Olfactory Coding in the Honeybee Lateral Horn
... calcium imaging, we show consistent neural activity in the honeybee lateral horn upon stimulation with both floral volatiles and social pheromones. Recordings reveal odorspecific maps in this brain region as stimulations with the same odorant elicit more similar spatial activity patterns than stimul ...
... calcium imaging, we show consistent neural activity in the honeybee lateral horn upon stimulation with both floral volatiles and social pheromones. Recordings reveal odorspecific maps in this brain region as stimulations with the same odorant elicit more similar spatial activity patterns than stimul ...
Peripheral Nervous System 1: The Somatic System
... • Axon: carries impulses away from cell body • Synapses: site of communication between neurons using chemical neurotransmitters • Myelin & myelin sheath: lipoprotein covering produced by glial cells (e.g., Schwann cells in PNS) that increases axonal conduction velocity • Demyelinating diseases: e.g. ...
... • Axon: carries impulses away from cell body • Synapses: site of communication between neurons using chemical neurotransmitters • Myelin & myelin sheath: lipoprotein covering produced by glial cells (e.g., Schwann cells in PNS) that increases axonal conduction velocity • Demyelinating diseases: e.g. ...
CLM UMR-S 839 INSERM/UPMC Institut du Fer a Moulin
... underlies nearly every aspect of nervous system function. Recent advances in molecular, electrophysiological, in vivo imaging techniques, as wells as circuit interrogation in behaving animals have led to a rapid enhancement in our understanding of the mechanisms that causally link structure, functio ...
... underlies nearly every aspect of nervous system function. Recent advances in molecular, electrophysiological, in vivo imaging techniques, as wells as circuit interrogation in behaving animals have led to a rapid enhancement in our understanding of the mechanisms that causally link structure, functio ...
View CV as a PDF - Cedars
... including non ethical issue, less immune-related problem, differentiating into several cell types. The main purpose of this project is to examine whether umbilical derived stem cells can preserve vision after subretinal injection into a rat model for retinal degeneration. We will evaluate the effica ...
... including non ethical issue, less immune-related problem, differentiating into several cell types. The main purpose of this project is to examine whether umbilical derived stem cells can preserve vision after subretinal injection into a rat model for retinal degeneration. We will evaluate the effica ...
Brain and mind - Scheme of work and lesson plan
... Opportunity for practical work: Mapping receptors. In this practical students use a pair for tweezers to touch various locations on the skin either with one tweezers point or both (keeping them about 2-3 mm apart). Students each time ask the subject if they can feel one or two points. Good places to ...
... Opportunity for practical work: Mapping receptors. In this practical students use a pair for tweezers to touch various locations on the skin either with one tweezers point or both (keeping them about 2-3 mm apart). Students each time ask the subject if they can feel one or two points. Good places to ...
A103 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... caudally, medial part of nucleus overlies rostral portion of substantia nigra. ...
... caudally, medial part of nucleus overlies rostral portion of substantia nigra. ...
Region Specific Micromodularity in the Uppermost Layers in Primate
... Preliminary screening with PV revealed a honeycomb configuration in several other areas in rat, as well as in several areas in cat and monkey (Ichinohe et al., 2003b). As a next step, it seemed important to assess more widely the specific features of this organization. We have accordingly carried ou ...
... Preliminary screening with PV revealed a honeycomb configuration in several other areas in rat, as well as in several areas in cat and monkey (Ichinohe et al., 2003b). As a next step, it seemed important to assess more widely the specific features of this organization. We have accordingly carried ou ...
Seeing faces and objects with the “mind`s eye”
... control of motor responses by internal representations (Cojan et al., 2009). It therefore seems that understanding the neural mechanisms of mental imagery could have far reaching implications for understanding conscious awareness and its various disorders. The main issue addressed in this review is ...
... control of motor responses by internal representations (Cojan et al., 2009). It therefore seems that understanding the neural mechanisms of mental imagery could have far reaching implications for understanding conscious awareness and its various disorders. The main issue addressed in this review is ...
NEUROSCIENCE Review Questions CHOOSE THE LETTER THAT
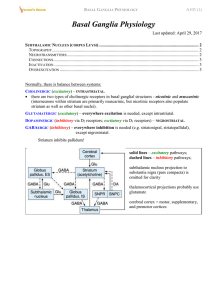
... D. axons from the globus pallidus terminate in the subthalamic nucleus E. it is part of the diencephalon 22. Which of the following symptoms is NOT associated with Basal Ganglia Disease: A. resting tremor B. ataxia C. muscle rigidity D. bradykinesia E. dystonic movements 23. Which of the following s ...
