Neuronal Calcium Signaling Review
... 1996). Calcium release in cardiac cells is mediated by the type 2 RYR, which is the predominant isoform found in the brain. In cardiac cells, these RYR2 channels are closely apposed to the Ca21 channels in the plasma membrane across the 15 nm junctional gap that separates the sarcolemma from the sar ...
... 1996). Calcium release in cardiac cells is mediated by the type 2 RYR, which is the predominant isoform found in the brain. In cardiac cells, these RYR2 channels are closely apposed to the Ca21 channels in the plasma membrane across the 15 nm junctional gap that separates the sarcolemma from the sar ...
CHAPTER 4
... – After the channel is open for a few milliseconds, the movement of K+ ions is “automatically” stopped by a process known as inactivation. – Can exist in three different states: open, inactivated, and closed. ...
... – After the channel is open for a few milliseconds, the movement of K+ ions is “automatically” stopped by a process known as inactivation. – Can exist in three different states: open, inactivated, and closed. ...
Response Suppression in V1 Agrees with Psychophysics of
... intervals, only the first of which was task relevant. Both intervals lasted 750 msec, with a 375 msec interstimulus interval (Fig. 3). The target stimulus always appeared in the first interval, with pedestal contrast set to 0% in block A and 60% in block B. There were three conditions, which differe ...
... intervals, only the first of which was task relevant. Both intervals lasted 750 msec, with a 375 msec interstimulus interval (Fig. 3). The target stimulus always appeared in the first interval, with pedestal contrast set to 0% in block A and 60% in block B. There were three conditions, which differe ...
Origins of language: A conspiracy theory
... innateness is achieved by hand-wiring the network and setting the weights prior to learning. At least some of the discussion regarding the origins of language appear to assume that representational innateness is what is assumed. Thus, for example, Pinker (1994) claims that, It is a certain wiring of ...
... innateness is achieved by hand-wiring the network and setting the weights prior to learning. At least some of the discussion regarding the origins of language appear to assume that representational innateness is what is assumed. Thus, for example, Pinker (1994) claims that, It is a certain wiring of ...
NEURAL NETWORK DYNAMICS
... a network model described in terms of neuronal firing rates that exhibits sustained and oscillatory activity and a network of spiking model neurons that displays chaotic activity. We begin the review with a discussion of sustained responses to transient stimuli. Neuronal activity evoked by a transien ...
... a network model described in terms of neuronal firing rates that exhibits sustained and oscillatory activity and a network of spiking model neurons that displays chaotic activity. We begin the review with a discussion of sustained responses to transient stimuli. Neuronal activity evoked by a transien ...
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters are the nervous system`s “off switches
... where these enzymes function can proved valuable insight about how dopamine is functioning in specific regions of the body. In order to understand these functions one must first realize Monoamine oxidase (MAO) is an enzyme present within the cytoplasm of neurons that breaks down dopamine to DOPAL. D ...
... where these enzymes function can proved valuable insight about how dopamine is functioning in specific regions of the body. In order to understand these functions one must first realize Monoamine oxidase (MAO) is an enzyme present within the cytoplasm of neurons that breaks down dopamine to DOPAL. D ...
The human medial geniculate body
... [3]. Other parts (for example, the medial division) contain neurons with much broader, often polysensory tuning curves, and an unknown number of representations of the basilar membrane [l]. Moreover. the pattern of brain stem input to these divisions is different [4,42]. Thus, not all parts of the m ...
... [3]. Other parts (for example, the medial division) contain neurons with much broader, often polysensory tuning curves, and an unknown number of representations of the basilar membrane [l]. Moreover. the pattern of brain stem input to these divisions is different [4,42]. Thus, not all parts of the m ...
3D Visual Response Properties of MSTd Emerge from an Efficient
... studies that concentrated on a small number of MSTd neurons preferring fore–aft (i.e., forward and backward) motion directions (Duffy and Wurtz, 1995), these more recent studies demonstrated that heading preferences in MSTd were distributed throughout the spherical stimulus space, and that there was ...
... studies that concentrated on a small number of MSTd neurons preferring fore–aft (i.e., forward and backward) motion directions (Duffy and Wurtz, 1995), these more recent studies demonstrated that heading preferences in MSTd were distributed throughout the spherical stimulus space, and that there was ...
