No Slide Title
... binding site it can have several effects depending upon the nature of the receptors it has attached to. a) Ionotropic effects: These are very rapid but short-lived. According to North (1989) a neurotransmitter having this effect opens the ion channels within 10ms after its release and keeps them ...
... binding site it can have several effects depending upon the nature of the receptors it has attached to. a) Ionotropic effects: These are very rapid but short-lived. According to North (1989) a neurotransmitter having this effect opens the ion channels within 10ms after its release and keeps them ...
Stress induces atrophy of apical dendrites of hippocampal CA3
... These results demonstrate that repeated restraint stress, which results in a moderate reduction in body weight gain and moderate changes in adrenal and thymus weights, resulted in a small but significant decrease in dendritic length and branch points of CA3 pyramidal neurons in the hippocampus. The ...
... These results demonstrate that repeated restraint stress, which results in a moderate reduction in body weight gain and moderate changes in adrenal and thymus weights, resulted in a small but significant decrease in dendritic length and branch points of CA3 pyramidal neurons in the hippocampus. The ...
Human Vision: Electrophysiology and Psychophysics
... Artificial neural networks are used to solve problems in fields as diverse as • pattern recognition • optimisation • locomotion and spatial recognition • sequence prediction ...
... Artificial neural networks are used to solve problems in fields as diverse as • pattern recognition • optimisation • locomotion and spatial recognition • sequence prediction ...
Principles of Neural Science
... physical properties of stimuli because the nervous system extracts only certain pieces of information from each stimulus, while ignoring others, and then interprets this information in the context of the brain's intrinsic structure and previous experience. Thus we receive electromagnetic waves of di ...
... physical properties of stimuli because the nervous system extracts only certain pieces of information from each stimulus, while ignoring others, and then interprets this information in the context of the brain's intrinsic structure and previous experience. Thus we receive electromagnetic waves of di ...
Chapter 13 - next2eden.net
... binds groups of fibers into bundles contains sensory neurons only ...
... binds groups of fibers into bundles contains sensory neurons only ...
Gradual increase in neuronal density of rats
... 13. Meyer G, Albus K. Topography and cortical projections of morphologically identified neurons in the visual thalamus of the cat. J Comp Neurol 1981; 201: 353-374. 14. Hitchcock PF, Hickey TL. Morphology of C-laminae neurons in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat: a Golgi ...
... 13. Meyer G, Albus K. Topography and cortical projections of morphologically identified neurons in the visual thalamus of the cat. J Comp Neurol 1981; 201: 353-374. 14. Hitchcock PF, Hickey TL. Morphology of C-laminae neurons in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat: a Golgi ...
PDF
... We photographed the series of 75 mm sections spanning the rostral / caudal extent of temporal cortex on the same day the sections were mounted and coverslipped. Several pictures (103 objective) were taken of each hemisphere that collectively circumscribed the cortical regions that contained labeled ...
... We photographed the series of 75 mm sections spanning the rostral / caudal extent of temporal cortex on the same day the sections were mounted and coverslipped. Several pictures (103 objective) were taken of each hemisphere that collectively circumscribed the cortical regions that contained labeled ...
Neurons and Neurotransmission with Nerve slides
... of the body that can turn other kinds of energy into action potentials that the nervous system can process •Receptor cells in the eye turn light into a neural impulse the brain understands. ...
... of the body that can turn other kinds of energy into action potentials that the nervous system can process •Receptor cells in the eye turn light into a neural impulse the brain understands. ...
6419982_1441921514
... concentrated within the cell. The intracellular K+ concentration is 150 mEq/L in the human body compared to an extracellular concentration of 5 mEq/L (mEq = milliequivalents, which is the millimolar concentration multiplied by the valence of the ion—in this case, by 1). As a result of the unequal di ...
... concentrated within the cell. The intracellular K+ concentration is 150 mEq/L in the human body compared to an extracellular concentration of 5 mEq/L (mEq = milliequivalents, which is the millimolar concentration multiplied by the valence of the ion—in this case, by 1). As a result of the unequal di ...
