The Nervous System - Home
... never replaced when they die. In fact, you have fewer neurons when you are old compared to when you are young. On the other hand, data published in November 1998 show that in one area of the brain (the hippocampus), new neurons CAN grow in adult humans. Neurons can be quite large - in some neurons, ...
... never replaced when they die. In fact, you have fewer neurons when you are old compared to when you are young. On the other hand, data published in November 1998 show that in one area of the brain (the hippocampus), new neurons CAN grow in adult humans. Neurons can be quite large - in some neurons, ...
12 - Mrs. Jensen's Science Classroom
... • Capable of spatial discrimination: identification of body region being stimulated • Somatosensory homunculus upside-down caricatures represent contralateral sensory input from body regions ...
... • Capable of spatial discrimination: identification of body region being stimulated • Somatosensory homunculus upside-down caricatures represent contralateral sensory input from body regions ...
nervous system
... originate in the PNS and terminate in the CNS. Motor Neurons (efferent neurons) transmit impulses from the CNS to effector organs (muscles and glands). They originate in the CNS and terminate in the PNS. Interneurons (association neurons) connect sensory neurons to motor neurons within the spina ...
... originate in the PNS and terminate in the CNS. Motor Neurons (efferent neurons) transmit impulses from the CNS to effector organs (muscles and glands). They originate in the CNS and terminate in the PNS. Interneurons (association neurons) connect sensory neurons to motor neurons within the spina ...
Therapeutic Options for Tay-Sachs Disease
... 1998). Presently, no published studies have incorporated engineered neural stem cells into alpha subunit deficient fetal brains. However, Flax et al. (1998) has shown that neural stem cells can be incorporated along developmental lineages when injected into developing mice brains. These stem cells w ...
... 1998). Presently, no published studies have incorporated engineered neural stem cells into alpha subunit deficient fetal brains. However, Flax et al. (1998) has shown that neural stem cells can be incorporated along developmental lineages when injected into developing mice brains. These stem cells w ...
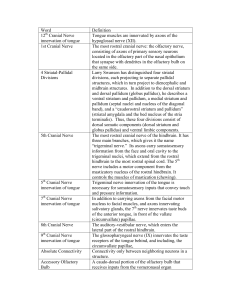
Word Definition 12 Cranial Nerve innervation of
... accessory optic tract (dorsal, lateral, and medial). The neurons of these nuclei are activated by simultaneous and matching movements of all objects and contours in large parts of the visual field. The directions of movement correspond to the head movements to which the semicircular canals of the ve ...
... accessory optic tract (dorsal, lateral, and medial). The neurons of these nuclei are activated by simultaneous and matching movements of all objects and contours in large parts of the visual field. The directions of movement correspond to the head movements to which the semicircular canals of the ve ...
Ultrastructure of Glial Cells in the Nervous System of Grillotia
... and the existence of isolated nerve fibers seems to constitute a breakthrough in the process of understanding the structural evolution of the flatworm nervous system. Ultrastructural studies have shown the presence of myelin-like envelopes of cords and ganglia that contain specialized cellular and i ...
... and the existence of isolated nerve fibers seems to constitute a breakthrough in the process of understanding the structural evolution of the flatworm nervous system. Ultrastructural studies have shown the presence of myelin-like envelopes of cords and ganglia that contain specialized cellular and i ...
Nervous System
... Neurotransmitters 100 types identified in the nervous system that are released by different neurons – some release more than one type Most synthesized in _________ and stored in ___________ After release some are decomposed by enzymes in the synaptic cleft while others can either diffuse to nearby ...
... Neurotransmitters 100 types identified in the nervous system that are released by different neurons – some release more than one type Most synthesized in _________ and stored in ___________ After release some are decomposed by enzymes in the synaptic cleft while others can either diffuse to nearby ...
Anatomy, pigmentation, ventral and dorsal subpopulations of
... of the SN and the ventral tegmental area for histological study. The half brain was placed in 10% neutral formol saline for at least four weeks, and the brainstem was then cut perpendicular to its axis, from the emerging oculomotor nerve fibres to the lower border of the superior colliculus. Two 4 m ...
