Working with Words Nouns, Pronouns, Verbs, Adjectives, and Adverbs
... EX: Jamal and Rick tried out for the team, and THEYboth made IT. **Draw an arrow from the pronoun to the antecedent! Personal pronouns take the place of a SPECIFIC PERSON.The most common personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, and it. Relative pronounsis both a PRONOUNand a CONNECTING WORD. EX: who, ...
... EX: Jamal and Rick tried out for the team, and THEYboth made IT. **Draw an arrow from the pronoun to the antecedent! Personal pronouns take the place of a SPECIFIC PERSON.The most common personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, and it. Relative pronounsis both a PRONOUNand a CONNECTING WORD. EX: who, ...
Parts of Speech Definitions
... Intransitive – verbs that can stand alone; ran, thought, shopped, swam Helping/Linking/verbs of “being” – am, is,are, was, were, have, had, will, Adverbs: (modifiers that describe how a verb is done. Most end in –ly) quickly, slowly, helpfully, happily, disgustingly, colorfully Conjunctions: (Words ...
... Intransitive – verbs that can stand alone; ran, thought, shopped, swam Helping/Linking/verbs of “being” – am, is,are, was, were, have, had, will, Adverbs: (modifiers that describe how a verb is done. Most end in –ly) quickly, slowly, helpfully, happily, disgustingly, colorfully Conjunctions: (Words ...
MBUPLOAD-5373-1
... On your own paper, identify each word’s PART OF SPEECH in the following sentence: She wanted to go to the movies. When you are ready, check your answers by looking at the end of this lesson!! Part 2. VOCABULARY Multiple Choice: Select the letter of the correct answer: ____1. Words that show action o ...
... On your own paper, identify each word’s PART OF SPEECH in the following sentence: She wanted to go to the movies. When you are ready, check your answers by looking at the end of this lesson!! Part 2. VOCABULARY Multiple Choice: Select the letter of the correct answer: ____1. Words that show action o ...
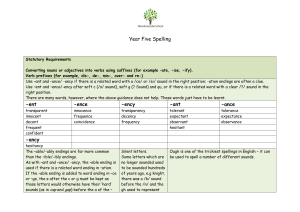
Year Five Spelling - Woodmancote School
... Converting nouns or adjectives into verbs using suffixes (for example –ate, -ise, -ify). Verb prefixes (for example, dis-, de-, mis-, over- and re-) Use –ant and –ance/ -ancy if there is a related word with a /ce/ or /ei/ sound in the right position; -ation endings are often a clue. Use –ent and –en ...
... Converting nouns or adjectives into verbs using suffixes (for example –ate, -ise, -ify). Verb prefixes (for example, dis-, de-, mis-, over- and re-) Use –ant and –ance/ -ancy if there is a related word with a /ce/ or /ei/ sound in the right position; -ation endings are often a clue. Use –ent and –en ...
Signposts Knowledge of Language
... Complex sentences have two or more verbs Clauses can be introduced by words such as who, which, that, when, after Conjunctions can go at the beginning of sentences, e.g. Although, despite P92 ...
... Complex sentences have two or more verbs Clauses can be introduced by words such as who, which, that, when, after Conjunctions can go at the beginning of sentences, e.g. Although, despite P92 ...
How To Study The Bible (#7)
... • pronouns - refers/substitutes to/for a noun • adjectives - modifies or attributes some quality • adverbs - qualifies adjectives, verbs, other adverbs with reference to time, manner, etc. • preposition - precedes a noun/pronoun to describe some relationship to another word • conjunction - connects ...
... • pronouns - refers/substitutes to/for a noun • adjectives - modifies or attributes some quality • adverbs - qualifies adjectives, verbs, other adverbs with reference to time, manner, etc. • preposition - precedes a noun/pronoun to describe some relationship to another word • conjunction - connects ...
B Pronouns - Hull University
... Beware a common spelling error: whose is the possessive form. Who’s is the contracted form of who is. (Contracted forms, like isn’t, I’m, she’s and can’t should be avoided in academic English writing.) Demonstrative pronouns show (demonstrate) what you are talking about. Don’t confuse them with demo ...
... Beware a common spelling error: whose is the possessive form. Who’s is the contracted form of who is. (Contracted forms, like isn’t, I’m, she’s and can’t should be avoided in academic English writing.) Demonstrative pronouns show (demonstrate) what you are talking about. Don’t confuse them with demo ...
File - Ms. Vanek`s English/Language Arts Weebly Website
... Interrogative – ask a question (Will you go to the dance with me?) Imperative – express a command or request (Take out the trash before you go to the dance.) Exclamatory – express strong emotion (Yuck, those are kale chips!) ...
... Interrogative – ask a question (Will you go to the dance with me?) Imperative – express a command or request (Take out the trash before you go to the dance.) Exclamatory – express strong emotion (Yuck, those are kale chips!) ...
PARTS OF SPEECH NOTES • NOUN – person, place, thing, or idea
... HINT: if there are questions left (who, where, what), it’s probably transitive ...
... HINT: if there are questions left (who, where, what), it’s probably transitive ...