Mirror Neurons Responding to Observation of Actions Made with
... small piece of food with its hand (E) or its mouth (F). Note that also the motor response, as the visual response, began during the approaching phase of grasping and peaked when the hand or the mouth closed on the food. Figure 2 shows an example of a neuron (Unit 102) selective for the observation o ...
... small piece of food with its hand (E) or its mouth (F). Note that also the motor response, as the visual response, began during the approaching phase of grasping and peaked when the hand or the mouth closed on the food. Figure 2 shows an example of a neuron (Unit 102) selective for the observation o ...
Document
... cortex and associated structures have been suggested to occur in several neuropsychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia, autism and obsessive compulsive disorder. The human cortex is about 1000‐fold greater than that of the mouse. This increase is largely due to an increase in surface area. Cor ...
... cortex and associated structures have been suggested to occur in several neuropsychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia, autism and obsessive compulsive disorder. The human cortex is about 1000‐fold greater than that of the mouse. This increase is largely due to an increase in surface area. Cor ...
Cranial nerves (L15)
... *sphincter pupillae constricts pupil to control light input *ciliary changes shape of lens to accommodate changes in distance vision *primary neurons in Edinger-Westphal nucleus in midbrain *synapse in ciliary ganglion – postganglionic axons travel to mm in eye via short ciliary nn. ...
... *sphincter pupillae constricts pupil to control light input *ciliary changes shape of lens to accommodate changes in distance vision *primary neurons in Edinger-Westphal nucleus in midbrain *synapse in ciliary ganglion – postganglionic axons travel to mm in eye via short ciliary nn. ...
lecture 1 () - Stanford Department of Mathematics
... Study the implications of these hypotheses and try to falsify the hypotheses. That is, try to eliminate biologically impossible ideas! We believe this approach has a better chance to succeed in the area of brain-like computers and intelligent robots than the first one. Why? So far the attempts to de ...
... Study the implications of these hypotheses and try to falsify the hypotheses. That is, try to eliminate biologically impossible ideas! We believe this approach has a better chance to succeed in the area of brain-like computers and intelligent robots than the first one. Why? So far the attempts to de ...
Sacrificing America On The Altar Of Mediocrity
... These neurons are cells composed of long arms (axons) with tiny branches at the end (dendrites). Axons take information away from the cell body and branch further from the cell body. Dendrites, on the other hand bring information to the cell body and branch near the cell body. Axons have been descri ...
... These neurons are cells composed of long arms (axons) with tiny branches at the end (dendrites). Axons take information away from the cell body and branch further from the cell body. Dendrites, on the other hand bring information to the cell body and branch near the cell body. Axons have been descri ...
Normalization as a canonical neural computation
... The numerator is the neuron’s driving input Dj; in sensory systems, this driving input provides the stimulus drive to the responses. Its units depend on the system under study. They could be in units of stimulus intensity in a sensory system, or in spikes per second if the input is considered to ari ...
... The numerator is the neuron’s driving input Dj; in sensory systems, this driving input provides the stimulus drive to the responses. Its units depend on the system under study. They could be in units of stimulus intensity in a sensory system, or in spikes per second if the input is considered to ari ...
On-line, voluntary control of human temporal lobe
... (Fig. 4). We normalized each unit’s response by its maximal firing rate over the entire experiment, and averaged over all trials for all subjects. For the same retinal input, the firing rate of neurons responding to the target pictures was much higher when subjects focused their attention on the tar ...
... (Fig. 4). We normalized each unit’s response by its maximal firing rate over the entire experiment, and averaged over all trials for all subjects. For the same retinal input, the firing rate of neurons responding to the target pictures was much higher when subjects focused their attention on the tar ...
Neural Correlates of Object-Associated Choice Behavior
... Task-factor analysis and multicollinearity control. Neurons that significantly modulated their activity during the task events were further subjected to a two-way ANOVA with the object category (toy and egg) and spatial choice (left and right touch responses) as main factors. If the ANOVA showed sig ...