Psychology Chapter A - Oxford University Press
... Although you are not aware of it, your nervous system is made up of billions of interconnected cells that are constantly communicating with one another. In order to understand the different kinds of cells in the nervous system, you could consider a simple action such as washing a cup. When you want ...
... Although you are not aware of it, your nervous system is made up of billions of interconnected cells that are constantly communicating with one another. In order to understand the different kinds of cells in the nervous system, you could consider a simple action such as washing a cup. When you want ...
KISHORE Aswathy - School of Computing
... representation’. Accordingly, different features of the object such as shape, texture and colour will be represented in different parts of the brain. Hence, in order to have a complete representation for the object, these individual localised representations have to be bound together to form a globa ...
... representation’. Accordingly, different features of the object such as shape, texture and colour will be represented in different parts of the brain. Hence, in order to have a complete representation for the object, these individual localised representations have to be bound together to form a globa ...
Ch 14: Peripheral Nervous System
... Varicella-zoster virus ( of the herpes family) In dorsal root ganglia and cranial nerves ...
... Varicella-zoster virus ( of the herpes family) In dorsal root ganglia and cranial nerves ...
Nat Methods 6:219-224 - University of British Columbia
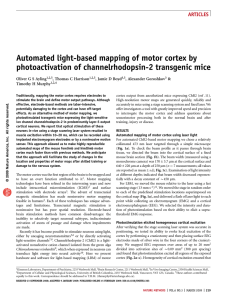
... Automated mapping of motor cortex using laser light For automated ChR2-based motor mapping we chose a relatively collimated 473 nm laser targeted through a simple microscope (Fig. 1a). To check the beam profile as it passes through brain tissue, we directed the beam into the cortical surface of a fi ...
... Automated mapping of motor cortex using laser light For automated ChR2-based motor mapping we chose a relatively collimated 473 nm laser targeted through a simple microscope (Fig. 1a). To check the beam profile as it passes through brain tissue, we directed the beam into the cortical surface of a fi ...
Action Potential: Resting State
... • Established by the total amount of current flowing through the membrane • Subthreshold: _ • Threshold: _ • All-or-none phenomenon – action potentials _ ...
... • Established by the total amount of current flowing through the membrane • Subthreshold: _ • Threshold: _ • All-or-none phenomenon – action potentials _ ...
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM NEURONAL MIGRATION
... defects in the radial glial system. Thus, reeler partially inhibits expression of the radial glial phenotype, leaving the cells shorter and disorganized (Pinto-Lord et al 1982, Hunter-Schaedle 1997). This is apparently an indirect effect of CR-50 antigen/Reelin. Cajal-Retzius cells make CR-50 antige ...
... defects in the radial glial system. Thus, reeler partially inhibits expression of the radial glial phenotype, leaving the cells shorter and disorganized (Pinto-Lord et al 1982, Hunter-Schaedle 1997). This is apparently an indirect effect of CR-50 antigen/Reelin. Cajal-Retzius cells make CR-50 antige ...
Transcripts/01_15 11
... ii. Project to widespread areas of cortex (gets info from everyway and sends it everywhere) and the Basal ganglia. iii. They produce general changes in cortical function including arousal, alertness, and cortical tone. This is brain stem reticular formation input. b. Reticular nucleus i. Reticular m ...
... ii. Project to widespread areas of cortex (gets info from everyway and sends it everywhere) and the Basal ganglia. iii. They produce general changes in cortical function including arousal, alertness, and cortical tone. This is brain stem reticular formation input. b. Reticular nucleus i. Reticular m ...
On the Nature of Visual-Oculomotor Connections
... show that Equation 1 does predict the behavior of motoneurons during all of these eye movement types. For example, the velocity term in Equation 1 would predict a high discharge rate during the highvelocity period of saccades which is clearly seen in Fig. 1. It appears that motoneurons obey Equation ...
... show that Equation 1 does predict the behavior of motoneurons during all of these eye movement types. For example, the velocity term in Equation 1 would predict a high discharge rate during the highvelocity period of saccades which is clearly seen in Fig. 1. It appears that motoneurons obey Equation ...
Figure 2.25
... • Prevents harmful substances in the blood from entering the brain • The cells that make up the walls of the blood vessel walls are squeezed close together, so many molecules cannot pass through ...