... of the SN and the ventral tegmental area for histological study. The half brain was placed in 10% neutral formol saline for at least four weeks, and the brainstem was then cut perpendicular to its axis, from the emerging oculomotor nerve fibres to the lower border of the superior colliculus. Two 4 m ...
Diversity of reporter expression patterns in transgenic mouse lines
... physiological and pathological phenomena (21). These include stress-related anxiety (22), memory problems (23, 24), addiction-relapse (25, 26), PTSD (22), and potentially other stress-associated conditions such as anhedonia and anorexia nervosa. Accurate interpretation of studies using cell type-spe ...
... physiological and pathological phenomena (21). These include stress-related anxiety (22), memory problems (23, 24), addiction-relapse (25, 26), PTSD (22), and potentially other stress-associated conditions such as anhedonia and anorexia nervosa. Accurate interpretation of studies using cell type-spe ...
The role of the hypothalamic dorsomedial nucleus in the central
... 5.2.2. PrRP-containing nerve fibers and terminals in the DMH PrRP immunolabeling was detected in different parts of the hypothalamus. PrRP-ir cell bodies appeared exclusively in the most caudal part of the DMH, while PrRP-ir fibers were present in the dorsal and ventral subdivisions of the DMH, as ...
... 5.2.2. PrRP-containing nerve fibers and terminals in the DMH PrRP immunolabeling was detected in different parts of the hypothalamus. PrRP-ir cell bodies appeared exclusively in the most caudal part of the DMH, while PrRP-ir fibers were present in the dorsal and ventral subdivisions of the DMH, as ...
Potential Utility of Optogenetics in the Study of
... models. This approach has already been used to understand DBS action in Parkinson’s disease: optogenetic studies of rodent Parkinson’s models indicate that the therapeutic effect of DBS on the subthalamic nucleus is achieved through activation of axonal inputs to this target region (57), a finding c ...
... models. This approach has already been used to understand DBS action in Parkinson’s disease: optogenetic studies of rodent Parkinson’s models indicate that the therapeutic effect of DBS on the subthalamic nucleus is achieved through activation of axonal inputs to this target region (57), a finding c ...
Interactions between Segmental Homologs and between
... of terminal fields. This process is not well understood, but experimental evidence in several systems suggests that, besides interactions with the target, interactions among axonal terminals of different cells and between different branches of the same neuron are important. Competitive interactions ...
... of terminal fields. This process is not well understood, but experimental evidence in several systems suggests that, besides interactions with the target, interactions among axonal terminals of different cells and between different branches of the same neuron are important. Competitive interactions ...
Saccadic Suppression of Retinotopically Localized Blood Oxygen
... Functional images were time and motion cor(see Materials and Methods, Eye movement recording and stimulus presentation). rected, unwarped, coregistered against a high resolution (1 ⫻ 1 ⫻ 1 mm voxel size) MPRAGE T1 image, and normalized to a standard template Japan, Yokohama, Japan) positioned outsid ...
... Functional images were time and motion cor(see Materials and Methods, Eye movement recording and stimulus presentation). rected, unwarped, coregistered against a high resolution (1 ⫻ 1 ⫻ 1 mm voxel size) MPRAGE T1 image, and normalized to a standard template Japan, Yokohama, Japan) positioned outsid ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM REVIEW
... Name that Nervous System Chase Utley consciously gets into his batting stance. He deliberately swings the bat a few time to get the right feel of its weight. He calculates the incoming pitch and purposefully drives the bat forward knocking in the game winning run. ...
... Name that Nervous System Chase Utley consciously gets into his batting stance. He deliberately swings the bat a few time to get the right feel of its weight. He calculates the incoming pitch and purposefully drives the bat forward knocking in the game winning run. ...
Receptive Fields and Binaural Interactions for Virtual
... Searle et al. 1976). Physiological studies under free-field stimulation have shown that many cells in the auditory midbrain are sensitive to the direction of sound sources (King and Palmer 1983; Knudsen 1982; Knudsen and Konishi 1978; Semple et al. 1983; see Irvine 1992 for review). However, free-fi ...
