Saccades and multisaccadic gaze shifts are gated by different
... neurons whose tonic firing stops during the duration of saccades, when the head is immobilized. In cats, they pause for the total duration of gaze shifts, when the head is free to move. In the present study, carried out on alert cats with fixed heads, we present observations made during self-initiat ...
... neurons whose tonic firing stops during the duration of saccades, when the head is immobilized. In cats, they pause for the total duration of gaze shifts, when the head is free to move. In the present study, carried out on alert cats with fixed heads, we present observations made during self-initiat ...
the functional properties of the light
... what are called associative functions, the neural mechanisms of those associations are still unclear. The second general concept is that the inferior parietal lobule is a higher order processing area of the visual system, for it is known to receive convergent inputs from both the geniculostriate and ...
... what are called associative functions, the neural mechanisms of those associations are still unclear. The second general concept is that the inferior parietal lobule is a higher order processing area of the visual system, for it is known to receive convergent inputs from both the geniculostriate and ...
descending projections from the trigeminal ganglion and
... aspartate) is undoubtedly associated with MTN neurons located throughout the nucleus (14, 47, 48), as in the pseudounipolar cells in the TG (80, 90, 92). Besides, this excitatory amino acid is responsible for monosynaptic transmission between MTN afferents and trigeminal jaw-closing motoneurons acti ...
... aspartate) is undoubtedly associated with MTN neurons located throughout the nucleus (14, 47, 48), as in the pseudounipolar cells in the TG (80, 90, 92). Besides, this excitatory amino acid is responsible for monosynaptic transmission between MTN afferents and trigeminal jaw-closing motoneurons acti ...
I dc
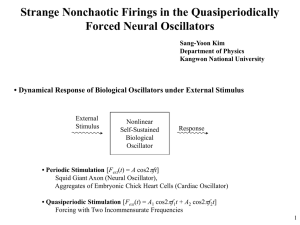
... • Sensitivity of an Attractor with respect to the Phase of the External Quasiperiodic Forcing Phase Sensitivity: Characterized by Differentiating V with respect to at a discrete time t=nP1 (P1=1/f1) ...
... • Sensitivity of an Attractor with respect to the Phase of the External Quasiperiodic Forcing Phase Sensitivity: Characterized by Differentiating V with respect to at a discrete time t=nP1 (P1=1/f1) ...
State-Dependent Computation Using Coupled Recurrent Networks
... networks of richly interconnected neurons, such as those observed in the superficial layers of the neocortex, can embed reliable, robust finite state machines. We show how a multistable neuronal network containing a number of states can be created very simply by coupling two recurrent networks whose ...
... networks of richly interconnected neurons, such as those observed in the superficial layers of the neocortex, can embed reliable, robust finite state machines. We show how a multistable neuronal network containing a number of states can be created very simply by coupling two recurrent networks whose ...
A local circuit approach to understanding integration of
... of nonclassical receptive field stimuli and, correspondingly, of long-range intracortical inputs is known to be context-dependent: the same long-range stimulus can either facilitate or suppress responses, depending on the level of local activation. By constructing a large-scale model of primary visu ...
... of nonclassical receptive field stimuli and, correspondingly, of long-range intracortical inputs is known to be context-dependent: the same long-range stimulus can either facilitate or suppress responses, depending on the level of local activation. By constructing a large-scale model of primary visu ...
Production of nerve growth factor by
... another 48 hr with 10 lM cytosine arabinoside, and then amplified to 2 3 104 cells/cm2 in a 35-mm Petri dish or glass coverslips. Astrocyte monolayers were >98% pure as determined by glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunoreactivity and were devoid of OX42-positive microglial cells. Hipoccampal ...
... another 48 hr with 10 lM cytosine arabinoside, and then amplified to 2 3 104 cells/cm2 in a 35-mm Petri dish or glass coverslips. Astrocyte monolayers were >98% pure as determined by glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunoreactivity and were devoid of OX42-positive microglial cells. Hipoccampal ...
Distribution of GABAergic neurons and axon terminals in the
... all layers of striate cortex. The density of GAD and GABA immunoreactive neurons is greatest in laminae 2-3A, 4A, and 4C,. The distribution of GABAergic neurons within lamina 3 does not appear to be correlated with the patchy distribution of cytochrome oxidase in this region; i.e., there is no signi ...
... all layers of striate cortex. The density of GAD and GABA immunoreactive neurons is greatest in laminae 2-3A, 4A, and 4C,. The distribution of GABAergic neurons within lamina 3 does not appear to be correlated with the patchy distribution of cytochrome oxidase in this region; i.e., there is no signi ...
