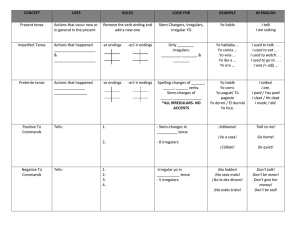
chapter five: nouns
... the English language leaves out the definite article, because a mistake in this type of case makes a very bad and "un-English" impression. 5.1.2 The other basic point to remember is that the gender of nouns is "natural" in English, which means that the foreign student learning English ought not to h ...
... the English language leaves out the definite article, because a mistake in this type of case makes a very bad and "un-English" impression. 5.1.2 The other basic point to remember is that the gender of nouns is "natural" in English, which means that the foreign student learning English ought not to h ...
Year 1: Terminology Taught • Letter • Capital letter • Word • Singular
... Verb: The easiest way to identify verbs is by the ways they can be used: they usually have a tense, either present or past. Sometimes, we think of verbs as being action or ‘doing’ words. They show what someone or something is, has or does. e.g. I jumped into the swimming pool. My brother likes choc ...
... Verb: The easiest way to identify verbs is by the ways they can be used: they usually have a tense, either present or past. Sometimes, we think of verbs as being action or ‘doing’ words. They show what someone or something is, has or does. e.g. I jumped into the swimming pool. My brother likes choc ...
History of English part 2
... use to convey mandatory information (grammatical categories) two aspects of grammatical change: - the number (list) grammatical categories changes: the emergence of feminine gender in Indo-European languages, the loss of dual in most Indo-European languages, the loss of aorist in Slovene, the genera ...
... use to convey mandatory information (grammatical categories) two aspects of grammatical change: - the number (list) grammatical categories changes: the emergence of feminine gender in Indo-European languages, the loss of dual in most Indo-European languages, the loss of aorist in Slovene, the genera ...
Actividad 3
... Many ______________________ that are used in Spanish are in reality the verb form known as the past participle. To form the past participle for –ar verbs we add _____________________. For most –er and –ir verbs we add _____________________. Some irregular past participles are ______________ ________ ...
... Many ______________________ that are used in Spanish are in reality the verb form known as the past participle. To form the past participle for –ar verbs we add _____________________. For most –er and –ir verbs we add _____________________. Some irregular past participles are ______________ ________ ...
Spanish - SFX Community
... The material will be provided by the tutor and will be taken from a variety of sources: texts and exercise books, videos, audios, newspaper (adapted) articles, etc. The course has a communicative approach, and speaking activities will help us to incorporate the grammar introduced in each session. Ea ...
... The material will be provided by the tutor and will be taken from a variety of sources: texts and exercise books, videos, audios, newspaper (adapted) articles, etc. The course has a communicative approach, and speaking activities will help us to incorporate the grammar introduced in each session. Ea ...
Chapter One - The Latin Library
... 2) Instrumental ablative: means, manner, accompaniment, description. a) Means: Phoebus filios reginae sagitta necavit. (with an arrow) b) Manner: Narcissus magna voce clamat. (in a loud voice) Cum is used if no adjective modifies the ablative noun, somtimes even when noun is modified: magno cum gaud ...
... 2) Instrumental ablative: means, manner, accompaniment, description. a) Means: Phoebus filios reginae sagitta necavit. (with an arrow) b) Manner: Narcissus magna voce clamat. (in a loud voice) Cum is used if no adjective modifies the ablative noun, somtimes even when noun is modified: magno cum gaud ...
PRESENT TENSE—I love, I warn, I rule, I hear
... Perfect Tense(have/has been = was/were) fui fuimus fuisti fuistis fuit fuerunt ADJECTIVES – agree with the nouns they modify in gender, number and case. – most of the adjectives you will find on the exam borrow endings from nouns from the 1st or 2nd declenstions. We call these 2-1-2 adjectives. To m ...
... Perfect Tense(have/has been = was/were) fui fuimus fuisti fuistis fuit fuerunt ADJECTIVES – agree with the nouns they modify in gender, number and case. – most of the adjectives you will find on the exam borrow endings from nouns from the 1st or 2nd declenstions. We call these 2-1-2 adjectives. To m ...
Grammar Basics - HCC Learning Web
... Adjectives modify nouns and pronouns by answering questions like Which one? What kind? How many? What size? What condition? Adverbs modify verbs, other adverbs, adjectives and whole clauses. They usually answer such questions as When? Where? How? How often? How much? To what degree? and Why? ...