... Searle et al. 1976). Physiological studies under free-field stimulation have shown that many cells in the auditory midbrain are sensitive to the direction of sound sources (King and Palmer 1983; Knudsen 1982; Knudsen and Konishi 1978; Semple et al. 1983; see Irvine 1992 for review). However, free-fi ...
descending projections from the trigeminal ganglion and
... The overview is an updated survey of our current knowledge about the trigeminal primary afferent neurons involved in the somatosensory processing from the orofacial region. The types of neurons, located in the trigeminal ganglion (TG) and mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus (MTN), are reviewed. Critica ...
... The overview is an updated survey of our current knowledge about the trigeminal primary afferent neurons involved in the somatosensory processing from the orofacial region. The types of neurons, located in the trigeminal ganglion (TG) and mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus (MTN), are reviewed. Critica ...
Central mechanisms regulating coordinated cardiovascular and
... clearly identify the particular neurons and pathways that mediate stress-evoked increases in arterial pressure, sympathetic activity, and respiratory activity. Furthermore, c-Fos expression occurs only after sustained stimulation of neurons and so this method cannot be used to identify cell populati ...
... clearly identify the particular neurons and pathways that mediate stress-evoked increases in arterial pressure, sympathetic activity, and respiratory activity. Furthermore, c-Fos expression occurs only after sustained stimulation of neurons and so this method cannot be used to identify cell populati ...
lec#37 by Dalin Mohammad corrected by Bayan
... The two point discrimination is a fine touch sensation therefore it’s fast. What we have in the fast conducting pathway they need higher processing to be meaningful. Proprioception is needed constantly to know in what position are you limbs. While in the slow conducting pathway does not need higher ...
... The two point discrimination is a fine touch sensation therefore it’s fast. What we have in the fast conducting pathway they need higher processing to be meaningful. Proprioception is needed constantly to know in what position are you limbs. While in the slow conducting pathway does not need higher ...
Unit 2: Biological Psychology
... What is the sequence of events in the firing of an action potential? ...
... What is the sequence of events in the firing of an action potential? ...
28. Nervous Systems
... A neuron may receive information from hundreds of other neurons via thousands of synaptic terminals ...
... A neuron may receive information from hundreds of other neurons via thousands of synaptic terminals ...
Responses of single neurons in the human brain during flash
... on one retina during the dichoptic period, the neuronal responses of these cells are very similar to those when the effective stimulus is presented monocularly. This supports the view that the neurons in the MTL primarily represent the percept rather than the visual input per se. Given that the dich ...
... on one retina during the dichoptic period, the neuronal responses of these cells are very similar to those when the effective stimulus is presented monocularly. This supports the view that the neurons in the MTL primarily represent the percept rather than the visual input per se. Given that the dich ...
Purves chs. 12, 13 - Weizmann Institute of Science
... kHz. Human infants can actually hear frequencies slightly higher than 20 kHz, but lose some high-frequency sensitivity as they mature; the upper limit in average adults is closer to 15–17 kHz. Not all mammalian species are sensitive to the same range of frequencies. Most small mammals are sensitive ...
... kHz. Human infants can actually hear frequencies slightly higher than 20 kHz, but lose some high-frequency sensitivity as they mature; the upper limit in average adults is closer to 15–17 kHz. Not all mammalian species are sensitive to the same range of frequencies. Most small mammals are sensitive ...
Stochastic fluctuations of the synaptic function
... synapses produced quantal Excitatory PostSynaptic Currents (EPSCs) with peak amplitudes having a 5-65 pA range. The histogram of the peak amplitudes showed a long right tail. If the variability of the postsynaptic response observed in hippocampal neurons should be extended to all the neurons of brai ...
... synapses produced quantal Excitatory PostSynaptic Currents (EPSCs) with peak amplitudes having a 5-65 pA range. The histogram of the peak amplitudes showed a long right tail. If the variability of the postsynaptic response observed in hippocampal neurons should be extended to all the neurons of brai ...