurrent network are sufficiently strong. It is only recently, beginning with the work by Amit and colleagues, that attractor network models have been implemented with realistic models of cortical neurons and synapses22–27. Figure 2 illustrates the biophysics of an attra ...
The Representation of Complex Images in Spatial Frequency
... well separated SF domains in cat area 17. The relative phase of the sine wave gratings was fixed to zero, such that the pair moved as a coherent whole. Both sinusoidal components therefore moved with the same speed, but each component grating had a different TF because they had different SFs. Exampl ...
... well separated SF domains in cat area 17. The relative phase of the sine wave gratings was fixed to zero, such that the pair moved as a coherent whole. Both sinusoidal components therefore moved with the same speed, but each component grating had a different TF because they had different SFs. Exampl ...
Habituation, sensitization and Pavlovian conditioning
... approaches aversive stimuli) have two properties in common: The first is the sequential pattern of behavior which requires persistent sign tracking and stimulus evaluation, presenting the animal with multiple check points before it finally commits the consumatory act. The second is both state- and s ...
... approaches aversive stimuli) have two properties in common: The first is the sequential pattern of behavior which requires persistent sign tracking and stimulus evaluation, presenting the animal with multiple check points before it finally commits the consumatory act. The second is both state- and s ...
Document
... electrical current. Taking the control signal as a dynamical dissipative force (8) around the target manifold, it does not demand a high-power pumping of energy into the system. The approach developed above can be extended for other classes of models: multidimensional differential model for a single ...
... electrical current. Taking the control signal as a dynamical dissipative force (8) around the target manifold, it does not demand a high-power pumping of energy into the system. The approach developed above can be extended for other classes of models: multidimensional differential model for a single ...
Neurons
... Integration Between the PNS and CNS • Nerves of the CNS • Composed on interneurons that • Process and receive sensory information • Direct information to specific CNS regions • Initiate appropriate motor responses • Transport information from one area of the CNS to another ...
... Integration Between the PNS and CNS • Nerves of the CNS • Composed on interneurons that • Process and receive sensory information • Direct information to specific CNS regions • Initiate appropriate motor responses • Transport information from one area of the CNS to another ...
Projections from the superior temporal sulcus to the agranular frontal
... appears to play an important role in learning conditional oculomotor responses, in encoding saccades relative to an object centred frame of reference, or in monitoring the consequences of eye movements as part of a brain's supervisory control system (see Stuphorn et al., 2000). The notion that F6 an ...
... appears to play an important role in learning conditional oculomotor responses, in encoding saccades relative to an object centred frame of reference, or in monitoring the consequences of eye movements as part of a brain's supervisory control system (see Stuphorn et al., 2000). The notion that F6 an ...
Chapter 12: The Central Nervous System
... 4. Right hemisphere a. Controls visual-spatial skills, emotion, and artistic skills Cerebral White Matter 1. Consists of deep myelinated fibers and their tracts 2. It is responsible for communication between a. Cerebral cortex and lower CNS center, and areas of the cerebrum 3. Types include a. Commi ...
... 4. Right hemisphere a. Controls visual-spatial skills, emotion, and artistic skills Cerebral White Matter 1. Consists of deep myelinated fibers and their tracts 2. It is responsible for communication between a. Cerebral cortex and lower CNS center, and areas of the cerebrum 3. Types include a. Commi ...