12.1 phrases and clauses
... Grammar is a complex – as you know – and controversial area of language study! Prescriptive approach/attitude = tends to see other varieties of language other than ‘standard’ English as incorrect or bad and is highly critical to uses of language that ‘deviates’ from established grammatical rules. De ...
... Grammar is a complex – as you know – and controversial area of language study! Prescriptive approach/attitude = tends to see other varieties of language other than ‘standard’ English as incorrect or bad and is highly critical to uses of language that ‘deviates’ from established grammatical rules. De ...
Parts of Speech Activity ()
... 1. verb- one of the major grammatical groups, and all sentences must contain one. Verbs refer to an action (do, break, walk, etc.) or a state (be, like, own). 2. noun- a word used to refer to people, animals, objects, substances, states, events and feelings. Nouns can be a subject or an object of a ...
... 1. verb- one of the major grammatical groups, and all sentences must contain one. Verbs refer to an action (do, break, walk, etc.) or a state (be, like, own). 2. noun- a word used to refer to people, animals, objects, substances, states, events and feelings. Nouns can be a subject or an object of a ...
Grammar Definition Example Conjunction Used to join two ideas
... time, change of place or change of speaker. It also enables children to organise their ideas. A clause using who, whom, which, whose to relate back to the noun. Clause does not make sense by itself. ...
... time, change of place or change of speaker. It also enables children to organise their ideas. A clause using who, whom, which, whose to relate back to the noun. Clause does not make sense by itself. ...
study guide grammar test
... You must be able to identify the subject of a sentence. Concrete and abstract nouns Count and non-count nouns. Know when to use “few” v. “less” and “some” v. “any” Nominative and objective case pronouns Indefinite pronouns: singular, plural, and those that can be both Possessive pronouns: my, ours, ...
... You must be able to identify the subject of a sentence. Concrete and abstract nouns Count and non-count nouns. Know when to use “few” v. “less” and “some” v. “any” Nominative and objective case pronouns Indefinite pronouns: singular, plural, and those that can be both Possessive pronouns: my, ours, ...
a quick english grammar review
... o Intransitive - action does not pass beyond the doer o Linking = Copulative = Verb of Being / Becoming - describes doer ADVERB - describes actions or adjectives PRONOUN - word which takes the place of a noun: o personal (I, you, they…), relative (who, which…), indefinite (some, any…), interrogative ...
... o Intransitive - action does not pass beyond the doer o Linking = Copulative = Verb of Being / Becoming - describes doer ADVERB - describes actions or adjectives PRONOUN - word which takes the place of a noun: o personal (I, you, they…), relative (who, which…), indefinite (some, any…), interrogative ...
Parts of Speech
... • Personal---I, me, my, you, our, we, they… • Reflexive---end in –self (myself, herself, themselves) NOT hisself or themself • Indefinite---refer to unnamed people, places, ideas (see pg. 33 for the list) • Demonstrative---this, that, these, those but only when used by themselves. NOT…This book is l ...
... • Personal---I, me, my, you, our, we, they… • Reflexive---end in –self (myself, herself, themselves) NOT hisself or themself • Indefinite---refer to unnamed people, places, ideas (see pg. 33 for the list) • Demonstrative---this, that, these, those but only when used by themselves. NOT…This book is l ...
Summer Reading Literary Terms
... 4. Simile—an explicit comparison between two unlike things using like or as. 5. Metaphor—an implicit comparison between two unlike things. 6. Personification—giving human characteristics non inanimate things. 7. Prose—Writing that is not poetry 8. Structure—a framework or system of organization of a ...
... 4. Simile—an explicit comparison between two unlike things using like or as. 5. Metaphor—an implicit comparison between two unlike things. 6. Personification—giving human characteristics non inanimate things. 7. Prose—Writing that is not poetry 8. Structure—a framework or system of organization of a ...
Lect. 7 The Syntax of English
... that is not readily countable, such water, music, justice. Mass as nouns have no plural, they occur in the singular such as, Information is useful. The information is useful. An information is useful(wrong) ...
... that is not readily countable, such water, music, justice. Mass as nouns have no plural, they occur in the singular such as, Information is useful. The information is useful. An information is useful(wrong) ...
Parts of Speech and Parts of a Sentence
... whole, these words may be used as plurals. As examples: Singular: The audience loved the play, and it showed its appreciation by clapping loudly. (one group as a whole) Plural: Management chose to give raises to all employees, and Jimmy thanked each one of them personally. (Here the writer separates ...
... whole, these words may be used as plurals. As examples: Singular: The audience loved the play, and it showed its appreciation by clapping loudly. (one group as a whole) Plural: Management chose to give raises to all employees, and Jimmy thanked each one of them personally. (Here the writer separates ...
Theme 5 Black Cowboy, Wild Horses PPoint
... In this sentence trail means “a trace left by a moving body.” He was glad to see the horses trail behind him. Trail is being used as a verb, “to follow.” Parts of speech are nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, articles, pronouns, ...
... In this sentence trail means “a trace left by a moving body.” He was glad to see the horses trail behind him. Trail is being used as a verb, “to follow.” Parts of speech are nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, articles, pronouns, ...