... • Prevents harmful substances in the blood from entering the brain • The cells that make up the walls of the blood vessel walls are squeezed close together, so many molecules cannot pass through ...
To Be or Not to Be … an Inhibitory Neurotransmitter
... George grinned at Jessica. “Hey, I’m all for making contact. Are you busy later tonight?” Jessica grinned back. “Sorry, George, I’m an old neuron. It takes a lot more than that to get me excited!” ...
... George grinned at Jessica. “Hey, I’m all for making contact. Are you busy later tonight?” Jessica grinned back. “Sorry, George, I’m an old neuron. It takes a lot more than that to get me excited!” ...
Neuron the Memory Unit of the Brain
... requires an even more rapid response. If we touch a hot stove, for instance, it is beneficial for us to pull back as quickly as possible. How does the nervous system handle this reflex response? When responding to input that requires a very fast response, our nervous system allows sensory neurons to ...
... requires an even more rapid response. If we touch a hot stove, for instance, it is beneficial for us to pull back as quickly as possible. How does the nervous system handle this reflex response? When responding to input that requires a very fast response, our nervous system allows sensory neurons to ...
Selectivity for the Shape, Size, and Orientation of Objects for
... neurons in the inferior parietal lobule are related to hand manipulation or grasping as well as to visually guided reaching (Hyvärinen and Poranen 1974; Mountcastle et al. 1975). Recently we studied a group of neurons that were related to visually guided hand-manipulation tasks in the anterior part ...
... neurons in the inferior parietal lobule are related to hand manipulation or grasping as well as to visually guided reaching (Hyvärinen and Poranen 1974; Mountcastle et al. 1975). Recently we studied a group of neurons that were related to visually guided hand-manipulation tasks in the anterior part ...
www.informatik.uni
... 3) Previous Models: Models of neural coordinate transformations originally dealt with “static” sensory-motor mappings, in which, for example, Cartesian coordinates (x1 , x2 ) of an object (e.g. as seen on the retina) are neurally transformed into joint angles (θ1 , θ2 ) of an arm required to reach t ...
... 3) Previous Models: Models of neural coordinate transformations originally dealt with “static” sensory-motor mappings, in which, for example, Cartesian coordinates (x1 , x2 ) of an object (e.g. as seen on the retina) are neurally transformed into joint angles (θ1 , θ2 ) of an arm required to reach t ...
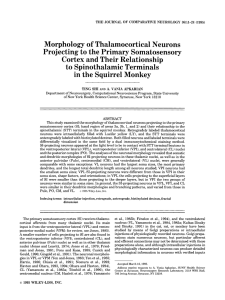
Morphology of Thalamocortical Neurons Projecting
... were quantitatively analyzed and compared between the nuclei, and their relationships with the spinothalamic (STT) terminals were studied. From the earliest studies of Golgi impregnated cells (e.g., Cajal1911; Guillery, 1966; Tombol, 1967,19691,it has been observed that dendritic shapes in any given ...
... were quantitatively analyzed and compared between the nuclei, and their relationships with the spinothalamic (STT) terminals were studied. From the earliest studies of Golgi impregnated cells (e.g., Cajal1911; Guillery, 1966; Tombol, 1967,19691,it has been observed that dendritic shapes in any given ...
Axons, but not cell bodies, are activated by electrical stimulation in
... matter is often used to determine the function of a given cortical area or pathway. However, when it is used to elicit postsynaptic effects, the presynaptic neuronal elements activated by electrical stimulation have never been clearly identified: it could be the excitable dendrites, the cell body, t ...
... matter is often used to determine the function of a given cortical area or pathway. However, when it is used to elicit postsynaptic effects, the presynaptic neuronal elements activated by electrical stimulation have never been clearly identified: it could be the excitable dendrites, the cell body, t ...
DOC - ADAM Interactive Anatomy
... The autonomic nervous system (ANS) consists two divisions, each innervating the effector organs. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) generally speeds up everything except digestion. The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) generally slows down everything but digestion. Signals from the SNS cause th ...
... The autonomic nervous system (ANS) consists two divisions, each innervating the effector organs. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) generally speeds up everything except digestion. The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) generally slows down everything but digestion. Signals from the SNS cause th ...