Moving the Shh Source over Time: What Impact on Neural Cell
... in the pMN domain [23]. However, Shh concentration is not the only level of regulation as duration of exposure to Shh also influences the response to the morphogen, with ventral identities requiring longer time of Shh exposure to be established [24,25]. Therefore, progenitor domains form sequentiall ...
... in the pMN domain [23]. However, Shh concentration is not the only level of regulation as duration of exposure to Shh also influences the response to the morphogen, with ventral identities requiring longer time of Shh exposure to be established [24,25]. Therefore, progenitor domains form sequentiall ...
World of Children 1st ed
... This multimedia product and its content are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: ...
... This multimedia product and its content are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: ...
Review - Wesleyan University
... Although NEP1–40 is clearly effective as an antagonist of Nogo66, its ability to promote neuronal regeneration is, even at high concentration in vitro, incomplete (39). Elements other than Nogo that reside within CNS myelin and inhibit neuronal regeneration must thus be considered. One such element ...
... Although NEP1–40 is clearly effective as an antagonist of Nogo66, its ability to promote neuronal regeneration is, even at high concentration in vitro, incomplete (39). Elements other than Nogo that reside within CNS myelin and inhibit neuronal regeneration must thus be considered. One such element ...
Medical Gross Anatomy - University of Michigan
... voluntary actions and some reflexive actions, and sensory signals about pain, temperature, touch, and position. In addition to these conscious functions, there is an entire set of functions that our nervous system regulates that we rarely, if ever, notice. These unnoticed functions are regulated by ...
... voluntary actions and some reflexive actions, and sensory signals about pain, temperature, touch, and position. In addition to these conscious functions, there is an entire set of functions that our nervous system regulates that we rarely, if ever, notice. These unnoticed functions are regulated by ...
Membrane Phospholipid Asymmetry Counters the
... a yeast ORP, suppresses the growth defect of a partial lossof-function mutant of Drs2p. On the other hand, Drs2p also antagonizes the activity of Kes1p in intracellular cholesterol trafficking (Muthusamy et al. 2009). The exact mechanism behind this mutual antagonistic activity between Drs2p and Kes1 ...
... a yeast ORP, suppresses the growth defect of a partial lossof-function mutant of Drs2p. On the other hand, Drs2p also antagonizes the activity of Kes1p in intracellular cholesterol trafficking (Muthusamy et al. 2009). The exact mechanism behind this mutual antagonistic activity between Drs2p and Kes1 ...
Goals of Explaining Brain Functions Underlying Anxiety Disorders
... • How do medications fit into this picture? • Three questions about medications: – How do they affect the anxiety response? – How do they affect the exposure process? • How do they affect the amygdala’s learning? ...
... • How do medications fit into this picture? • Three questions about medications: – How do they affect the anxiety response? – How do they affect the exposure process? • How do they affect the amygdala’s learning? ...
The organization of the central control of micturition in cats and
... lateral part of the ventral horn of the cervical and lumbosacral enlargements. Sympathetic preganglionic motoneurons are present in the lateral horn of the thoracic and upper lumbar cord, whereas parasympathetic preganglionics are located in certain brain stem nuclei, and in the sacral cord (see Hol ...
... lateral part of the ventral horn of the cervical and lumbosacral enlargements. Sympathetic preganglionic motoneurons are present in the lateral horn of the thoracic and upper lumbar cord, whereas parasympathetic preganglionics are located in certain brain stem nuclei, and in the sacral cord (see Hol ...
The role of NADPH oxidase (NOX) enzymes in neurodegenerative
... (ALS), Alzheimer’s (AD), Parkinson’s (PD) and polyglutamine disease, have arisen. NOX enzymes are transmembrane proteins and generate reactive oxygen species by transporting electrons across lipid membranes. Under normal healthy conditions, low levels of ROS produced by NOX enzymes have been shown t ...