... Adjectives modify nouns and pronouns by answering questions like Which one? What kind? How many? What size? What condition? Adverbs modify verbs, other adverbs, adjectives and whole clauses. They usually answer such questions as When? Where? How? How often? How much? To what degree? and Why? ...
Verbs
... Learning outcome:---Students will be able to learn the definition of the parts of speech . the classification of parts of speech. how to fill up the gap by parts of speech. ...
... Learning outcome:---Students will be able to learn the definition of the parts of speech . the classification of parts of speech. how to fill up the gap by parts of speech. ...
Multi Sensory Grammar
... house, past the house, near the house, etc. These are all prepositional phrases. • A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and ends with either a noun or pronoun. The preposition is underlined in green and the entire prepositional phrase is circled in green. ...
... house, past the house, near the house, etc. These are all prepositional phrases. • A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and ends with either a noun or pronoun. The preposition is underlined in green and the entire prepositional phrase is circled in green. ...
Introduction to Old Persian Morphology
... “Active” form means that the verb takes “active” endings, rather than “middle” endings. A verb can have “middle” forms but still have “active” meaning, that is, take a direct object (transitive). Passive morphology is more innovative, which the following attested: (i) forms built from the passive st ...
... “Active” form means that the verb takes “active” endings, rather than “middle” endings. A verb can have “middle” forms but still have “active” meaning, that is, take a direct object (transitive). Passive morphology is more innovative, which the following attested: (i) forms built from the passive st ...
parts of speech presentation
... used to explain that one thing happened before another in the past (Past Perfect Tense) Yesterday I ran. Today I’m running. Tomorrow I will run. ...
... used to explain that one thing happened before another in the past (Past Perfect Tense) Yesterday I ran. Today I’m running. Tomorrow I will run. ...
document
... Words in English have gender. However, we aren’t conscious of it. However, it is easy to think of the word “woman” as feminine, “man” as masculine, and “book” as neuter (neuter is the Latin word for neither). Most of the gender assignations in English make sense, the only odd one being “ship” whic ...
... Words in English have gender. However, we aren’t conscious of it. However, it is easy to think of the word “woman” as feminine, “man” as masculine, and “book” as neuter (neuter is the Latin word for neither). Most of the gender assignations in English make sense, the only odd one being “ship” whic ...
Types of noun - Maiden Erlegh School
... Collective: groups of people or things audience, team, family, class ...
... Collective: groups of people or things audience, team, family, class ...
Grammar Cards - Word types(1) DOCX File
... Collective: groups of people or things audience, team, family, class ...
... Collective: groups of people or things audience, team, family, class ...
Nouns and Verbs - Mrs. Paton`s Language Arts
... Common Nouns: A common noun is a general, universal, basic, person, place, thing or idea. Example: ...
... Common Nouns: A common noun is a general, universal, basic, person, place, thing or idea. Example: ...
introduction to latin 2010
... a. Transitive: a verb that can take a direct object (i.e. elect, rectify, deny). Intransitive: a verb that indicates a complete action without being accompanied by a direct object (i.e. sit, lie, think, am/are/is). Linking: a verb used to join or unite a subject with a predicate (i.e. am/are/is) b. ...
... a. Transitive: a verb that can take a direct object (i.e. elect, rectify, deny). Intransitive: a verb that indicates a complete action without being accompanied by a direct object (i.e. sit, lie, think, am/are/is). Linking: a verb used to join or unite a subject with a predicate (i.e. am/are/is) b. ...
Noun
... Information. It provides the “subject” for the people to talk about. The Predicate of a sentence gives New Information. It provides new and insightful information about the ...
... Information. It provides the “subject” for the people to talk about. The Predicate of a sentence gives New Information. It provides new and insightful information about the ...
morphology_001
... Information. It provides the “subject” for the people to talk about. The Predicate of a sentence gives New Information. It provides new and insightful information about the ...
... Information. It provides the “subject” for the people to talk about. The Predicate of a sentence gives New Information. It provides new and insightful information about the ...
Morphology
... Information. It provides the “subject” for the people to talk about. The Predicate of a sentence gives New Information. It provides new and insightful information about the ...
... Information. It provides the “subject” for the people to talk about. The Predicate of a sentence gives New Information. It provides new and insightful information about the ...