... D. axons from the globus pallidus terminate in the subthalamic nucleus E. it is part of the diencephalon 22. Which of the following symptoms is NOT associated with Basal Ganglia Disease: A. resting tremor B. ataxia C. muscle rigidity D. bradykinesia E. dystonic movements 23. Which of the following s ...
Volitional enhancement of firing synchrony and oscillation by
... In this review, we focus on neuronal operant conditioning in which increments in neuronal activities are directly rewarded without behaviors. We discuss the potential of this approach to elucidate neuronal plasticity for enhancing specific brain functions and its interaction with the progress in neu ...
... In this review, we focus on neuronal operant conditioning in which increments in neuronal activities are directly rewarded without behaviors. We discuss the potential of this approach to elucidate neuronal plasticity for enhancing specific brain functions and its interaction with the progress in neu ...
Proprioception and Discriminatory Touch – Dorsal Column/Medial
... sense). Ask patient to stand upright with eyes closed. If patient is positive for Romberg, he/she sways from side to side and may fall. Tabes dorsalis – Destruction of dorsal columns due to ...
... sense). Ask patient to stand upright with eyes closed. If patient is positive for Romberg, he/she sways from side to side and may fall. Tabes dorsalis – Destruction of dorsal columns due to ...
Physiology
... The human nervous system consists of billions of nerve cells (or neurons)plus supporting (neuroglial) cells. Neurons are able to respond to stimuli (such as touch, sound, light, and so on), conduct impulses, and communicate with each other (and with other types of cells like muscle .)cells The nucle ...
... The human nervous system consists of billions of nerve cells (or neurons)plus supporting (neuroglial) cells. Neurons are able to respond to stimuli (such as touch, sound, light, and so on), conduct impulses, and communicate with each other (and with other types of cells like muscle .)cells The nucle ...
Brain Uncoupling Protein 2: Uncoupled Neuronal Mitochondria
... groups were identified by placing marks on them and were processed in the same vials using the same reagents and timetable. The number of c-fos-expressing cells was calculated for each region. After determination of homogeneity within treatment groups using an F test, values were compared between ex ...
... groups were identified by placing marks on them and were processed in the same vials using the same reagents and timetable. The number of c-fos-expressing cells was calculated for each region. After determination of homogeneity within treatment groups using an F test, values were compared between ex ...
PPT - Ohio University
... • Axon: carries impulses away from cell body • Synapses: site of communication between neurons using chemical neurotransmitters • Myelin & myelin sheath: lipoprotein covering produced by glial cells (e.g., Schwann cells in PNS) that increases axonal conduction velocity • Demyelinating diseases: e.g. ...
... • Axon: carries impulses away from cell body • Synapses: site of communication between neurons using chemical neurotransmitters • Myelin & myelin sheath: lipoprotein covering produced by glial cells (e.g., Schwann cells in PNS) that increases axonal conduction velocity • Demyelinating diseases: e.g. ...
nerve - Ohio University
... • Axon: carries impulses away from cell body • Synapses: site of communication between neurons using chemical neurotransmitters • Myelin & myelin sheath: lipoprotein covering produced by glial cells (e.g., Schwann cells in PNS) that increases axonal conduction velocity • Demyelinating diseases: e.g. ...
... • Axon: carries impulses away from cell body • Synapses: site of communication between neurons using chemical neurotransmitters • Myelin & myelin sheath: lipoprotein covering produced by glial cells (e.g., Schwann cells in PNS) that increases axonal conduction velocity • Demyelinating diseases: e.g. ...
Peripheral Nervous System 1: The Somatic System
... • Axon: carries impulses away from cell body • Synapses: site of communication between neurons using chemical neurotransmitters • Myelin & myelin sheath: lipoprotein covering produced by glial cells (e.g., Schwann cells in PNS) that increases axonal conduction velocity • Demyelinating diseases: e.g. ...
... • Axon: carries impulses away from cell body • Synapses: site of communication between neurons using chemical neurotransmitters • Myelin & myelin sheath: lipoprotein covering produced by glial cells (e.g., Schwann cells in PNS) that increases axonal conduction velocity • Demyelinating diseases: e.g. ...