The Rat Ventromedial Thalamic Nucleus and Motor Control: Role of
... ACh acting on muscarinic receptors. The present study investigates the behavioral and motor consequences of local injections of drugs into the VM, which specifically interact with NMDA, GABA, and muscarine receptors. Both the NMDA antagonist (-)2-amino-7-phosphonoheptanoate [( -)AW], and the GABA ag ...
... ACh acting on muscarinic receptors. The present study investigates the behavioral and motor consequences of local injections of drugs into the VM, which specifically interact with NMDA, GABA, and muscarine receptors. Both the NMDA antagonist (-)2-amino-7-phosphonoheptanoate [( -)AW], and the GABA ag ...
Hindbrain Glucoprivation Effects on Gastric Vagal Reflex Circuits
... for iontophoretic marking of recording sites, was used in the identification and recording of activity of gastric-NST or -DMN neurons, as described previously (McCann et al., 1992; Viard et al., 2012). Extracellular signals from the micropipette were amplified (5000⫻; WPI DAM 50 Differential Amplifi ...
... for iontophoretic marking of recording sites, was used in the identification and recording of activity of gastric-NST or -DMN neurons, as described previously (McCann et al., 1992; Viard et al., 2012). Extracellular signals from the micropipette were amplified (5000⫻; WPI DAM 50 Differential Amplifi ...
Reverse pharmacology of orexin
... attenuated by the H1 antagonist, pyrilamine [35]. Furthermore, the effect of orexin-A on wakefulness in mice is almost completely absent in H1-receptor deficient mice [42]. Furthermore, OX 2 R knockout mice exhibit a narcoleptic phenotype, while OX 1 R knockout mice show only mild fragmentation of b ...
... attenuated by the H1 antagonist, pyrilamine [35]. Furthermore, the effect of orexin-A on wakefulness in mice is almost completely absent in H1-receptor deficient mice [42]. Furthermore, OX 2 R knockout mice exhibit a narcoleptic phenotype, while OX 1 R knockout mice show only mild fragmentation of b ...
brain derived neurotrophic factor transport and physiological
... huntingtin (Htt) result in the degeneration of striatal neurons. The underlying mechanism of BDNF transport and release is remains to be investigated. ...
... huntingtin (Htt) result in the degeneration of striatal neurons. The underlying mechanism of BDNF transport and release is remains to be investigated. ...
lecture16-pulm
... perfused? What factors insure that perfused lung is ventilated? How do we turn off perfusion or ventilation when the lung is not ventilating or perfusing? ...
... perfused? What factors insure that perfused lung is ventilated? How do we turn off perfusion or ventilation when the lung is not ventilating or perfusing? ...
The Structure of Spatial Receptive Fields of Neurons in Primary
... In the present study, stimuli derived from the same transient signals were used, and sound-source directions were referred to the same spherical coordinate system centered on the cat’s interaural plane that covered 3608 in azimuth and 1268 in elevation. Measurements were not made at elevations below ...
... In the present study, stimuli derived from the same transient signals were used, and sound-source directions were referred to the same spherical coordinate system centered on the cat’s interaural plane that covered 3608 in azimuth and 1268 in elevation. Measurements were not made at elevations below ...
Applying Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation to the Study of Spike Timing Dependent Plasticity in Neural Networks
... It has been seen clinically that tACS applied at the resting frequency of a neural system causes an increase in synaptic weights and synchrony between the neurons: an effect that remains for approximately an hour after tACS ceases [1]. If the effects of tACS could be made to be semi-permanent it has ...
... It has been seen clinically that tACS applied at the resting frequency of a neural system causes an increase in synaptic weights and synchrony between the neurons: an effect that remains for approximately an hour after tACS ceases [1]. If the effects of tACS could be made to be semi-permanent it has ...
Effect of Methamphetamine Neurotoxicity on Learning- Arc Efferent Neurons
... humans (Wilson et al., 1996; Volkow et al., 2001; Wang et al., 2004). Previous work also has shown that such METH-induced monoamine depletions are associated with impaired cognitive function both in humans (Volkow et al., 2001) and rodents (Friedman et al., 1998; Chapman et al., 2001; Belcher et al. ...
... humans (Wilson et al., 1996; Volkow et al., 2001; Wang et al., 2004). Previous work also has shown that such METH-induced monoamine depletions are associated with impaired cognitive function both in humans (Volkow et al., 2001) and rodents (Friedman et al., 1998; Chapman et al., 2001; Belcher et al. ...
