Foundations of Sanskrit Chapter 2 – Introduction to Grammar This
... Martha-NOM Conneticut-ABL (Martha from Conneticut) ...
... Martha-NOM Conneticut-ABL (Martha from Conneticut) ...
Year 2: Detail of content to be introduced
... Subordination (using when, if, that, because) and co-ordination (using or, and, but) Expanded noun phrases for description and specification [for example, the blue butterfly, plain flour, the man in the moon] How the grammatical patterns in a sentence indicate its function as a statement, question, ...
... Subordination (using when, if, that, because) and co-ordination (using or, and, but) Expanded noun phrases for description and specification [for example, the blue butterfly, plain flour, the man in the moon] How the grammatical patterns in a sentence indicate its function as a statement, question, ...
Summary - UvA-DARE - University of Amsterdam
... In the introduction, constituting the first chapter of the thesis, the genetic and ethnolinguistic issues are in focus. TY is identified as one of the two surviving Yukaghir languages, the other being Kolyma Yukaghir. Both languages are most probably remotely linked to the Uralic family although the ...
... In the introduction, constituting the first chapter of the thesis, the genetic and ethnolinguistic issues are in focus. TY is identified as one of the two surviving Yukaghir languages, the other being Kolyma Yukaghir. Both languages are most probably remotely linked to the Uralic family although the ...
Mandatos en “usted” - Mahtomedi High School
... Mandatos formales (Ud./Uds.) Mandatos en “usted” For regular verbs, to form an affirmative or negative command do the following: 1) Take the present tense yo form of the verb. 2) Drop the –o ending (or oy in the verb estar) 3) For –ar verbs add an e For -er/-ir verbs add an a ...
... Mandatos formales (Ud./Uds.) Mandatos en “usted” For regular verbs, to form an affirmative or negative command do the following: 1) Take the present tense yo form of the verb. 2) Drop the –o ending (or oy in the verb estar) 3) For –ar verbs add an e For -er/-ir verbs add an a ...
Grammar Rules!
... of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb. Ask the question, "Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?" and the answer to that question is the subject ...
... of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb. Ask the question, "Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?" and the answer to that question is the subject ...
Pronoun: a word used in place of one or more nouns. We use
... An adjective can come before or after the noun it describes: Tired and hungry, the campers finally reached the lodge. The campers, tired and hungry, finally reached the lodge. (What kind of campers?) Tall players and intelligent coaches were interviewed by the interested reporter. Which players? Wh ...
... An adjective can come before or after the noun it describes: Tired and hungry, the campers finally reached the lodge. The campers, tired and hungry, finally reached the lodge. (What kind of campers?) Tall players and intelligent coaches were interviewed by the interested reporter. Which players? Wh ...
Part I: Give the best answer to the following questions: X points
... above type that are expressed in English by the first person plural “let’s (let us).” b. The ______________________ refers to the present subjunctive of the above type in the third person singular expressing a mild command or suggestion. 2. What conjunction is used to introduce these subjunctive cla ...
... above type that are expressed in English by the first person plural “let’s (let us).” b. The ______________________ refers to the present subjunctive of the above type in the third person singular expressing a mild command or suggestion. 2. What conjunction is used to introduce these subjunctive cla ...
Glossary Literacy L3 - Skills for Life Network
... active and passive voice Verbs can be in the active voice (Rob stole a car) or the passive voice (Our car was stolen). In the active voice the subject does the action. In the passive voice the subject receives the action. agreement In a few cases in English, verbs agree with their subjects (so in st ...
... active and passive voice Verbs can be in the active voice (Rob stole a car) or the passive voice (Our car was stolen). In the active voice the subject does the action. In the passive voice the subject receives the action. agreement In a few cases in English, verbs agree with their subjects (so in st ...
Year 5 - Crossley Fields
... they are used to name the subject or object of the verb. For example, in the phrase ‘Max ate chips’, ‘ate’ is the verb, ‘Max’ is the subject and ‘chips’ is the object. Adjective: Adjectives tell you more about a noun (for example: ‘the red dress’). Verb: A verb is the word that indicates what is hap ...
... they are used to name the subject or object of the verb. For example, in the phrase ‘Max ate chips’, ‘ate’ is the verb, ‘Max’ is the subject and ‘chips’ is the object. Adjective: Adjectives tell you more about a noun (for example: ‘the red dress’). Verb: A verb is the word that indicates what is hap ...
WL Parts of Speech
... language as easily as you can nouns or verbs. Also, another way of understanding the difference between main and linking verbs is to think about main verbs as an open class (you can add to them) while auxiliary verbs are closed (you cannot). 6. Prepositions. The “little words” that establish either ...
... language as easily as you can nouns or verbs. Also, another way of understanding the difference between main and linking verbs is to think about main verbs as an open class (you can add to them) while auxiliary verbs are closed (you cannot). 6. Prepositions. The “little words” that establish either ...
Parts of Speech Review Notes
... B: because, before, by the time E: even if, even though I: if, in order that, in case L: lest O: once, only if P: provided that S: since, so that T: than, that, though, till U: unless, until W: when, whenever, where, wherever, while o Even though you like to eat ice cream, as soon as you eat it you ...
