PAIN
... excitability (central sensitization) which constitute a memory of the C fiber input. Can lead to spontaneous pain and decreases in the threshold for the production of pain. Carpal tunnel syndrome: median nerve frequently injured at the flexor retinaculum. Pain ends up affecting the entire arm. (rat ...
... excitability (central sensitization) which constitute a memory of the C fiber input. Can lead to spontaneous pain and decreases in the threshold for the production of pain. Carpal tunnel syndrome: median nerve frequently injured at the flexor retinaculum. Pain ends up affecting the entire arm. (rat ...
The basic nonuniformity of the cerebral cortex
... mm2 that was predicted by Rockel et al. (10) from which a nominal value of 147,000/mm2 was corrected for 18% shrinkage in each of two dimensions (P ⫽ 0.1903, one sample t test). Because exclusion of Tupaia sp. from the analyses did not modify the results (data not shown), all comparisons henceforth ...
... mm2 that was predicted by Rockel et al. (10) from which a nominal value of 147,000/mm2 was corrected for 18% shrinkage in each of two dimensions (P ⫽ 0.1903, one sample t test). Because exclusion of Tupaia sp. from the analyses did not modify the results (data not shown), all comparisons henceforth ...
“Electrical Properties of Neuron”
... We represent it by I m which is current/unit area of membrane Jj Amount of current flowing through each channel is equal to driving force (the difference between equilibrium potential Ei and membrane potential) multiplied by channel conductance gi Therefore: im = gi(V - Ei) Conductance change ...
... We represent it by I m which is current/unit area of membrane Jj Amount of current flowing through each channel is equal to driving force (the difference between equilibrium potential Ei and membrane potential) multiplied by channel conductance gi Therefore: im = gi(V - Ei) Conductance change ...
The Ventrolateral Hypothalamic Area and the Parvafox Nucleus
... the first wave would form the lateral hypothalamus; those during the second wave would give rise to an intermediate hypothalamic layer containing large, recognizable nuclei (ventromedial and dorsomedial); and those during the third wave would give rise to the periventricular (viz., the most medial) ...
... the first wave would form the lateral hypothalamus; those during the second wave would give rise to an intermediate hypothalamic layer containing large, recognizable nuclei (ventromedial and dorsomedial); and those during the third wave would give rise to the periventricular (viz., the most medial) ...
Unilateral Ibotenic Acid Lesions of the Prefrontal Cortex Reduce
... which influence the activity of the STN-GP network directly via excitatory projections. However, anatomical and electrophysiological findings have shown that the STN also receives direct excitatory afferents from the medial division of the prefrontal cortex (PFC) [9, 10]. Stimulation of the PFC has bee ...
... which influence the activity of the STN-GP network directly via excitatory projections. However, anatomical and electrophysiological findings have shown that the STN also receives direct excitatory afferents from the medial division of the prefrontal cortex (PFC) [9, 10]. Stimulation of the PFC has bee ...
Full Text PDF - Jaypee Journals
... By around day 20 (even before the closure of the neural tube), the primordia of three brain vesicles (fore brain or prosencephalon, midbrain or mesencephalon and rhombencephalon) can be identified as thicken ings of the cranial neural ectoderm (Fig. 4A). Soon after the closure of the neural tube, ...
... By around day 20 (even before the closure of the neural tube), the primordia of three brain vesicles (fore brain or prosencephalon, midbrain or mesencephalon and rhombencephalon) can be identified as thicken ings of the cranial neural ectoderm (Fig. 4A). Soon after the closure of the neural tube, ...
peripheral nervous system
... by a perpetual axoplasmic motion. Some organelles, structural protein and neurotransmitters contained within cytoplasm are carried by axoplasmic flow which moves in both directions and with varying velocity. This phenomenon is called axoplasmic transport. ...
... by a perpetual axoplasmic motion. Some organelles, structural protein and neurotransmitters contained within cytoplasm are carried by axoplasmic flow which moves in both directions and with varying velocity. This phenomenon is called axoplasmic transport. ...
Chapter 11 Part 1 - Trimble County Schools
... The two principal cell types of the nervous system are: 1. Neurons – excitable cells that transmit electrical signals 2. Supporting cells – cells that surround and wrap ...
... The two principal cell types of the nervous system are: 1. Neurons – excitable cells that transmit electrical signals 2. Supporting cells – cells that surround and wrap ...
The Cerebellum
... Function: play an important role in control of muscle tone and coordination of muscle movement on the same side of the body ...
... Function: play an important role in control of muscle tone and coordination of muscle movement on the same side of the body ...
spinal cord - Dr Magrann
... GANGLION is the term for a group of neuron cell bodies (both sensory and motor) found in the peripheral nervous system only. SENSORY NEURONS come in (via the spinal nerve) through the posterior root; their cell body is in the posterior root ganglion, and its axon goes into the posterior horn and syn ...
... GANGLION is the term for a group of neuron cell bodies (both sensory and motor) found in the peripheral nervous system only. SENSORY NEURONS come in (via the spinal nerve) through the posterior root; their cell body is in the posterior root ganglion, and its axon goes into the posterior horn and syn ...
Spinal Cord - Lamont High
... Spinal Cord Contains 2 types of nerve tissue---gray and white matter ...
... Spinal Cord Contains 2 types of nerve tissue---gray and white matter ...
6 - smw15.org
... • Bitter receptors are sensitive to a wide range of chemicals with varying degrees of toxicity • About 25 types of bitter receptors exist • Most taste cells contain only a small number of these receptors • We are sensitive to a wide range of harmful substances, but not highly sensitive to any single ...
... • Bitter receptors are sensitive to a wide range of chemicals with varying degrees of toxicity • About 25 types of bitter receptors exist • Most taste cells contain only a small number of these receptors • We are sensitive to a wide range of harmful substances, but not highly sensitive to any single ...