Structure and Function of Visual Area MT
... Gestalt map of major routes into MT in the manner of Felleman & Van Essen (1991). Line thickness is roughly proportional to the magnitude of the inputs, on the basis of a combination of projection neuron numbers and, where data are available, the characteristics of their axon terminals (see Figure 3 ...
... Gestalt map of major routes into MT in the manner of Felleman & Van Essen (1991). Line thickness is roughly proportional to the magnitude of the inputs, on the basis of a combination of projection neuron numbers and, where data are available, the characteristics of their axon terminals (see Figure 3 ...
The basic nonuniformity of the cerebral cortex
... relationships are obtained if cortical volume (V) is used instead of M (data not shown). These exponents indicate that cortical surface (A) increases slightly slower than cortical mass (M), and, thus, also more slowly than the number of neurons in the cortex (N). N/A ⴝ D ⴛ T: Predictions Are Not Sup ...
... relationships are obtained if cortical volume (V) is used instead of M (data not shown). These exponents indicate that cortical surface (A) increases slightly slower than cortical mass (M), and, thus, also more slowly than the number of neurons in the cortex (N). N/A ⴝ D ⴛ T: Predictions Are Not Sup ...
Drosophila GABA, short neuropeptide F and their receptors
... noduli and the protocerebral bridge and is believed to serve as integration centre for motor and sensory functions (Hanesch et al., 1989; Homberg, 2008). Flies with mutations in the central body have defective walking activity and learning behavior [see (Davis, 1996)]. 1.2. Neurotransmitters and neu ...
... noduli and the protocerebral bridge and is believed to serve as integration centre for motor and sensory functions (Hanesch et al., 1989; Homberg, 2008). Flies with mutations in the central body have defective walking activity and learning behavior [see (Davis, 1996)]. 1.2. Neurotransmitters and neu ...
PDF
... comparing firing to unexpected reward (or reward omission) to background firing (average firing during inter-trial intervals) showed significant interactions between trial period and trial number in each case (reward versus background, F19,532 = 4.37, P < 0.0001; omission versus background, F19,532 ...
... comparing firing to unexpected reward (or reward omission) to background firing (average firing during inter-trial intervals) showed significant interactions between trial period and trial number in each case (reward versus background, F19,532 = 4.37, P < 0.0001; omission versus background, F19,532 ...
Realizing Biological Spiking Network Models in a Configurable
... this hardware architecture: First, a continuous-time serial bus system using on-chip and post-processing lines for intrawafer communication (“Layer-1”). Second, a packet-based dynamic routing network implemented by separate custom hardware components which interface the network chips via contacts on ...
... this hardware architecture: First, a continuous-time serial bus system using on-chip and post-processing lines for intrawafer communication (“Layer-1”). Second, a packet-based dynamic routing network implemented by separate custom hardware components which interface the network chips via contacts on ...
Reward-Related Neuronal Activity During Go - Research
... rarely the conditioned auditory reinforcer. The activations also preceded expected drops of liquid delivered outside the task, suggesting a primary appetitive rather than a task-reinforcing relationship that apparently was related to the expectation of reward. Responses after the reinforcer occurred ...
... rarely the conditioned auditory reinforcer. The activations also preceded expected drops of liquid delivered outside the task, suggesting a primary appetitive rather than a task-reinforcing relationship that apparently was related to the expectation of reward. Responses after the reinforcer occurred ...
Pre-Bötzinger complex

The pre-Bötzinger complex (preBötC) is a cluster of interneurons in the ventrolateral medulla of the brainstem. This complex has been proven to be essential for the generation of respiratory rhythm in mammals. The exact mechanism of the rhythm generation and transmission to motor nuclei remains controversial and the topic of much present research.Several synthetic compounds have been shown to act on neurons specific to the preBötC, most being selective agonists or antagonists to receptor subtypes on neurons in the vicinity. Since many of these neurons express GABA, glutamate, serotonin and adenosine receptors, chemicals custom tailored to bind at these sites are most effective at altering respiratory rhythm.Adenosine modulates the preBötC output via activation of the A1 and A2A receptor subtypes. An adenosine A1 receptor agonist has been shown to depress preBötC rhythmogenesis independent of the neurotransmitters GABA and glycine in ""in vitro"" preparations from 0-7 day old mice. Another synthetic drug specific to the adenosine A2A receptor subtype is CGS-21680 that has been shown to cause apneas in 14-21 day old rat pups in vivo. For this reason, it has been used as a model to study pathological conditions such as apnea of prematurity and SIDS in neonatal infants.