... B: because, before, by the time E: even if, even though I: if, in order that, in case L: lest O: once, only if P: provided that S: since, so that T: than, that, though, till U: unless, until W: when, whenever, where, wherever, while o Even though you like to eat ice cream, as soon as you eat it you ...
Daily Grammar Practice (DGP) Notes
... 2. 1st person=___, 2nd person=___, 3rd person=___ 3. Define and give an example of the following types of pronouns: subjective objective possessive reflexive relative 4. Brady and Jill walked with _____ _____. (one another/each other) ...
... 2. 1st person=___, 2nd person=___, 3rd person=___ 3. Define and give an example of the following types of pronouns: subjective objective possessive reflexive relative 4. Brady and Jill walked with _____ _____. (one another/each other) ...
Please be prepared to take Cornell notes.
... the rest of the alphabet excluding the vowels. Y exception: Y can be either a vowel or consonant depending on its sound; If y has a vowel sound (for example, e as in fairy or I as in sky) its considered a vowel. Y in words such as yard and year is a consonant ...
... the rest of the alphabet excluding the vowels. Y exception: Y can be either a vowel or consonant depending on its sound; If y has a vowel sound (for example, e as in fairy or I as in sky) its considered a vowel. Y in words such as yard and year is a consonant ...
Subject/Verb Agreement
... Words that come from Latin. “Data” and “agenda” are both plural; although they are often treated as singular in informal conversation, for the purpose of professional writing they should be treated with technical accuracy as plural. Wrong: “The data does not support this conclusion.” Right: “The dat ...
... Words that come from Latin. “Data” and “agenda” are both plural; although they are often treated as singular in informal conversation, for the purpose of professional writing they should be treated with technical accuracy as plural. Wrong: “The data does not support this conclusion.” Right: “The dat ...
VERBS
... When a verb cannot work alone, it needs a helper. Helping verb + main verb = verb phrase Common helping verbs: am, is, are, was, were, will, would, has, can, could, have, had, may, might Example: ...
... When a verb cannot work alone, it needs a helper. Helping verb + main verb = verb phrase Common helping verbs: am, is, are, was, were, will, would, has, can, could, have, had, may, might Example: ...
Prepositions - MultiMediaPortfolio
... • Prepositions show relationships between nouns or pronouns and other words in a sentence. ...
... • Prepositions show relationships between nouns or pronouns and other words in a sentence. ...
Tricky bits….
... His first thought on getting out of bed – if he had any thought at all – was to get back in again. ...
... His first thought on getting out of bed – if he had any thought at all – was to get back in again. ...
Grammar Study Guide 2013
... Pronouns Replace nouns (usually short words) Endings one, body, thing, self, and selves make words pronouns Antecedent – The noun the pronoun replaces Indefinite Pronouns (plus words ending in one, body, and thing) all both few more neither several another each little most none some any either many ...
... Pronouns Replace nouns (usually short words) Endings one, body, thing, self, and selves make words pronouns Antecedent – The noun the pronoun replaces Indefinite Pronouns (plus words ending in one, body, and thing) all both few more neither several another each little most none some any either many ...
Adjectives/Adverbs - Mrs. Moore`s 7th Grade English Class
... Adjectives – words we use to describe people, places, and things words that modify nouns and pronouns tell what kind, which one, how many, or how much includes possessive nouns and pronouns (my, our, your, his, her, its, their) includes demonstrative pronouns (this, that these those) inclu ...
... Adjectives – words we use to describe people, places, and things words that modify nouns and pronouns tell what kind, which one, how many, or how much includes possessive nouns and pronouns (my, our, your, his, her, its, their) includes demonstrative pronouns (this, that these those) inclu ...
Grammar Condensed
... Answer these questions: when, where, why, how, how much, in what way? They modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. ...
... Answer these questions: when, where, why, how, how much, in what way? They modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. ...
English glossary - Rainford CE Primary School
... A punctuation mark used to break up sentences so that they are easier to understand. They can be used in lists. A sentence consisting of two main clauses joined by a connective. A sentence consisting of a main clauses and one or more subordinate clause. The ending of a piece of writing. A word or gr ...
... A punctuation mark used to break up sentences so that they are easier to understand. They can be used in lists. A sentence consisting of two main clauses joined by a connective. A sentence consisting of a main clauses and one or more subordinate clause. The ending of a piece of writing. A word or gr ...
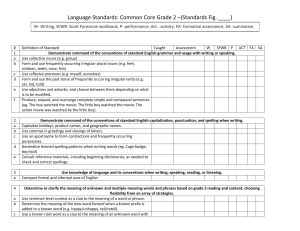
Language Standards: Common Core Grade 2 –(Standards Fig
... Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage with writing or speaking. Use collective nouns (e.g. group) Form and use frequently occurring irregular plural nouns (e.g. feet, children, teeth, mice, fish) Use reflexive pronouns (e.g. myself, ourselves) Form and use the ...
... Demonstrate command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage with writing or speaking. Use collective nouns (e.g. group) Form and use frequently occurring irregular plural nouns (e.g. feet, children, teeth, mice, fish) Use reflexive pronouns (e.g. myself, ourselves) Form and use the ...