Central Nervous System CNS
... asociated with highly processed sensory info; also planning of movements Frontal eye fields (inferior 8): voluntary movements of eyes ...
... asociated with highly processed sensory info; also planning of movements Frontal eye fields (inferior 8): voluntary movements of eyes ...
Topographic maps in human frontal and parietal cortex
... Visualization of periodic mapping signals on computationally flattened patches of parietal cortex often reveals regions of the topographic maps which contain ...
... Visualization of periodic mapping signals on computationally flattened patches of parietal cortex often reveals regions of the topographic maps which contain ...
Human Physiology/The Nervous System
... two types of summation: spatial and temporal. Spatial summation requires several excitatory synapses (firing several times) to add up,thus causing an axon discharge. It also occurs within inhibitory synapses, where just the opposite will occur. In temporal summation, it causes an increase of the fre ...
... two types of summation: spatial and temporal. Spatial summation requires several excitatory synapses (firing several times) to add up,thus causing an axon discharge. It also occurs within inhibitory synapses, where just the opposite will occur. In temporal summation, it causes an increase of the fre ...
How do Human Sensors Work?
... (spinal cord and brain), which is the coordinator. The coordinator makes the decision of how to react, and then commands the hand muscles (the effector) to jerk back quickly. In summary: We go from stimulus (touch) to response (movement of hand). Do This: Sketch out the stimulus-to-response sequence ...
... (spinal cord and brain), which is the coordinator. The coordinator makes the decision of how to react, and then commands the hand muscles (the effector) to jerk back quickly. In summary: We go from stimulus (touch) to response (movement of hand). Do This: Sketch out the stimulus-to-response sequence ...
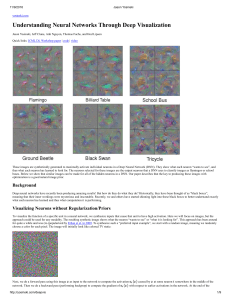
DeepNetUnderstand
... How are these figures produced? Specifically, we found four forms of regularization that, when combined, produce more recognizable, optimizationbased samples than previous methods. Because the optimization is stochastic, by starting at different random initial images, we can produce a set of optimi ...
... How are these figures produced? Specifically, we found four forms of regularization that, when combined, produce more recognizable, optimizationbased samples than previous methods. Because the optimization is stochastic, by starting at different random initial images, we can produce a set of optimi ...
Philosophy of Mind and Neuroscience: the Case of Mirror Neurons
... which are both active during the implementation of actions related to objects: they are simple and familiar gestures like grabbing something with your hand or bringing food to your mouth. The surprising thing is that these two groups of pre-motor neurons are also activated in the absence of any enfo ...
... which are both active during the implementation of actions related to objects: they are simple and familiar gestures like grabbing something with your hand or bringing food to your mouth. The surprising thing is that these two groups of pre-motor neurons are also activated in the absence of any enfo ...
Mechanism of relation among heart meridian, referred cardiac pain
... of fluorescent tracers into the pericardium and left medial (heart meridian) or lateral (lung meridian) brachium. Our results clearly indicate that more dichotomizing fibers that supply both the pericardium and the medial brachium exist and a closer relation between heart meridian and heart is obser ...
... of fluorescent tracers into the pericardium and left medial (heart meridian) or lateral (lung meridian) brachium. Our results clearly indicate that more dichotomizing fibers that supply both the pericardium and the medial brachium exist and a closer relation between heart meridian and heart is obser ...
Neurons in red nucleus and primary motor cortex exhibit similar
... reaching (Sinkjaer et al., 1995; van Kan and McCurdy, 2001, 2002a,b). A recent hypothesis proposes that the volitional motor system may act like an optimal feedback controller (Todorov and Jordan, 2002; Todorov, 2004). This framework highlights the importance of afferent feedback for voluntary contr ...
... reaching (Sinkjaer et al., 1995; van Kan and McCurdy, 2001, 2002a,b). A recent hypothesis proposes that the volitional motor system may act like an optimal feedback controller (Todorov and Jordan, 2002; Todorov, 2004). This framework highlights the importance of afferent feedback for voluntary contr ...
Expression and Functional Interaction of Hepatocyte Growth Factor
... cortical plate, most prominently in the frontal part (Fig. 2). At P4, there was prominent expression in the ependymal layer with a weaker expression in the hippocampus, the outer layers of the cortex, and the medial habenula (Fig. 3). In the adult, low levels of HGF-SF mRNA were detected widespread ...
... cortical plate, most prominently in the frontal part (Fig. 2). At P4, there was prominent expression in the ependymal layer with a weaker expression in the hippocampus, the outer layers of the cortex, and the medial habenula (Fig. 3). In the adult, low levels of HGF-SF mRNA were detected widespread ...
Cortical modulation of pain
... been as problematic in animals as it has been in humans. It was not until relatively recently that nociresponsive cells were recorded in the rat SI region [27–29] using a variety of mechanical or electrical stimuli. Even so, the percentage of cells responding to noxious stimuli was low and raised qu ...
... been as problematic in animals as it has been in humans. It was not until relatively recently that nociresponsive cells were recorded in the rat SI region [27–29] using a variety of mechanical or electrical stimuli. Even so, the percentage of cells responding to noxious stimuli was low and raised qu ...
Lecture 3 Slides
... • Decreased cerebellar size has been observed in ADHD, autism • Neuroimaging studies show activation of cerebellum during higher-level cognitive tasks – Ask for references if you are interested ...
... • Decreased cerebellar size has been observed in ADHD, autism • Neuroimaging studies show activation of cerebellum during higher-level cognitive tasks – Ask for references if you are interested ...