... (ALS), Alzheimer’s (AD), Parkinson’s (PD) and polyglutamine disease, have arisen. NOX enzymes are transmembrane proteins and generate reactive oxygen species by transporting electrons across lipid membranes. Under normal healthy conditions, low levels of ROS produced by NOX enzymes have been shown t ...
Pacemaker Potentials for the Periodic Burst Discharge in the Heart
... Somata in the pacemaker region of the heart ganglion of a stomatopod crustacean, Squilla oratoria de Haan, have been penetrated with intracellular electrodes to record membrane potential changes. The structure of the material is described in detail in the preceding paper (Watanabe, Obara, Akiyama, a ...
... Somata in the pacemaker region of the heart ganglion of a stomatopod crustacean, Squilla oratoria de Haan, have been penetrated with intracellular electrodes to record membrane potential changes. The structure of the material is described in detail in the preceding paper (Watanabe, Obara, Akiyama, a ...
PDF of article - Janelia Research Campus
... traverse the unlabeled primary neuron cell body clusters and end up in the neuropile of primary neuron arborizations (Fig. 2). While identifying a SAT as such is simple, the assignment of a precise identity in relation to published descriptions and nomenclature (Pereanu and Hartenstein, 2006) is ext ...
... traverse the unlabeled primary neuron cell body clusters and end up in the neuropile of primary neuron arborizations (Fig. 2). While identifying a SAT as such is simple, the assignment of a precise identity in relation to published descriptions and nomenclature (Pereanu and Hartenstein, 2006) is ext ...
Ethanol Facilitates Glutamatergic Transmission to Dopamine
... excitatory transmission, but how it affects excitatory synapses on dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area (VTA), a crucial site for the development of drug addiction, is not known. We report here that in midbrain slices from rats, clinically relevant concentrations of ethanol (10–80 mM) incr ...
... excitatory transmission, but how it affects excitatory synapses on dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area (VTA), a crucial site for the development of drug addiction, is not known. We report here that in midbrain slices from rats, clinically relevant concentrations of ethanol (10–80 mM) incr ...
Orientadora de Dissertação DOUTORA RAQUEL DE ORNELAS
... Lusitanian toadifish H. didactylus. Differences are based in Kruskal-Wallis tests, followed by pairwise comparison post-hoc tests to verify group-specific differences. * P<0,05; ** P<0.01. Bars represent means ± standard deviation and different letters represent significant differences between group ...
... Lusitanian toadifish H. didactylus. Differences are based in Kruskal-Wallis tests, followed by pairwise comparison post-hoc tests to verify group-specific differences. * P<0,05; ** P<0.01. Bars represent means ± standard deviation and different letters represent significant differences between group ...
Sequence of information processing for emotions based on the
... posterior medial cortices, and the sparsest in anterior lateral prefrontal areas, especially area 10. Prefrontal projection neurons directed to the amygdala originated in layer 5, but significant numbers were also found in layers 2 and 3 in posterior medial and orbitofrontal cortices. Amygdalar axon ...
... posterior medial cortices, and the sparsest in anterior lateral prefrontal areas, especially area 10. Prefrontal projection neurons directed to the amygdala originated in layer 5, but significant numbers were also found in layers 2 and 3 in posterior medial and orbitofrontal cortices. Amygdalar axon ...
Apparent Loss and Hypertrophy of Interneurons in a Mouse Model
... lipopigment is most pronounced in presumed GABAergic neurons We used the autofluorescent properties of the accumulated lipopigment to produce spatial and temporal maps of affected cells in the mnd/mnd mouse brain. Using conventional fluorescence microscopy, we examined unstained coronal sections thr ...
... lipopigment is most pronounced in presumed GABAergic neurons We used the autofluorescent properties of the accumulated lipopigment to produce spatial and temporal maps of affected cells in the mnd/mnd mouse brain. Using conventional fluorescence microscopy, we examined unstained coronal sections thr ...