... Task-factor analysis and multicollinearity control. Neurons that significantly modulated their activity during the task events were further subjected to a two-way ANOVA with the object category (toy and egg) and spatial choice (left and right touch responses) as main factors. If the ANOVA showed sig ...
Regional and laminar distribution of the vesicular glutamate
... Abbreviations: A1, auditory area 1 (core); AChE, acetylcholinesterase; AL, anterolateral area (belt); CB, calbindin; CL, caudolateral area (belt); CM, caudomedial area (belt); CO, cytochrome oxidase; CPB, caudal parabelt area (parabelt); CS, central sulcus; Ins, insula; IPS, intraparietal sulcus; LG ...
... Abbreviations: A1, auditory area 1 (core); AChE, acetylcholinesterase; AL, anterolateral area (belt); CB, calbindin; CL, caudolateral area (belt); CM, caudomedial area (belt); CO, cytochrome oxidase; CPB, caudal parabelt area (parabelt); CS, central sulcus; Ins, insula; IPS, intraparietal sulcus; LG ...
Cell Bio 5- SDL Spinal Reflexes Circuits A neuron never works
... These neurons are organized into circuits – Local circuits • Spinal reflex circuits are a type of local circuit Local circuits generally have three elements 1. Input • The main input to the spinal cord is through afferent sensory axons in the dorsal root • Sensory signals travel to two destinations ...
... These neurons are organized into circuits – Local circuits • Spinal reflex circuits are a type of local circuit Local circuits generally have three elements 1. Input • The main input to the spinal cord is through afferent sensory axons in the dorsal root • Sensory signals travel to two destinations ...
Bioinspired Computing Lecture 5
... Thus, we would expect to find very few ‘redundant’ neurons with co-varying outputs in that network. Accordingly, an optimal temporal coding circuit might tend to eliminate redundancy in the pattern of inputs to different neurons. On the other hand, if neural information is carried by a noisy rate-ba ...
... Thus, we would expect to find very few ‘redundant’ neurons with co-varying outputs in that network. Accordingly, an optimal temporal coding circuit might tend to eliminate redundancy in the pattern of inputs to different neurons. On the other hand, if neural information is carried by a noisy rate-ba ...
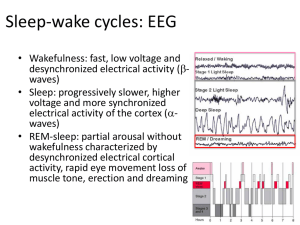
Sleep-wake cycles: EEG
... • REM-sleep: partial arousal without wakefulness characterized by desynchronized electrical cortical activity, rapid eye movement loss of muscle tone, erection and dreaming ...
... • REM-sleep: partial arousal without wakefulness characterized by desynchronized electrical cortical activity, rapid eye movement loss of muscle tone, erection and dreaming ...
(SCI) patients in the United States
... Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms packed in a hexagonal (honey-comb) lattice with a carbon-to-carbon distance of around 0.142 nm. Graphene is also practically transparent: the optical region it absorbs only 2.3% of the light. In contrast to low temperature 2D systems based on semiconductors ...
... Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms packed in a hexagonal (honey-comb) lattice with a carbon-to-carbon distance of around 0.142 nm. Graphene is also practically transparent: the optical region it absorbs only 2.3% of the light. In contrast to low temperature 2D systems based on semiconductors ...
Functional Motifs Composed of Morphologically Homologous
... from serial horizontal sections of paired, recorded, and intracellularly labeled the M-cells in r4 (black) and RSNs in r4 –r6. The detail than that in a previous study that somata of all of types of RSNs fell into tidy segments, but their dendrites protruded away from their own segments and projecte ...
... from serial horizontal sections of paired, recorded, and intracellularly labeled the M-cells in r4 (black) and RSNs in r4 –r6. The detail than that in a previous study that somata of all of types of RSNs fell into tidy segments, but their dendrites protruded away from their own segments and projecte ...