Neurotic Overview
... internal capsule → cerebral peduncles/basis pontis/pyramids where form lateral (crossed) and anterior (uncrossed) corticospinal tracts → terminate in ventral horn of spinal cord → axon out via ventral root to muscle b. Discriminitive touch/vibration and positional sense info to DRG → dorsal columns ...
... internal capsule → cerebral peduncles/basis pontis/pyramids where form lateral (crossed) and anterior (uncrossed) corticospinal tracts → terminate in ventral horn of spinal cord → axon out via ventral root to muscle b. Discriminitive touch/vibration and positional sense info to DRG → dorsal columns ...
Cerebellum- and forebrain-derived stem cells possess intrinsic
... neuronal subtypes (granule cells, Golgi, stellate, basket neurons and Purkinje cells) and into the less common neuronal subtypes (Lugaro, brush and candelabrum neurons) (Flace et al., 2004; Laine and Axelrad, 1994). The only excitatory neurons residing in the cerebellum are the granule cells [except ...
... neuronal subtypes (granule cells, Golgi, stellate, basket neurons and Purkinje cells) and into the less common neuronal subtypes (Lugaro, brush and candelabrum neurons) (Flace et al., 2004; Laine and Axelrad, 1994). The only excitatory neurons residing in the cerebellum are the granule cells [except ...
Cerebellum- and forebrain-derived stem cells
... neuronal subtypes (granule cells, Golgi, stellate, basket neurons and Purkinje cells) and into the less common neuronal subtypes (Lugaro, brush and candelabrum neurons) (Flace et al., 2004; Laine and Axelrad, 1994). The only excitatory neurons residing in the cerebellum are the granule cells [except ...
... neuronal subtypes (granule cells, Golgi, stellate, basket neurons and Purkinje cells) and into the less common neuronal subtypes (Lugaro, brush and candelabrum neurons) (Flace et al., 2004; Laine and Axelrad, 1994). The only excitatory neurons residing in the cerebellum are the granule cells [except ...
Neural Correlates of Vibrissa Resonance: Band
... and these tasks are known to depend on an intact primary somatosensory cortex (Carvell and Simons, 1990, 1995; Guic-Robles et al., 1989, 1992). Vibrissa resonance has several potentially important neural coding implications. Neural transmission of vibrissa inputs begins in the peripheral input nerve ...
... and these tasks are known to depend on an intact primary somatosensory cortex (Carvell and Simons, 1990, 1995; Guic-Robles et al., 1989, 1992). Vibrissa resonance has several potentially important neural coding implications. Neural transmission of vibrissa inputs begins in the peripheral input nerve ...
Research paper : Why the Mirror Neurons Cannot Support
... pantomime [13-15], whereas the monkey mirror neuron system does not [16]. Why do the human mirror neuron system and the macaque one differ from each other in the case of a pantomime? The human mirror system can be activated when a person watches the pantomime because, despite the absence of an objec ...
... pantomime [13-15], whereas the monkey mirror neuron system does not [16]. Why do the human mirror neuron system and the macaque one differ from each other in the case of a pantomime? The human mirror system can be activated when a person watches the pantomime because, despite the absence of an objec ...
Neurons & the Nervous System
... Refractory period – delay after flushing when the toilet can not be flushed again ...
... Refractory period – delay after flushing when the toilet can not be flushed again ...
Central projections of auditory receptor neurons of crickets
... viewed and photographed with standard or confocal fluorescent microscopy and drawn by tracing the image of a negative projected with a photographic enlarger. Receptor neurons were classified physiologically on the basis of their responses to 30-ms sound pulses, presented twice per second. Sound freque ...
... viewed and photographed with standard or confocal fluorescent microscopy and drawn by tracing the image of a negative projected with a photographic enlarger. Receptor neurons were classified physiologically on the basis of their responses to 30-ms sound pulses, presented twice per second. Sound freque ...
Peripheral Nervous System The Somatic System
... • Axon: carries impulses away from cell body • Synapses: site of communication between neurons using chemical neurotransmitters • Myelin & myelin sheath: lipoprotein covering produced by glial cells (e.g., Schwann cells in PNS) that increases axonal conduction velocity • Demyelinating diseases: e.g. ...
... • Axon: carries impulses away from cell body • Synapses: site of communication between neurons using chemical neurotransmitters • Myelin & myelin sheath: lipoprotein covering produced by glial cells (e.g., Schwann cells in PNS) that increases axonal conduction velocity • Demyelinating diseases: e.g. ...