Expression of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating
... responses. The present study builds on our previous observations of sensory SP- and CGRP-containing nerves in the cervix and was designed to determine if the neuropeptide pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) could also play a role in cervical function, such as cervical ripening ...
... responses. The present study builds on our previous observations of sensory SP- and CGRP-containing nerves in the cervix and was designed to determine if the neuropeptide pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) could also play a role in cervical function, such as cervical ripening ...
Motif distribution, dynamical properties, and computational
... We investigate these two cortical microcircuit templates with regard to structural and functional properties. In order to evaluate the computational properties of microcircuit templates we carried out computer simulations of detailed cortical microcircuit models consisting of 560 Hodgkin–Huxley type ...
... We investigate these two cortical microcircuit templates with regard to structural and functional properties. In order to evaluate the computational properties of microcircuit templates we carried out computer simulations of detailed cortical microcircuit models consisting of 560 Hodgkin–Huxley type ...
OSBP coupled with ER-resident protein FAN is essential
... of Kes1p/Osh4p, a yeast ORP, suppresses the growth defect of a partial loss-of-function mutant of Drs2p. On the other hand, Drs2p also antagonizes the activity of Kes1p in intracellular cholesterol trafficking (MUTHUSAMY et al. 2009). The exact mechanism behind this mutual antagonistic activity betw ...
... of Kes1p/Osh4p, a yeast ORP, suppresses the growth defect of a partial loss-of-function mutant of Drs2p. On the other hand, Drs2p also antagonizes the activity of Kes1p in intracellular cholesterol trafficking (MUTHUSAMY et al. 2009). The exact mechanism behind this mutual antagonistic activity betw ...
Document
... Figure 15–1 An Overview of Neural Integration. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Figure 15–1 An Overview of Neural Integration. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
TREBALL 6
... starting with a first interspike interval of <80 ms and ending with a interspike interval of 160 ms or greater (Grace and Bunney, 1984). We also examined the responses elicited by ARI in pyramidal neurons of the mPFC in anesthetized rats. Recordings were made essentially as described in Puig et al. ...
... starting with a first interspike interval of <80 ms and ending with a interspike interval of 160 ms or greater (Grace and Bunney, 1984). We also examined the responses elicited by ARI in pyramidal neurons of the mPFC in anesthetized rats. Recordings were made essentially as described in Puig et al. ...
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous
... Figure 15–1 An Overview of Neural Integration. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Figure 15–1 An Overview of Neural Integration. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
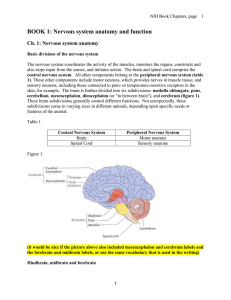
BOOK 1: Nervous system anatomy and function
... typically made of glass or metal -- to record the number of action potentials a dopamine neuron generates. This technique is called electrophysiology or monitoring the “electrical functioning” of the neuron. The frequency of action potentials or firing rate (the number of action potentials “fired” o ...
... typically made of glass or metal -- to record the number of action potentials a dopamine neuron generates. This technique is called electrophysiology or monitoring the “electrical functioning” of the neuron. The frequency of action potentials or firing rate (the number of action potentials “fired” o ...
I dc
... [Strength of a Stimulus > Threshold Generation and Transmission of Spikes by Neurons] ...
... [Strength of a Stimulus > Threshold Generation and Transmission of Spikes by Neurons] ...
Differential effects of 10-Hz and 40
... cuing tasks—one to assess endogenous attention and one to assess exogenous attention. Experimental sessions were conducted in an electrically-shielded, sound-attenuated booth, and stimuli were presented on a cathode ray tube (CRT) monitor positioned 75 cm from the participant, using Presentation sof ...
... cuing tasks—one to assess endogenous attention and one to assess exogenous attention. Experimental sessions were conducted in an electrically-shielded, sound-attenuated booth, and stimuli were presented on a cathode ray tube (CRT) monitor positioned 75 cm from the participant, using Presentation sof ...